Credit: ETH Zurich
The rate at which evolution produces new species of plants and animals, or at which existing species die out, is a subject of much interest – and not only to scientists. That’s because the rates of speciation and extinction can tell us much about the history of our planet. If lots of new species emerge during an interval, this would indicate favourable conditions for life on earth. In contrast, extraordinary events can trigger mass extinctions, the most famous example of which was the event that wiped out the dinosaurs 66 million years ago, probably caused by a meteorite impact.
Mysterious discrepancy
It is difficult to determine the frequency with which species in the past emerged and then went extinct again. “There was no one there to witness these processes as they occurred,” says Rachel Warnock, a postdoc in the Computational Evolution research group at ETH Zurich. This is why scientists attempt to deduce the rates of speciation and extinction through indirect methods. Some information comes from fossils dated to different geological eras.
Another source of information comes from species that exist today. In particular, from what are known as phylogenetic (or evolutionary) trees of living species, which are based on DNA analysis. By applying statistical methods to these trees, scientists can determine how often new species emerged and old ones died off in the past.
However, these two approaches are problematic in that they often produce conflicting results: the speciation and extinction rates derived from the fossil record are often much higher than those calculated through phylogenetic methods. To date, it has been unclear what was responsible for this discrepancy.
Combining different approaches
But now, in collaboration with other scientists, Rachel Warnock and head of the Computational Evolution research group Tanja Stadler have found an explanation. “The two methods are based on different assumptions about how new species are formed,” Warnock says. This is why they arrive at different conclusions. But if they account for these different assumptions, then it is possible to harmonise the results.
The researchers were able to demonstrate this by looking at various groups of animals, such as whales, canines and bovines. Their success was due in part to a computer model they developed themselves: “Now we’re able to unify both perspectives,” says Warnock. The results of their work were published in the respected journal Nature Communications.
Insights into speciation
Current thinking maintains that there is not one, but rather multiple mechanisms by which new species emerge (see box). Each mechanism leads to different results; the process may produce one or two new species, while the original species either continues to exist or dies out. “When using the statistical methods to analyse phylogenies and fossils, scientists have thus far not taken these different possibilities explicitly into account,” Warnock says.
The new model now incorporates them, thus ensuring that fossil-based and phylogenetic information produce compatible speciation and extinction rates.
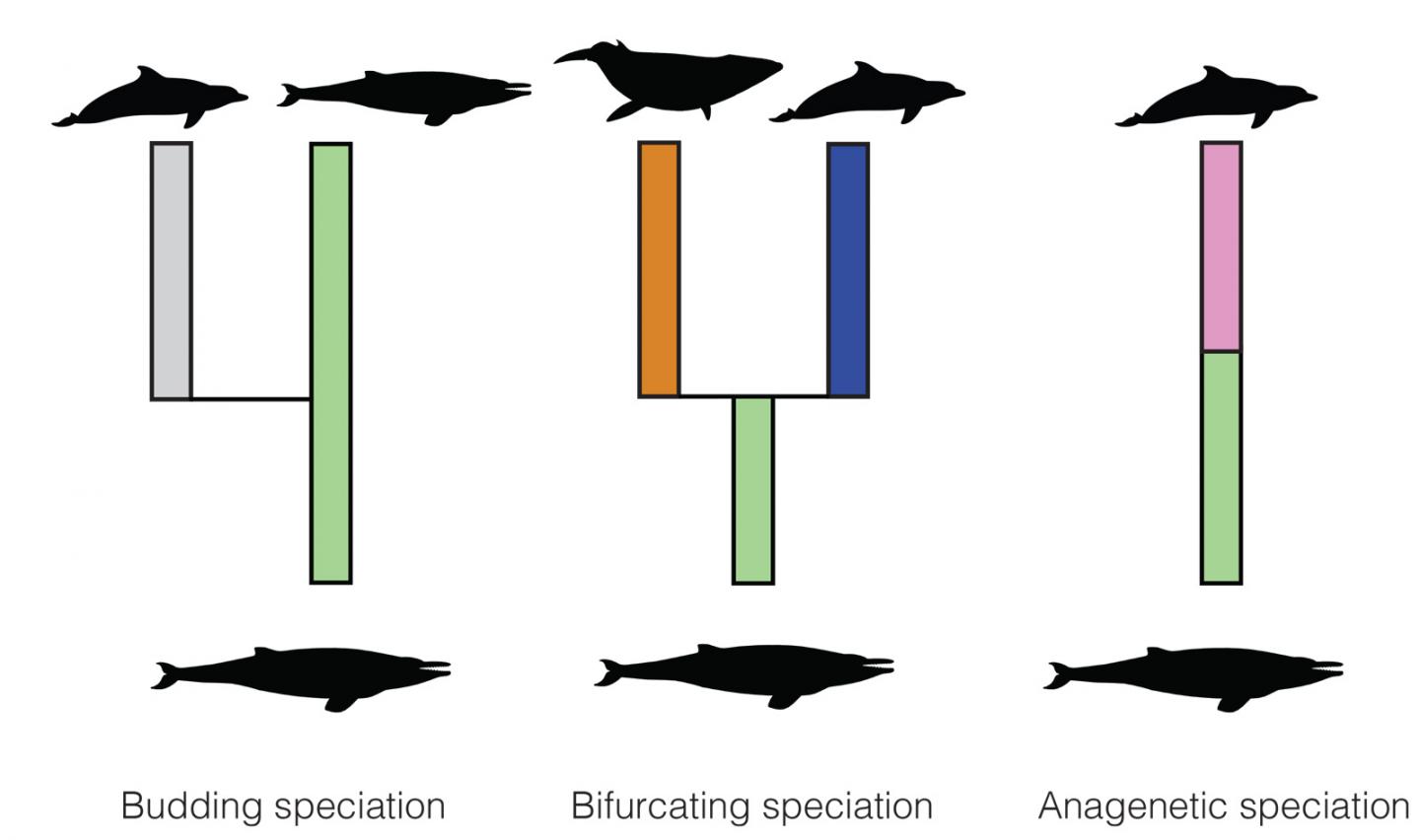
It also provides indications as to which speciation mechanism predominated in a particular animal or plant group. For example, the evolutionary tree and the fossil record of whales reveals that the most frequent mode may be anagenesis; that is, original species are gradually transformed into new ones (mode 3; see box). In consequence, the model could be used in future studies to gain new insights into the evolution of organisms. It also helps to harmonise the results of fossil based and phylogenetic analysis better than before.
###
Box:
Three ways in which new species can emerge:
- Budding: A new species branches off from an existing one, which continues to exist (1 new, 0 extinct).
- Cladogenesis: A species splits into two new species, with the ancestral form dying out (2 new, 1 extinct).
- Anagenesis: A species develops further into a new species, with the ancestral form dying out in the process (1 new, 1 extinct).
Starting with a single species, new species may emerge in any of the three ways. In their study, ETH researchers examined whether certain species gave rise to new ones in one predominant way.
Media Contact
Tanja Stadler
[email protected]
41-613-873-410
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




