Detection of preterm labor early by sensing the signals of uterine contractions with the use of a non-invasive electroceutical. Prevention of preterm labor by inhibiting uterine contractions via electrical signals that modulate autonomic nerves.
Credit: Korea Institute of Science and Technology(KIST)
Preterm labor comprises 12.7% of all pregnancies. Although the overall rate of pregnancy is decreasing, the occurrence of premature birth due to preterm labor in south korea has been increasing over the past 7 years. Not only is preterm birth accountable for about a half of all neonatal mortality cases, the neurological deficits in surviving premature infants often lead to problems later in life, such as developmental disorders and respiratory complications. Currently, preterm labor is detected only when expecting mothers experience abnormal symptoms, or when they undergo a routine test like abdominal ultrasound or a laboratory test for vaginal secretions. It is difficult to detect preterm labor early, and there are few treatment options available other than pharmaceutical agents such as anti-contraction medications, with which side effects are of concern.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that in collaboration with the research team led by Ki Hoon Ahn, Professor at the Department of OB/GYN, Korea University Anam Hospital and Dr. Soo Hyun Lee, the team at KIST Brain Science Institute (BSI) developed a non-invasive electroceutical for the early detection and simultaneous treatment of preterm labor.
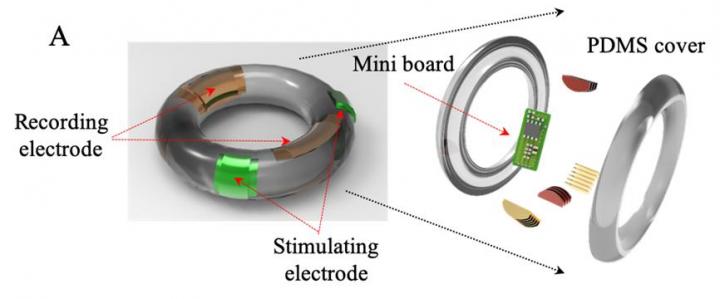
While preterm labor is generally known to have various causes, including naturally occurring early contractions and premature rupture of membranes, a final symptom is irregular uterine contractions. The KIST research team developed a donut-shaped electrode that is inserted into the cervix to sense the signals of uterine contractions in real time, making the early diagnosis of preterm labor possible. Moreover, after sensing the signal of uterine contractions, the electrode can generate an electrical signal, thus functioning as an electroceutical to suppress uterine contractions by relaxing uterine muscles via sympathetic nerve stimulation.
The research team tested the safety and functioning of this electroceutical system for preterm labor detection and treatment using preterm-labor mouse and pig models, and confirmed that electrical stimulation generated from the system could delay and inhibit uterine contractions.
Professor Ki Hoon Ahn of Korea University Anam Hospital said, “Although new drug research and development (R&D) has been actively performed worldwide, the efficacy was not sufficient enough and there were side effects. We developed this system because there was a clinical need for a medical equipment with a novel mechanism.” He also added that, “Infant mortality and the occurrence of sequelae due to preterm labor are expected to drastically decrease with the use of the first-ever medical device controlling uterine contractions.”
Soo Hyun Lee, PhD, of KIST, contributed by saying that, “The donut-shaped electroceutical is not a therapy based on the existing pharmaceuticals, but a therapeutic tool to inhibit uterine contractions via electrical stimulation, and is likely to be developed further as a new concept-based medical technology.” He added that, “The research was initiated as a project of the KIST-Korea University Anam Hospital Translation Research Center. In near future, we plan to conduct clinical research with government research grants, like an interagency program for medical device R&D.”
###
The research was conducted as a research project at the KIST-Korea University Anam Hospital Translational Research Center and funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT). The study findings were published in the latest issue of ‘IEEE Transactions on neural systems and rehabilitation engineering‘ and, an international journal in the field of electrical and electronic engineering.
Media Contact
Do-Hyun Kim
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




