A new large-scale study uncovers recent genetic connectivity between chimpanzee subspecies despite past isolation events
Credit: © PanAf
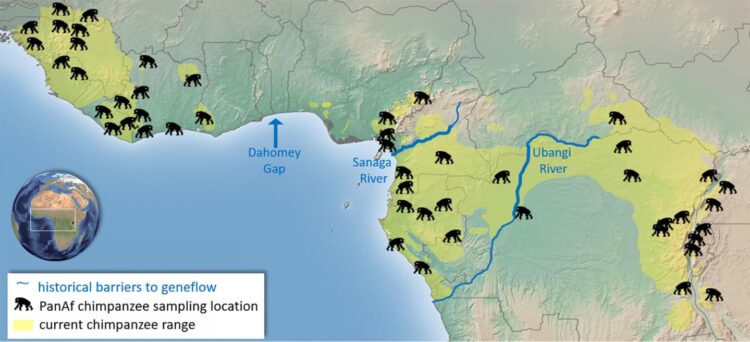
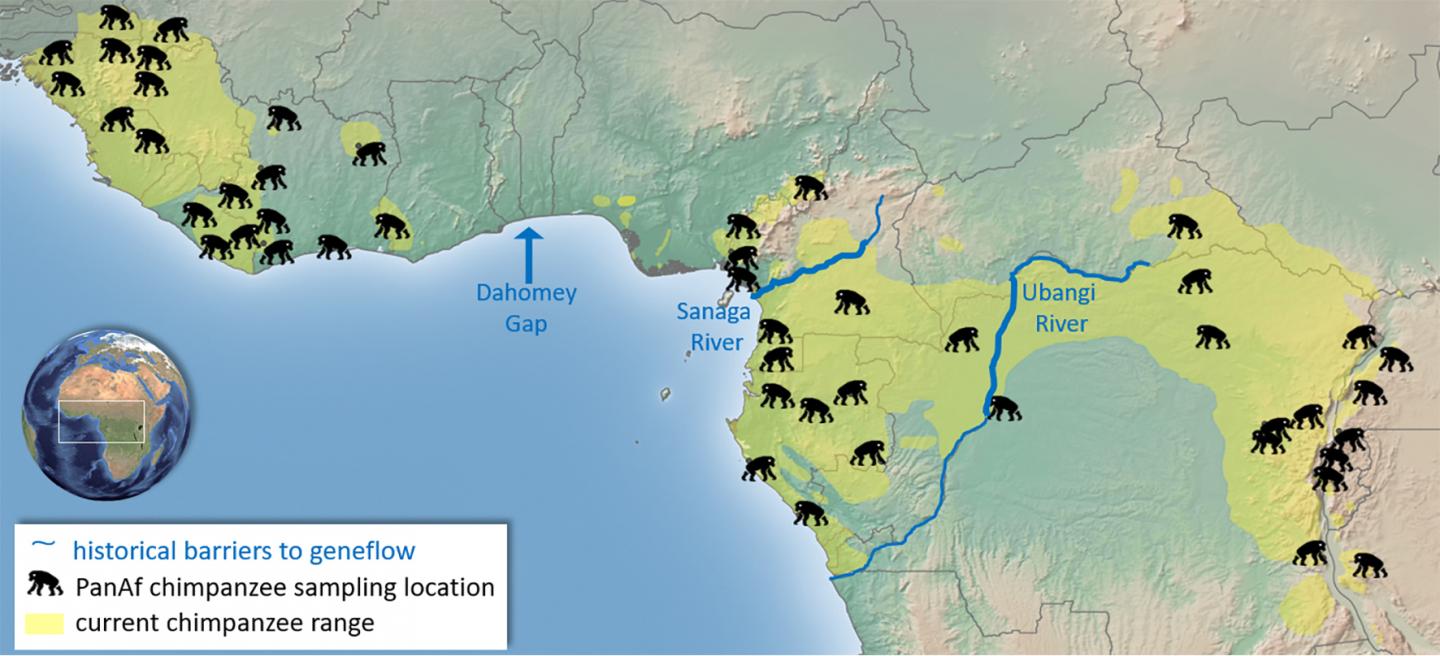
Researchers from the Pan African Programme: The Cultured Chimpanzee (PanAf) at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology (MPI-EVA) and a team of international researchers, collected over 5000 fecal samples from 55 sites in 18 countries across the chimpanzee range over 8 years. This is by far the most complete sampling of the species to date, with a known location of origin for every sample, thus addressing the sampling limitations of previous studies. “Collecting these samples was often a daunting task for our amazing field teams. The chimpanzees were almost all unhabituated to human presence, so it took a lot of patience, skill and luck to find chimpanzee dung at each of the sites,” explains Mimi Arandjelovic, co-director of the PanAf and senior author of the study.
Jack Lester, first author of the study, explains: “We used rapidly-evolving genetic markers that reflect the recent population history of species and, in combination with the dense sampling from across their range, we show that chimpanzee subspecies have been connected, or, more likely, reconnected, for extended periods during the most recent maximal expansion of African forests.”
So although chimpanzees were separated into different subspecies in their distant past, prior to the rise of recent anthropogenic disturbances, the proposed subspecies-specific geographic barriers were permeable to chimpanzee dispersal. Paolo Gratton, co-author of the study and researcher at the Università di Roma “Tor Vergata” adds: “It is widely thought that chimpanzees persisted in forest refugia during glacial periods, which has likely been responsible for isolating groups of populations which we now recognize as subspecies. Our results from fast-evolving microsatellite DNA markers however indicate that genetic connectivity in the most recent millennia mainly mirrors geographic distance and local factors, masking the older subspecies subdivisions.”
Furthermore, “these results suggest that the great behavioural diversity observed in chimpanzees are therefore not due to local genetic adaptation but that they rely on behavioural flexibility, much like humans, to respond to changes in their environment,” notes Hjalmar Kuehl, co-director of the PanAf and researcher at the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv).
The team also observed signals of reductions in diversity at some sites that appeared to be associated with recent anthropogenic pressures. In fact, at some locations PanAf teams visited no, or few, chimpanzees were detected despite recordings of their presence within the last decades. “Although not unforeseen, we were disheartened to already find the influence of human impacts at some field sites where genetic diversity was markedly lower than what we expected,” says Jack Lester.
These results highlight the importance of genetic connectivity for chimpanzees in their recent history. “Every effort should be made to re-establish and maintain dispersal corridors across their range, with perhaps special attention to trans-national protected areas,” notes Christophe Boesch, co-director of the PanAf and director of the Wild Chimpanzee Foundation. Chimpanzees are known to be adaptable to human disturbance and can survive in human-modified landscapes, however, habitat loss, zoonotic diseases, bushmeat and pet trades are all threats to chimpanzee survival. These results warn of future critical impacts on their genetic health and viability if habitat fragmentation and isolation continue unabated.
###
Original publication:
Jack D. Lester et al.
Recent genetic connectivity and clinal variation in chimpanzees
Communications Biology, 5 March 2021
Contact:
Jack Lester
Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, Leipzig
+49 341 3550-262
[email protected]
Dr. Mimi Arandjelovic
Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, Leipzig
+49 341 3550-239
[email protected]
Dr. Hjalmar Kühl
German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv) &
Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, Leipzig
+49 341 3550-236
[email protected]
Media Contact
Sandra Jacob
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.