Researchers find the best time to consume proteins for building and strengthening muscles is during breakfast
Credit: Waseda University
Proteins constitute an essential dietary component that help in the growth and repair of the body. Composed of long chains of amino acids, proteins promote the growth of skeletal muscles, the group of muscles that help us move. Humans have been aware of the benefits of proteins for long. However, recent studies have shown that having the right amount of protein at the right time of the day is essential for proper growth. This is called ‘Chrononutrition,’ in which when you eat is as important as what and how you eat.
The reason behind this is the body’s internal biological clock, called the ‘circadian rhythm.’ This rhythm is followed by all cells and controls life functions like metabolism and growth. Interestingly, protein digestion and absorption have been found to fluctuate across day and night according to this clock. Moreover, earlier studies have reported that intake of protein at breakfast and lunch promotes skeletal muscle growth in adults. However, details on the effect of the time of protein intake on muscle growth and function have remained elusive till date.
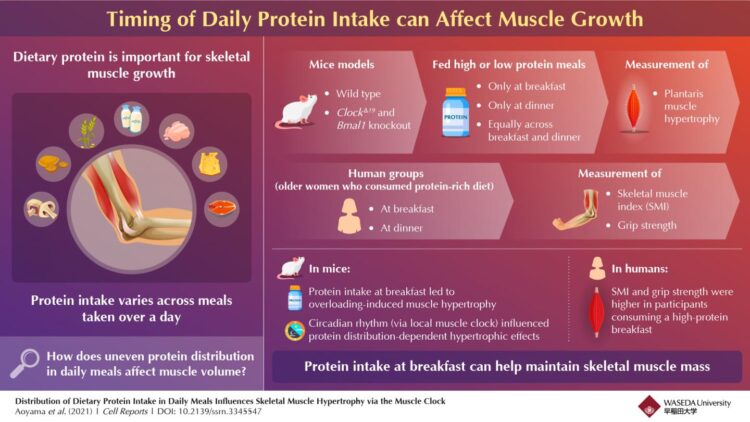
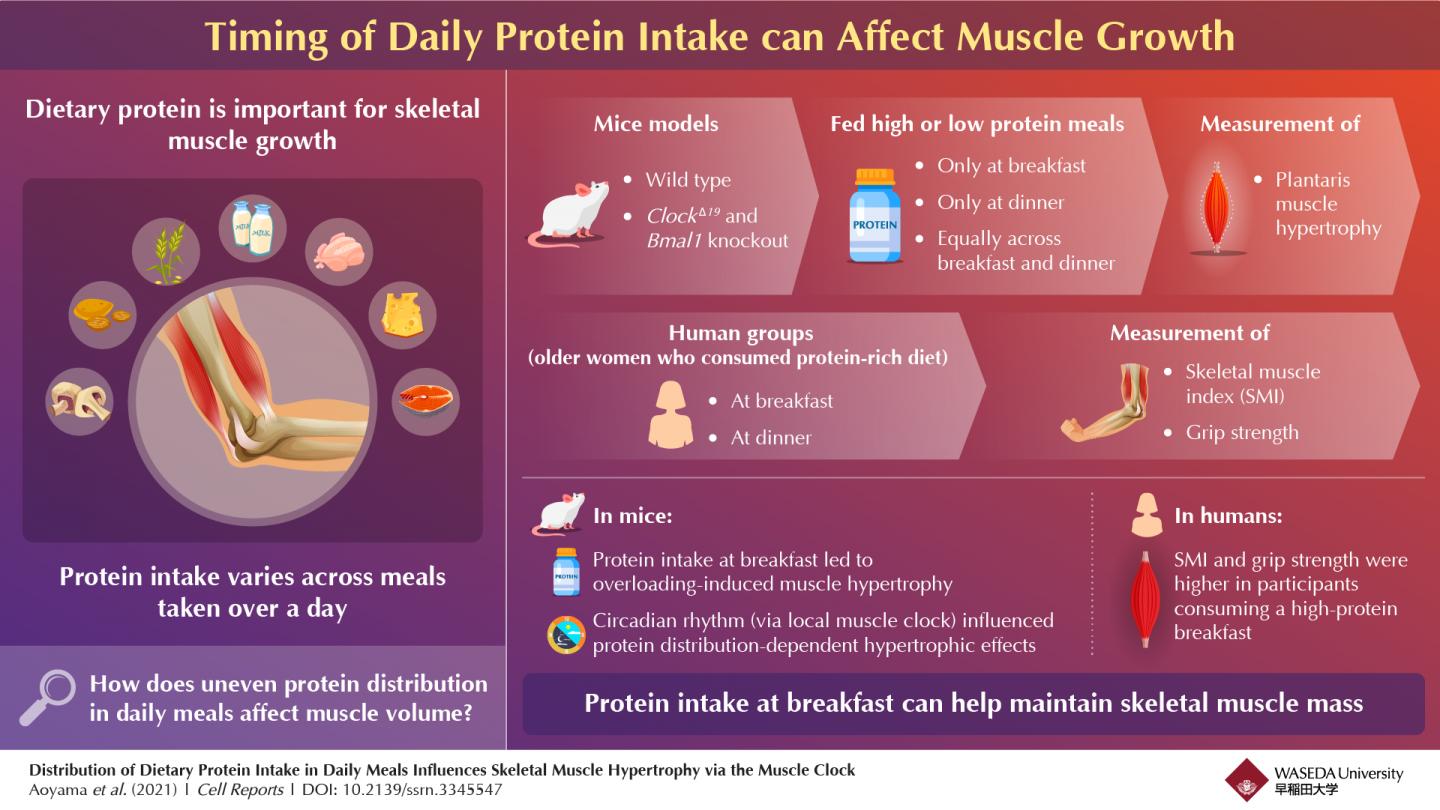
Fortunately, researchers from Waseda University, led by Professor Shigenobu Shibata, recently endeavored to understand the effect of the distribution of protein intake through the day on muscles. They fed laboratory mice two meals per day containing either high (11.5% by proportion) or low (8.5% by proportion) protein concentrations. The researchers noted that protein intake at breakfast induced an increase in muscle growth, determined by assessing induced hypertrophy of the plantaris muscle in the leg, when compared with the effects of protein intake at dinner. Specifically, the ratio of muscle hypertrophy determined against the growth of the control muscle was 17% higher in mice fed 8.5% protein at breakfast, than that in mice fed 11.5% protein at dinner, despite the former group consuming a low proportion of protein overall. They also found that intake of a type of protein called the BCCA, short for branched-chain amino acids, early in the day increased the size of skeletal muscles specifically.
