Credit: Author
In a paper to be published in the forthcoming issue in NANO, researchers from Zhejiang have uncovered a novel method of using nanocarrier-based biological fluorescent probes for detecting amphetamine and ketamine in latent fingermark, in a bid to combat drug abuse. This method has the potential to be extended to other drugs and molecules.
Drug abuse has become an increasingly serious problem all over the world. How to determine whether a person is taking drugs? Fingermark imaging as well as drug detection in fingermark residues can combine the chemical information with personal identification for forensic purposes. Nanocarrier-based biolabeling has been employed to develop latent fingermarks and simultaneously collect additional chemical information from fingermarks with advantages of good sensitivity and selectivity. However, present immunoassay methods show the limitation that only one drug can be checked in a single fingermark by one test.
In practical cases, the types of drugs in fingerprints are generally unknown. Moreover, the number of fingerprints obtained at the crime scene is usually limited. Therefore, it is necessary to identify more than one drug in a single fingerprint simultaneously with simple procedures.
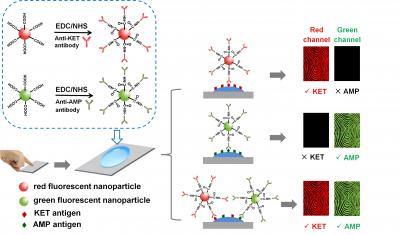
In this work, color fluorescent polystyrene nanoparticles are introduced as nanocarrier in biological fluorescent probes (BFPs) for simultaneous detection of ketamine (KET) and amphetamine (AMP) in latent fingermarks. Ketamine and amphetamine are two of the most commonly abused synthetic drugs in China during recent years, both of which cause adverse effects on human central nervous system as well as other health problems. Antibodies are assembled on carboxyl modified nanoparticles by amide linkage with the assistance of carbodiimide (EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS). Each fluorescent color corresponds to a specific drug antibody, i.e., red corresponds to ketamine and green to amphetamine. BFPs can selectively combine with target analyte in ridge residue when incubated over the fingermark. After removing the unbound BFPs, fluorescence signal originated from nanoparticles of the bound probes contributes to fingermark imaging. Meanwhile, presence or absence of drug(s) can be directly determined by the fluorescent colors when the fingermark is checked in red and green channels. Therefore, fingermark imaging and simultaneous identification of dual-drug in a single fingermark is realized by a one-step test without using secondary antibodies.
###
This work is supported by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LQ16B050002), Project of Educational Commission of Zhejiang Province of China (Y201533271) and National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFC0803606).
Corresponding author for this study is Jing Zhou, [email protected].
For more insight into the research described, readers are invited to access the paper on NANO.
IMAGE
Caption: A schematic illustration of nanocarrier-based biological fluorescent probes for simultaneous detection of ketamine and amphetamine in latent fingermark. Antibodies are assembled on carboxyl modified nanoparticles by amide linkage with the assistance of carbodiimide (EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS). Red fluorescent color corresponds to ketamine and green to amphetamine. Biological fluorescent probes can selectively combine with target analyte in ridge residue when incubated over the fingermark. After removing the unbound BFPs, fluorescence signal originated from nanoparticles of the bound probes contributes to fingermark imaging. Meanwhile, presence or absence of drug(s) can be directly determined by the fluorescent colors when the fingermark is checked in red and green channels.
NANO is an international peer-reviewed monthly journal for nanoscience and nanotechnology that presents forefront fundamental research and new emerging topics. It features timely scientific reports of new results and technical breakthroughs and publishes interesting review articles about recent hot issues.
About World Scientific Publishing Co.
World Scientific Publishing is a leading independent publisher of books and journals for the scholarly, research, professional and educational communities. The company publishes about 600 books annually and about 135 journals in various fields. World Scientific collaborates with prestigious organizations like the Nobel Foundation and US National Academies Press to bring high quality academic and professional content to researchers and academics worldwide. To find out more about World Scientific, please visit http://www.
For more information, contact Tay Yu Shan at [email protected].
Media Contact
Tay Yu Shan
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




