Chemotherapy with only one injection, repeated phototherapy, and no side effects. Development of a cancer-targeted single component supramolecular peptide phototherapeutic agent
Credit: Korea Institute of Science and Technology(KIST)
Researchers in South Korea have developed a phototherapy technology that can significantly increase efficiency while reducing the pain of chemotherapy and minimizing side effects after treatment. The President of Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), Seok-Jin Yoon announced that a research team led by Dr. Se-hoon Kim at the Theragnosis Research Center (KU-KIST Graduate School of Converging Science and Technology) has developed a cancer-targeted phototherapeutic agent that promises complete elimination of cancer cells without side effects. It involves only one injection and repeated phototherapy. This development was made through joint research with Professor Dong-June Ahn of Korea University and Professor Yoon-Sik Lee of Seoul National University.
Phototherapy technology, a cancer treatment modality that uses light, injects a photosensitizer that destroys cancer cells in response to a laser, which accumulates in only cancerous tissues. Further, it shoots light to selectively destroy the cancer cells. It has far fewer side effects than radiation therapy or general chemotherapy (that inevitably damage the tissues surrounding the cancer cells), allowing repeated treatment.
Whereas the effect of the conventional photosensitizers only lasted for one session, and the photosensitizer had to be administered each time the treatment procedure was repeated. Moreover, the residual photosensitizer after treatment accumulated in the skin or eyes causing side effects due to light; thus, it was recommended to isolate the patient from sunlight and indoor lighting for some time after treatment. Overall, the patients receiving treatment have had to suffer from the pain of the injection and the inconvenience of living in isolation each time. Recently, photosensitizers with phototherapeutic effects that get activated only in cancer tissues have been developed; however, they are still toxic and have to be injected for every repeat treatment.
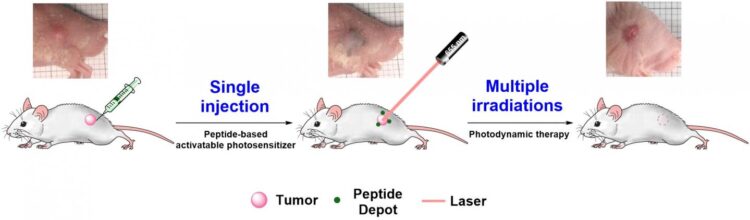
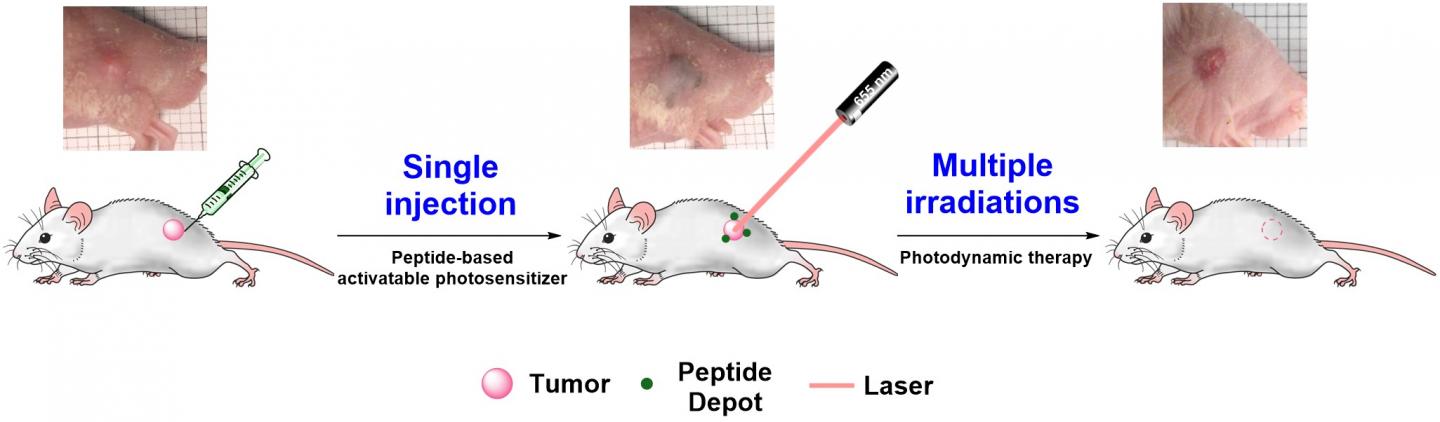
Dr. Se-hoon Kim and his team at KIST used peptides that selectively target cancer tissues and assemble themselves in a specific order to resolve the problems associated with the phototherapy technology. The research team developed a peptide-based photosensitizer that activates phototherapeutic effects only in cancer tissues by using the internalizing RGD peptide (iRGD) that can selectively penetrate and target cancer tissues as the skeleton, and by properly designing a matting agent for the modulation of its reaction to light.
When this newly developed photosensitizer is injected into a living body, it is activated by the body temperature and aggregates into a supramolecular array designed by the research team, to be stored around cancer cells. The subsequent phototherapy can destroy only cancer cells without affecting normal cells.
The phototherapeutic agent developed by the researchers was injected into a mouse model implanted with a tumor, and the photosensitizer was stored around the tumor and was continuously released for a long time (2 to 4 weeks), demonstrating the ability of selectively targeting the tumor with just one injection around the cancerous tissues. Moreover, no toxicity was found to destroy the tissues and major organs around the cancer, even with repeated exposure to light. The cancerous tissues were completely removed through repeated procedures.
“We developed a cancer-targeting peptide phototherapeutic agent that forms a reservoir through supramolecular self-assembly without additional adjuvants when injected in vivo,” said KIST Center Director Se-hoon Kim. “The developed phototherapeutic agent is expected to be useful in future phototherapy as it allows long-term repeated phototherapy without toxicity after only one injection around the cancer until the complete removal of the cancer, and has a simple formulation with a single component,” he added.
###
This study was carried out with a grant from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), as part of the Institutional R&D Program of KIST. The results of this study were published in the latest issue of “ACS Nano” (IF: 14.588, the top 5.25% in JCR), an international journal in the field of nanotechnology.
Media Contact
Do-Hyun Kim
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.