Credit: NAOJ
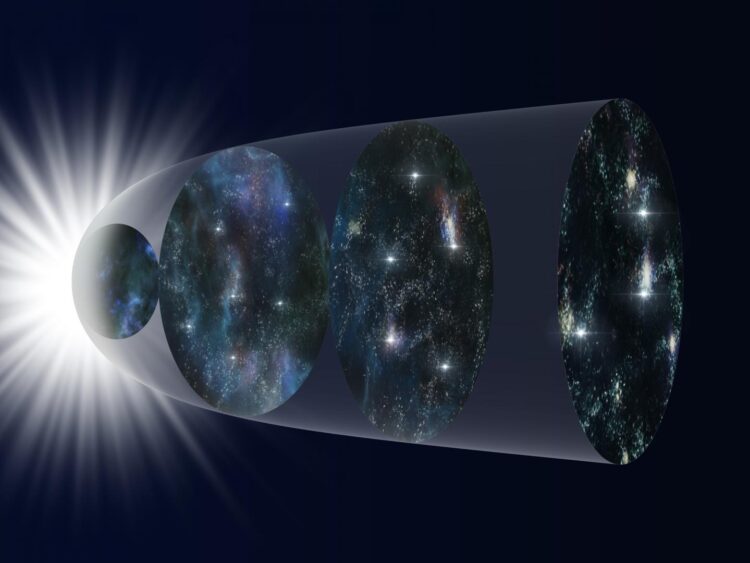
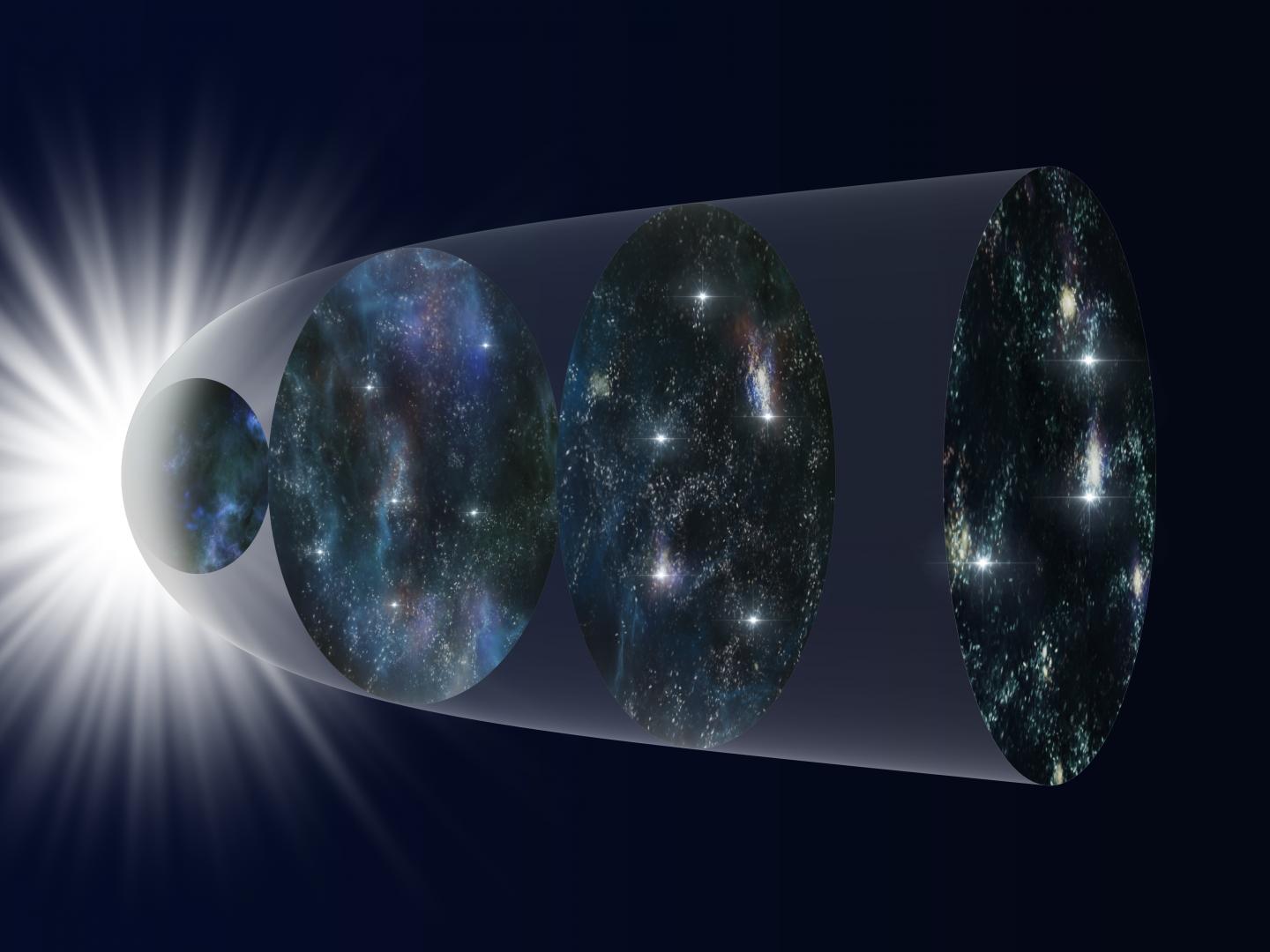
An international research team analyzed a database of more than 1000 supernova explosions and found that models for the expansion of the Universe best match the data when a new time dependent variation is introduced. If proven correct with future, higher-quality data from the Subaru Telescope and other observatories, these results could indicate still unknown physics working on the cosmic scale.
Edwin Hubble’s observations over 90 years ago showing the expansion of the Universe remain a cornerstone of modern astrophysics. But when you get into the details of calculating how fast the Universe was expanding at different times in its history, scientists have difficulty getting theoretical models to match observations.
To solve this problem, a team led by Maria Dainotti (Assistant Professor at the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan and the Graduate University for Advanced Studies, SOKENDAI in Japan and an affiliated scientist at the Space Science Institute in the U.S.A.) analyzed a catalog of 1048 supernovae which exploded at different times in the history of the Universe. The team found that the theoretical models can be made to match the observations if one of the constants used in the equations, appropriately called the Hubble constant, is allowed to vary with time.
There are several possible explanations for this apparent change in the Hubble constant. A likely but boring possibility is that observational biases exist in the data sample. To help correct for potential biases, astronomers are using Hyper Suprime-Cam on the Subaru Telescope to observe fainter supernovae over a wide area. Data from this instrument will increase the sample of observed supernovae in the early Universe and reduce the uncertainty in the data.
But if the current results hold-up under further investigation, if the Hubble constant is in fact changing, that opens the question of what is driving the change. Answering that question could require a new, or at least modified, version of astrophysics.
These results will appear as M.G. Dainotti et al. “On the Hubble Constant Tension in the SNe Ia Pantheon Sample” in the Astrophysical Journal on May 17, 2021.
###
Media Contact
Dr. Hitoshi Yamaoka
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.