– advance could improve carbon capture technology
Credit: ESRI, Swansea University
A fast, green and one-step method for producing porous carbon spheres, which are a vital component for carbon capture technology and for new ways of storing renewable energy, has been developed by Swansea University researchers.
The method produces spheres that have good capacity for carbon capture, and it works effectively at a large scale.
Carbon spheres range in size from nanometers to micrometers. Over the past decade they have begun to play an important role in areas such as energy storage and conversion, catalysis, gas adsorption and storage, drug and enzyme delivery, and water treatment.
They are also at the heart of carbon capture technology, which locks up carbon rather than emitting it into the atmosphere, thereby helping to tackle climate change.
The problem is that existing methods of making carbon spheres have drawbacks. They can be expensive or impractical, or they produce spheres that perform poorly in capturing carbon. Some use biomass, making them more environmentally friendly, but they require a chemical to activate them.
This is where the work of the Swansea team, based in the University’s Energy Safety Research Institute, represents a major advance. It points the way towards a better, cleaner and greener way of producing carbon spheres.
The team adapted an existing method known as CVD – chemical vapour deposition. This involves using heat to apply a coating to a material. Using pyromellitic acid as both carbon and oxygen source, they applied the CVD method at different temperatures, from 600-900 °C. They then studied how efficiently the spheres were capturing CO2 at different pressures and temperatures
They found that:
- 800 °C was the optimum temperature for forming carbon spheres
- The ultramicropores in the spheres that were produced gave them a high carbon capture capacity at both atmospheric and lower pressures
- Specific surface area and total pore volume were influenced by the deposition temperature, leading to an appreciable change in overall carbon dioxide capture capacity
- At atmospheric pressure the highest CO2 adsorption capacities, measured in millimolars per gram, for the best carbon spheres, were around 4.0 at 0 °C and 2.9 at 25 °C.
This new approach brings several advantages over existing methods of producing carbon spheres. It is alkali-free and it doesn’t need a catalyst to trigger the shaping of the spheres. It uses a cheap and safe feedstock which is readily available in the market. There is no need for solvents to purify the material. It is also a rapid and safe procedure.
Dr Saeid Khodabakhshi of the Energy Safety Research Institute at Swansea University, who led the research, said:
“Carbon spheres are fast becoming vital products for a green and sustainable future. Our research shows a green and sustainable way of making them.
