This article by Dr. Baozhong Shen et al. is published in Current Protein & Peptide Science, Volume 19, Issue 11, 2018
Credit: Bentham Science Publishers, Baozhong Shen, Xilin Sun
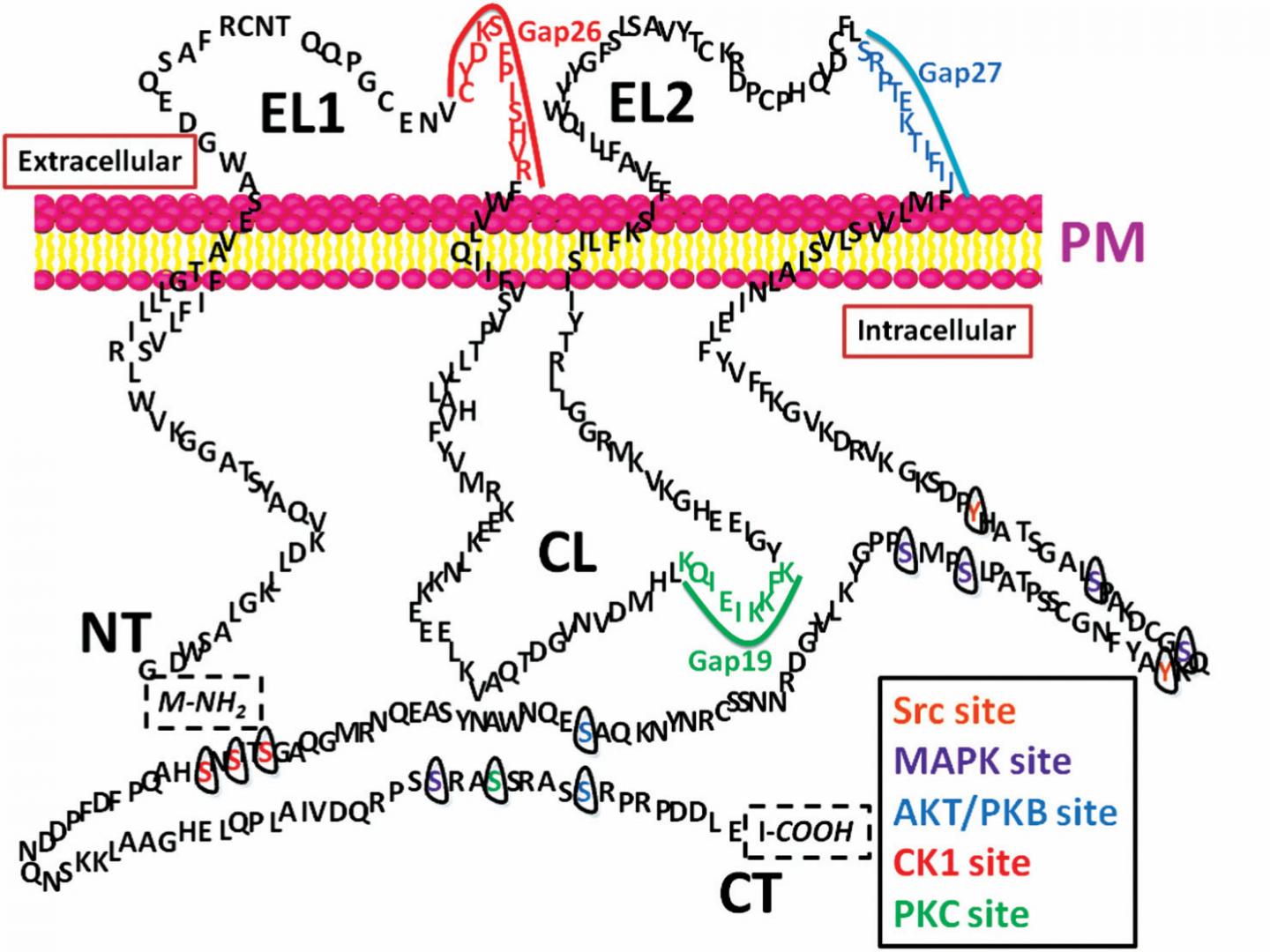
Connexins (Cx), also known as gap junction proteins, are trans-membrane proteins that assemble to form vertebrate gap junctions. Connexins are widely distributed throughout human body. However, gap junctions allow exchange of ions as they are an organized junction of intercellular protein channels which are present in cell-to-cell interfaces. They also send chemical signals and energy substrates from one cell to the other.
Connexin43 (Cx43) or Gap Junction alpha-1 protein (GJA1), is a protein that is encoded on chromosome 6. Connexin43 is one of the most abundant gap junction protein isoforms present in heart tissue which play an important role in myocardium disease. Previous studies have shown that Cx43 can affect tumor migration due to its effect in gap junctions. Therefore, understanding its role in this setting can give researchers some insight into the processes which can affect the spread of tumor cells.
The review presents knowledge about how abnormalities in gap junctions and hemichannels can lead to diseases in the heart and to cancer, along with the pharmacology of associated compounds which target these areas. The knowledge can be useful for researchers looking to discover a new spectrum of therapeutic options for approaching cancer and myocardial disease diagnosis and therapy.
###
This article is Open Access. To obtain the article please visit http://www.
Media Contact
Faizan ul Haq
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




