Overturning conventional knowledge, what these scientists have discovered about the circadian oscillations of a cyanobacterium could lead to unveiling a great mystery with physiological and evolutionary significance in the future
Credit: Iwasaki Laboratory, Waseda University
Circadian rhythms are driven by a highly autonomous, self-sustaining circadian clock in our cells, telling us when to sleep or wake up in a 24-hour cycle.
This mechanism can also be found in other organisms, including in primitive, photosynthetic bacteria known as cyanobacteria. In cyanobacteria, three types of proteins known as KaiA, KaiB, and KaiC work together like gears of a clock to create the rhythms. According to previous studies, all three Kai proteins are required for the circadian clock of cyanobacteria to function, and lacking KaiA could abolish oscillations.
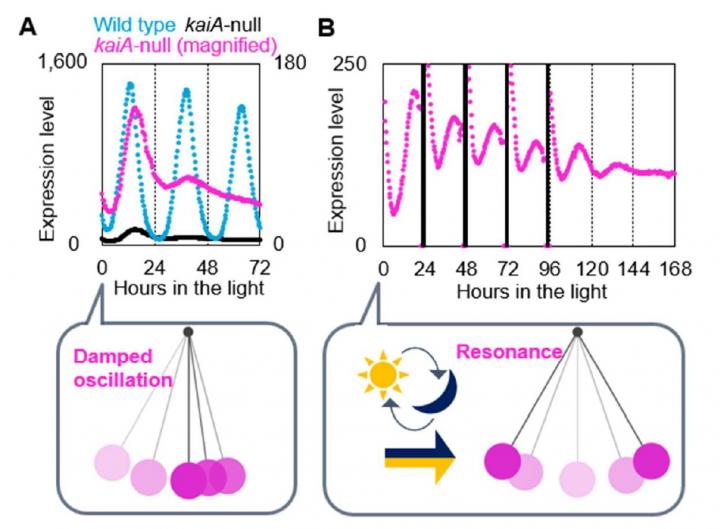
However, in a recent study published in Nature Communications, scientists from Waseda University, Kyushu University, and Ritsumeikan University presented an observation of damped, low-amplitude (damped) circadian oscillations in the absence of KaiA in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus.
Hideo Iwasaki, professor of cell biology at Waseda University and the corresponding author of this study, actually recorded such weak circadian rhythms during an experiment conducted more than 20 years ago retrospectively, but at the time, it was dismissed as a discrepancy and overlooked. However, when a graduate student from his laboratory pointed out the same subtle oscillations while they were observing gene expression patterns of a genomic variant of cyanobacteria lacking KaiA, Iwasaki knew something was going on.
“We spent much time and energy in conducting experiments, such as monitoring rhythms with a technique called the bioluminescence reporter, to understand physiological importance and molecular mechanisms of the damp circadian oscillations, as well as to establish our theoretical perspective because we had a hunch that our findings would overturn conventional knowledge,” Iwasaki says. “Our findings are the results of efforts made by the graduate student who noticed the oscillations, who is the first author of this paper, and by the talented researchers we collaborated with. I would like to thank everyone involved for their dedication and hard work.”
Iwasaki adds, “We also found that the damped rhythms resonate with external cycles with a period of 24 to 26 hours, meaning that its natural frequency is similar to that of a circadian clock. So, in a day-night altered environment, low-amplitude oscillations could theoretically act as a circadian clock to regulate various activities within cells and adapt to change in the cyclic environment.”
Though much research has been done on the circadian clock, there has been a tendency for researchers to shy away from studying damped circadian oscillations because of the difficulty in analyzing them and their phenotypes being not particularly intriguing, but Iwasaki believes that there needs to be more focus on the topic.
“Based on our results, we could hypothesize that the circadian clock did not become autonomous and self-sustaining all the sudden but instead gradually evolved from low-amplitude oscillations,” says Iwasaki. “From the evidence that some cyanobacteria in the natural environment do not possess KaiA, perhaps obtaining and losing KaiA happened multiple times along its evolution, and it could be that some cyanobacteria do not have KaiA for good reasons. Through further studies on damp circadian oscillations, we could be unveiling a great mystery with physiological and evolutionary significance.”
Iwasaki and his team are interested in further investigating the roles that damp circadian oscillations play. If similar circadian mechanisms can be observed among higher plants and mammals, it may be able to manipulate our circadian rhythms more accurately by applying damped circadian oscillations and resonation.
###
Reference
Journal: Nature Communications
Article title: Damped circadian oscillation in the absence of KaiA in Synechococcus
Authors: Naohiro Kawamoto, Hiroshi Ito, Isao T. Tokuda, and Hideo Iwasaki
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-16087-x
About Waseda University
Located in the heart of Tokyo, Waseda University is a leading private research university that has long been dedicated to academic excellence, innovative research, and civic engagement at both the local and global levels since 1882. Today, the student body at Waseda is approximately 50,000, nearly 8,000 of whom are from overseas, hailing from 125 countries. To learn more about Waseda University, visit https:/
Media Contact
Jasper Lam
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




