Credit: Helena Volk, Kristina Marton, Marko Flajšman, et al.
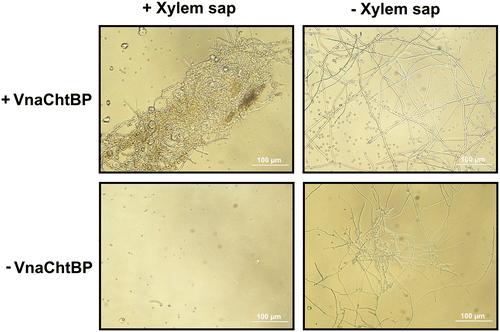
An insoluble complex carbohydrate, chitin makes up fungal walls and plays a significant role in the interaction between fungal pathogens and their plant hosts. Plant cells harbor immune receptors that perceive chitin and work to stop fungal infection. However, fungal plant pathogens then release chitin-binding proteins that perturb the chitin-triggered immunity.
A recent Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions article studies one of these chitin-binding proteins from a soilborne fungus (Verticillium nonalfalfae) that causes vascular wilt in plants. This fungus binds a particular protein (VnaChtBP) to chitin in order to abolish the host plant’s chitin-triggered burst of reactive oxygen species and shield the fungus from being digested by the plant.
The scientists used 3D homology modelling, molecular docking, CD measurements, and a Y2H assay to determine, for the first time, the probable molecular mechanism of chitin-binding to carbohydrate-binding module family 18 (CBM18)-containing fungal effectors. In addition, this research highlights that, apart from the well-studied Avr4 (CBM14) and LysM (CBM50) fungal effectors, which can interfere with plant chitin perception and activation of immune responses, other structurally unrelated fungal effectors with CBM18 domains have evolved with similar function, suggesting a convergent evolution.
Learn more by reading “Chitin-Binding Protein of Verticillium nonalfalfae Disguises Fungus from Plant Chitinases and Suppresses Chitin-Triggered Host Immunity,” which describes the characterization of this protein and determines the probable molecular mechanism of CBM18 chitin-binding fungal effectors.
###
Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions (MPMI) publishes fundamental and advanced applied research on the genetics, genomics, molecular biology, biochemistry, and biophysics of pathological, symbiotic, and associative interactions of microbes, insects, nematodes, or parasitic plants with plants.
Follow us on Twitter @MPMIjournal and visit https:/
Media Contact
Ashley Bergman Carlin
[email protected]
651-994-3832
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




