Credit: Joep Schaeffer
A big problem with dinosaurs is that there seem to be too many meat-eaters. From studies of modern animals, there is a feeding pyramid, with plants at the bottom, then plant-eaters, and then meat-eaters at the top.
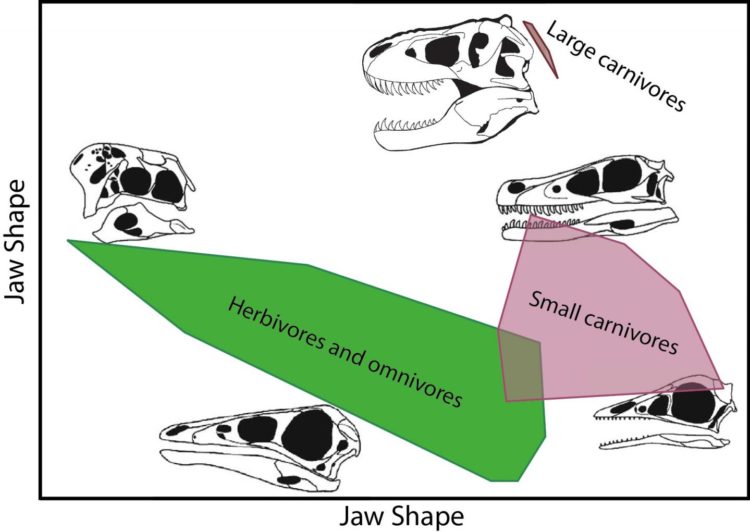
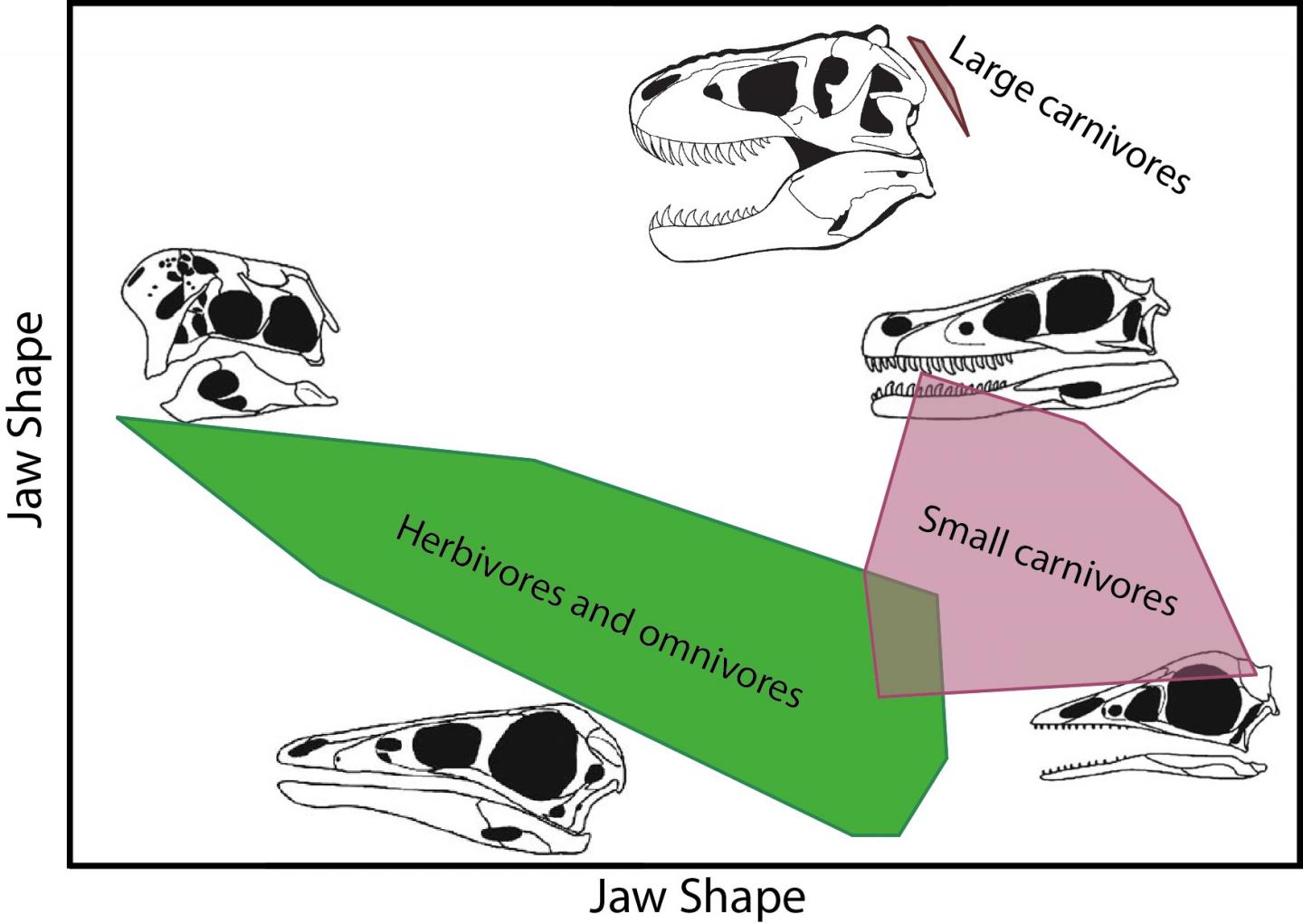
A new study by scientists at the University of Bristol’s School of Earth Sciences, published in the journal Palaeontology, shows that dinosaurian meat-eaters, the theropod dinosaurs, specialised a great deal, and so broadened their food base.
The big ones, such as Allosaurus and Tyrannosaurs Rex, fed on other dinosaurs. But there were also lots of small meat-eaters that probably fed on other animals such as lizards and mammals. And some of the theropods even became plant-eaters.
Joep Schaeffer carried out the study as part of his studies for the MSc in Palaeobiology at Bristol. He said: “I was always mad about tyrannosaurs and other meat-eating dinosaurs, but this study tested my computing ability.
“I measured everything I could from the jaws and teeth of 83 theropod dinosaurs, including the giants, but also small ones the size of a turkey.”
Professor Emily Rayfield, who co-led the research, added: “Our idea was to describe every possible jaw shape and tooth shape in terms of about 80 measurements.
“Were all these meat-eaters feeding in the same way on the same things? If so, that would mean a lot of competition.”
Professor Mike Benton, who also co-led the research, said: “We also had problems in deciding which computational method to use.
“We could simply treat all the separate measurements as part of the mix, or we could measure so-called landmarks, where we make an outline of the jaw and tooth shape by marking dots round the edge.
