New method of fluid gating has implications for drug delivery, power generation and other uses
Credit: ACS Applied Nano Materials
The movement of fluids through small capillaries and channels is crucial for processes ranging from blood flow through the brain to power generation and electronic cooling systems, but that movement often stops when the channel is smaller than 10 nanometers.
Researchers led by a University of Houston engineer have reported a new understanding of the process and why some fluids stagnate in these tiny channels, as well as a new way to stimulate the fluid flow by using a small increase in temperature or voltage to promote mass and ion transport.
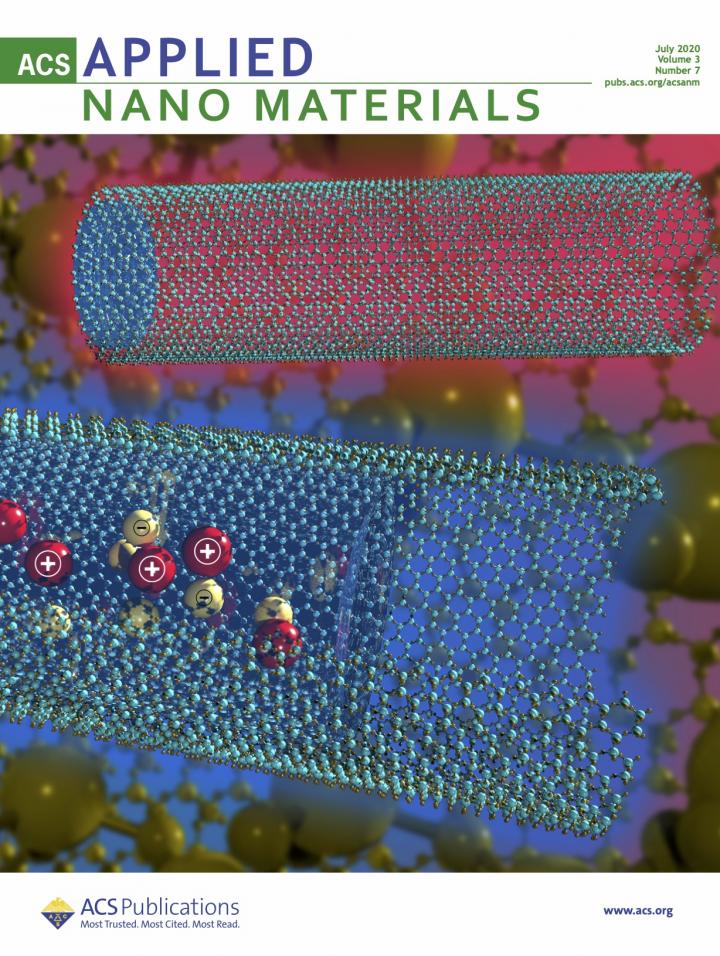
The work, published in ACS Applied Nano Materials, explores the movement of fluids with lower surface tension, which allows the bonds between molecules to break apart when forced into narrow channels, stopping the process of fluid transport, known as capillary wicking. The research was also featured on the journal’s cover.
Hadi Ghasemi, Cullen Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering at UH and corresponding author for the paper, said this capillary force drives liquid flow in small channels and is the critical mechanism for mass transport in nature and technology – that is, in situations ranging from blood flow in the human brain to the movement of water and nutrients from soil to plant roots and leaves, as well as in industrial processes.
But differences in the surface tension of some fluids causes the wicking process – and therefore, the movement of the fluid – to stop when those channels are smaller than 10 nanometers, he said. The researchers reported that it is possible to prompt continued flow by manipulating the surface tension through small stimuli, such as raising the temperature or using a small amount of voltage.
Ghasemi said raising the temperature even slightly can activate movement by changing surface tension, which they dubbed “nanogates.” Depending on the liquid, raising the temperature between 2 degrees Centigrade and 3 degrees C is enough to mobilize the fluid.
“The surface tension can be changed through different variables,” he said. “The simplest one is temperature. If you change temperature of the fluid, you can activate this fluid flow again.” The process can be fine-tuned to move the fluid, or just specific ions within it, offering promise for more sophisticated work at nanoscale.
“The surface tension nanogates promise platforms to govern nanoscale functionality of a wide spectrum of systems, and applications can be foreseen in drug delivery, energy conversion, power generation, seawater desalination, and ionic separation,” the researchers wrote.
###
In addition to Ghasemi and first author Masoumeh Nazari, researchers involved with the project include Sina Nazifi, Zixu Huang, Tian Tong and Jiming Bao, all with the University of Houston, and Kausik Das and Habilou Ouro-Koura, both with the University of Maryland Eastern Shore.
Funding for the project came from the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, the National Science Foundation and the U.S. Department of Education.
Media Contact
Jeannie Kever
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