We demonstrated a safe, clean and rapid way of producing the spheres. Crucially, the micropores in our spheres means they perform very well in capturing carbon.
Unlike other CVD methods, our procedure can produce spheres at large scale without relying on hazardous gas and liquid feedstocks.
Carbon spheres are also being examined for potential use in batteries and supercapacitors. So in time, they could become essential to renewable energy storage, just as they already are for carbon capture.”
###
The research was published in the journal Carbon.
Picture:
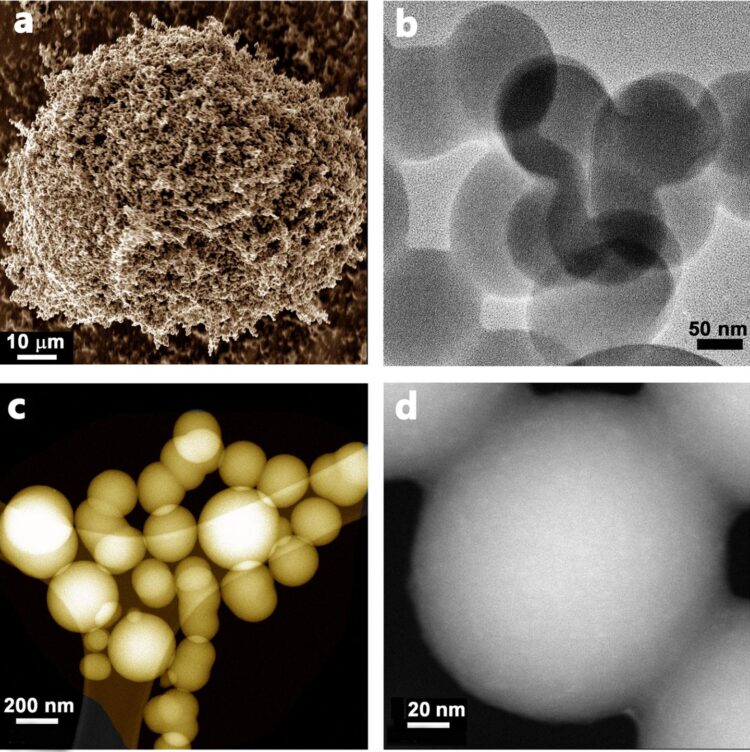
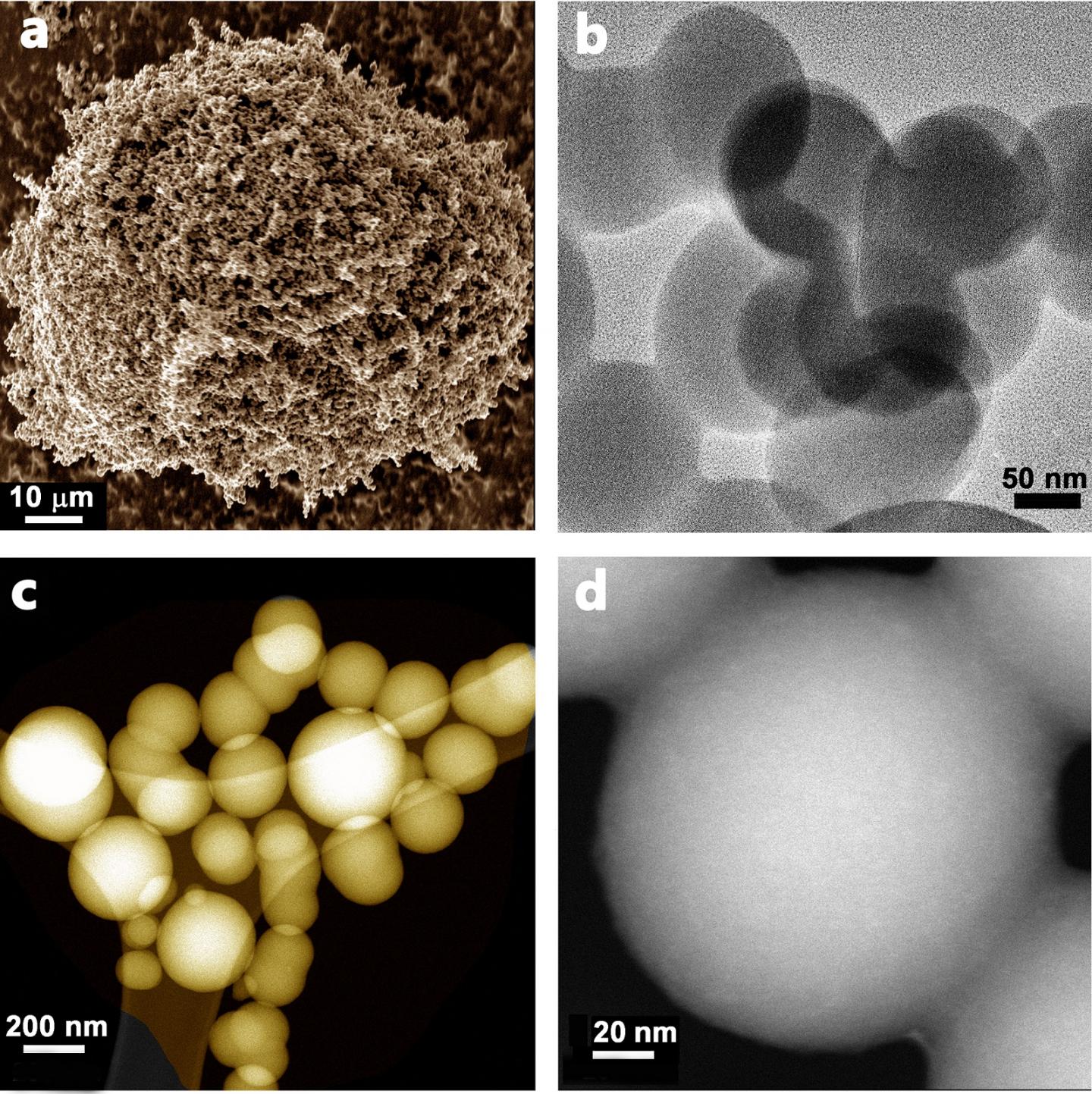
Carbon spheres: microscopy image a) shows agglomerated spheres while single spheres
can be seen from images b-d)
Credit: ESRI, Swansea University
Notes to editors
Link to research paper: “Facile and environmentally friendly synthesis of ultramicroporous carbon spheres: A significant improvement in CVD method”
https:/
Swansea University is a world-class, research-led, dual campus university offering a first-class student experience and has one of the best employability rates of graduates in the UK. The University has the highest possible rating for teaching – the Gold rating in the Teaching Excellence Framework (TEF) in 2018 and was commended for its high proportions of students achieving consistently outstanding outcomes.
Swansea climbed 14 places to 31st in the Guardian University Guide 2019, making us Wales’ top ranked university, with one of the best success rates of graduates gaining employment in the UK and the same overall satisfaction level as the Number 1 ranked university.
The 2014 Research Excellence Framework (REF) 2014 results saw Swansea make the ‘biggest leap among research-intensive institutions’ in the UK (Times Higher Education, December 2014) and achieved its ambition to be a top 30 research University, soaring up the league table to 26th in the UK.
The University is in the top 300 best universities in the world, ranked in the 251-300 group in The Times Higher Education World University rankings 2018. Swansea University now has 23 main partners, awarding joint degrees and post-graduate qualifications.
The University was established in 1920 and was the first campus university in the UK. It currently offers around 350 undergraduate courses and 350 postgraduate courses to circa 20,000 undergraduate and postgraduate students. The University has ambitious expansion plans as it moves towards its centenary in 2020 and aims to continue to extend its global reach and realise its domestic and international potential.
Swansea University is a registered charity. No.1138342. Visit http://www.
For more information:
Kevin Sullivan,
senior press officer,
Swansea University
[email protected]
Follow us on Twitter: http://www.
Find us on Facebook: http://www.
Media Contact
Kevin Sullivan
[email protected]