Researchers at Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s call for expanding children’s access to experimental cancer therapies
Credit: Patrick Bibbins / Boston Children’s Hospital
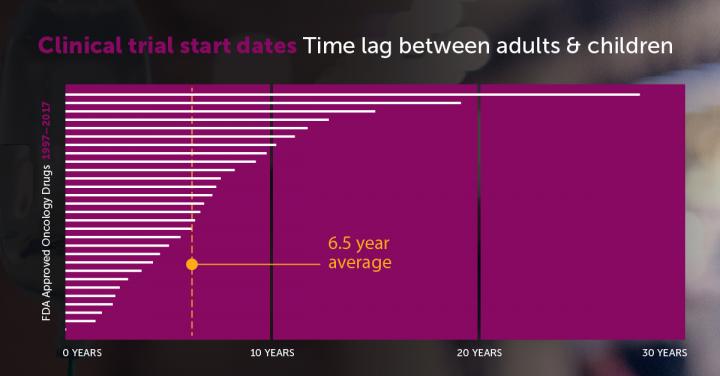
Cancer drugs approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) took a median of 6.5 years to go from the first clinical trial in adults to the first trial in children, according to a study at the Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center. The study was published in the May issue of the European Journal of Cancer.
“Despite knowing that these agents are effective anticancer drugs, it’s taking too long to even start studying these therapies in children,” says Steven G. DuBois, MD, Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center, corresponding author on the study. “As a doctor taking care of young cancer patients, this is tremendously frustrating. If I were a parent of a child with cancer, I wouldn’t stand for this.”
The team at Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s conducted a systematic analysis of the time from first-in-human trials to first-in-child trials of agents first approved by the FDA for any oncology indication from 1997 to 2017. The investigators utilized clinical trials registry data, published literature and oncology abstracts to identify relevant trials and start dates.
Delayed pediatric trials
In that timeframe, 126 drugs received initial FDA approval for an oncology indication. After excluding hormonal modulators (not relevant to children’s cancers), 117 agents remained for analysis. Fifteen of 117 drugs (12.8%) had not yet had a pediatric trial, while 6 of 117 drugs (5.1%) included children in the initial FDA approval.
The data showed a median 6.5-year lag between first-in-human and first-in-child clinical trials, with a range of 0 to 27.7 years.
“Some may argue that this lag is appropriate to ensure safety of a vulnerable pediatric population and to only study agents in children that are on a path to FDA approval, based upon activity in adults with cancer,” says DuBois. “Others may argue that this lag is too long for children with life-threatening diseases and that some agents that fail in adult indications may nevertheless prove to be important drugs for pediatric indications.”
In the U.S., the recent RACE for Children Act strengthens the requirement that new cancer therapies with potential biological relevance to pediatric cancers be evaluated in children. This study can serve as a benchmark as this new policy is enacted, says DuBois.
###
Coauthors on the paper were Dylan V. Neel, Harvard Medical School student, and David S. Shulman, MD, from Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s. The study was supported by Alex’s Lemonade Stand Foundation and the National Institutes of Health.
About Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center
Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center – one of the nation’s top pediatric cancer centers, according to U.S. News & World Report – brings together two internationally known research and teaching institutions that have provided comprehensive care for pediatric oncology and hematology patients since 1947. The Harvard Medical School affiliates share a clinical staff that delivers inpatient care at Boston Children’s Hospital and most outpatient care at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. Follow the Center on Twitter at @childcancercare.
Media Contact
Peter Cohenno
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