So, in the end, Joep ran his analyses using each possible measurement method, and we compared the results.”
Dr Tom Stubbs, who also worked on the study, added: “These kinds of studies are very informative. We have a huge amount of data from many excellent specimens, but there are many different ways of analyzing the data.
“We were able to show that it didn’t matter which was used to do the calculations, we found the same results – tyrannosaurs were different from all the other theropods, and there were big differences between the theropods.”
The analyses separated out three groups – the large dinosaur-eaters, the small carnivores and the herbivores. In particular, the tyrannosaurs such as T. rex were quite distinct – they had deeper jaws and more powerful teeth than any of the other theropods, and so had evidently evolved particular ways of dealing with large prey.
The other key finding is that the maniraptoriform theropods – those most closely related to birds – show the greatest amount of variation in jaw shapes. This suggests, but does not prove, that they had the greatest range of functions.
Joep Schaffer added: “Tyrannosaurs were good at subduing large prey with their massive jaws. So, they all had the same kinds of jaws and teeth. But the maniraptoriforms were experimenting with a wide range of smaller prey, maybe from small dinosaurs to early mammals and lizards… even some large, juicy insects.
“This meant they had evolved a much wider array of kinds of jaws and teeth, and while many probably continued to hunt prey on the ground, others might have become specialized to hunting in the trees and pursuing fast-moving prey.”
###
Media Contact
Mike Benton
[email protected]