Credit: Nripan Mathews NTU, Singapore
Perovskites are a class of materials made up of organic materials bound to a metal. Their fascinating structure and properties have propelled perovskites into the forefront of materials’ research, where they are studied for use in a wide range of applications. Metal-halide perovskites are especially popular, and are being considered for use in solar cells, LED lights, lasers, and photodetectors.
For example, the power-conversion efficiency of perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have increased from 3.8% to 25.5% in only ten years, surpassing other thin-film solar cells – including the market-leading, polycrystalline silicon.
Perovskites are usually made by mixing and layering various materials together on a transparent conducting substrate., which produces thin, lightweight films. The process, known as “chemical deposition”, is sustainable and relatively cost-effective.
But there is a problem. Since 2014, metal halide perovskites have been made by mixing cations or halides with formamidinium (FAPbI3). The reason is that this recipe results in high power-conversion efficiency in perovskite solar cells. But at the same time, the most stable phase of FAPbI3 is photoinactive, meaning that it does not react to light – the opposite of what a solar power harvester ought to do. In addition, solar cells made with FAPbI3 show long-term stability issues.
Now, researchers led by Michael Grätzel and Anders Hafgeldt at EPFL, have developed a deposition method that overcomes the formamidinium issues while maintaining the high conversion of perovskite solar cells. The work has been published in Science.
In the new method, the materials are first treated with a vapor of methylammonium thiocyanate (MASCN) or formamidinium thiocyanate FASCN. This innovative tweak turns the photoinactive FAPbI3 perovskite films to the desired photosensitive ones.
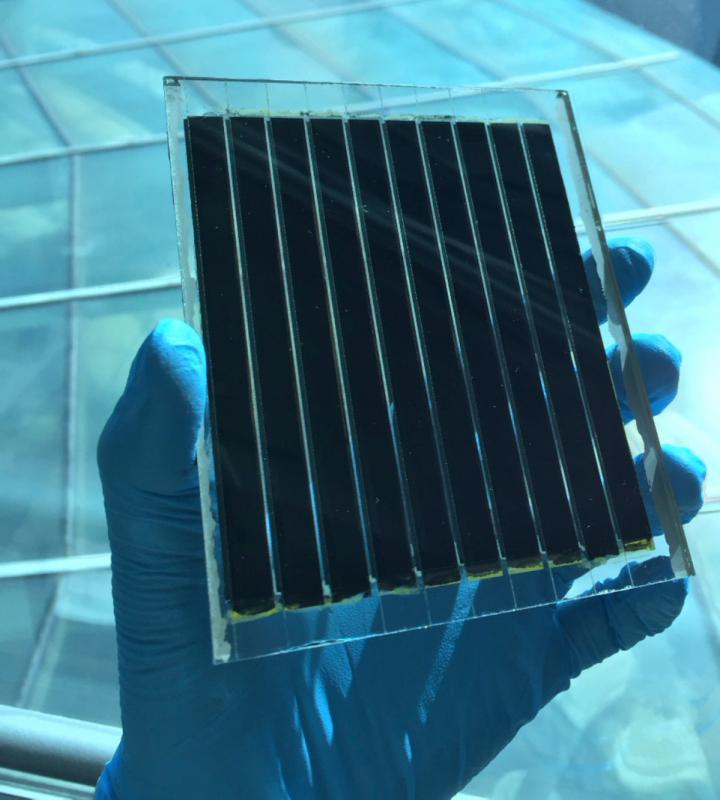
The scientists used the new FAPbI3 films to make perovskite solar cells. The cells showed more than 23% power-conversion efficiency and long-term operational and thermal stability. They also featured low (330 mV) open-circuit voltage loss and a low (0.75 V) turn-on voltage of electroluminescence.
###
Professor Michael Grätzel’s lab and Professor Anders Hgfeldt’s lab are part of EPFL’s Institute of Chemical Science and Engineering (ISIC), situated in the School of Basics Sciences.
Other contributors
EPFL Laboratory of Computational Chemistry and Biochemistry,
EPFL Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance
Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF)
Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology
Fudan University
Reference
Haizhou Lu, Yuhang Liu, Paramvir Ahlawat, Aditya Mishra, Wolfgang R. Tress, Felix T. Eickemeyer, Yingguo Yang, Fan Fu, Zaiwei Wang, Claudia E. Avalos, Brian I. Carlsen, Anand Agarwalla, Xin Zhang, Xiaoguo Li, Yiqiang Zhan, Shaik M. Zakeeruddin, Lyndon Emsley, Ursula Roethlisberger, Lirong Zheng, Anders Hagfeldt, Michael Graetzel. Vapor-assisted deposition of highly efficient, stable black-phase FAPbI3 perovskite solar cells. Science 369, eabb8985, 2 October 2020.
Media Contact
Nik Papageorgiou
[email protected]




