Credit: by Sicong Wang, Chen Wei, Yuanhua Feng, Hongkun Cao, Wenzhe Li, Yaoyu Cao, Bai-Ou Guan, Arata Tsukamoto, Andrei Kirilyuk, Alexey V. Kimel, and Xiangping Li
The development of ultrafast all-optical switches has long been a popular topic in photonics, while the speed of magnetization reversal triggered by means other than magnetic fields has recently attracted intense interest in spintronics. The discovery of all-optical helicity-dependent switching in metallic GdFeCo has promised a merger of the fields of photonics and spintronics, paving the way for faster and more energy-efficient information processing technologies. However, the real potential of all-optical switching is still poorly understood because it is still unclear whether magnetic switching by light can keep up with the GHz frequencies required by photonics technologies. Another serious obstacle is the skepticism regarding the scalability of all-optical magnetic switching down to the sizes of spintronic devices, which are well below the diffraction limit.
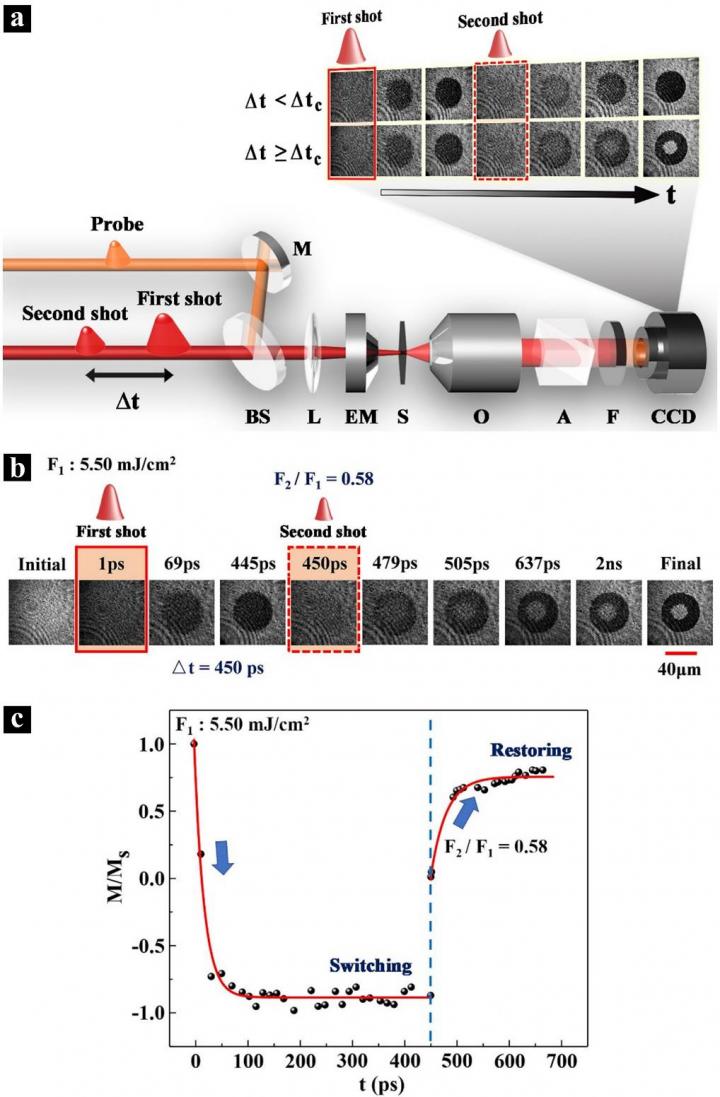
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Applications, a team of scientists, led by Professor Xiangping Li at Jinan University in China and Professor Alexey V. Kimel at Radboud University in The Netherlands have proposed a dual-shot opto-magnetic switching method and studied its dynamics through a time-resolved magneto-optical imaging system. They experimentally unveiled the ultimate frequency of repetitive all-optical magnetization reversal through time-resolved studies of the dual-shot magnetization dynamics in Gd27Fe63.87Co9.13. Varying the intensities of the shots and the shot-to-shot separation, they revealed the conditions for ultrafast writing and the fastest possible restoration of magnetic bits. It is shown that although magnetic writing launched by the first shot is completed after 100 ps, a reliable rewriting of the bit by the second shot requires separating the shots by at least 300 ps. Using two shots partially overlapping in space and minimally separated by 300 ps, they demonstrated an approach for GHz magnetic writing that can be scaled down to sizes below the diffraction limit.
These scientists forecast: “Our findings demonstrate the potential of all-optical magnetic writing with a repetition rate of up to 3 GHz and a spatial resolution below the diffraction limit, which fills a knowledge gap and completes missing technology to promote its widespread applicability in the next revolution of information processing. The advanced features observed in this work may favour the realization of spatially and temporally confined magnetization control through light and greatly promote the development of ultrafast and highly compact devices at the intersection of photonics and spintronics.”
###
Media Contact
Alexey V. Kimel
[email protected]