To confirm the association of these effects with the workings of the circadian rhythm, the researchers next engineered whole-body mutant ClockΔ19 or muscle-specific Bmal1 knockout mice lacking the genes that control the biological clock. They repeated diet distribution experiments on these mice but did not observe similar muscle change, which confirmed the involvement of the circadian rhythm in muscle growth in the context of protein intake.
Excited about the findings of their study published in a recent issue of the Cell Reports, Prof. Shibata emphasizes, “Protein-rich diet at an early phase of the daily active period, that is at breakfast, is important to maintain skeletal muscle health and enhance muscle volume and grip strength.”
To check if their findings were applicable to humans, the team recruited women in their study and tested if their muscle function, determined by measuring skeletal muscle index (SMI) and grip strength, varied with the timing of the protein-rich diet consumed. Sixty women aged 65 years and above who took protein at breakfast rather than at dinner showed better muscle functions, suggesting the possibility of the findings to be true across species. Additionally, the researchers also found a strong association between SMI and the proportion of protein intake at breakfast relative to total protein intake through the day.
Prof. Shibata is hopeful that the findings of their study will lead to a widespread modification in the current diet regime of most people across the Western and Asian countries, who traditionally consume low amounts of protein at breakfast. He therefore stresses, “For humans, in general, the protein intake at breakfast averages about 15 grams, which is less than what we consume at dinner, which is roughly 28 grams. Our findings strongly support changing this norm and consuming more protein at breakfast or morning snacking time.”
It seems, a simple change in our dietary regime can be our key to ensuring healthy muscles!
###
Reference
Authors: Shinya Aoyama (1,2,5), Hyeon-Ki Kim (1,2), Rina Hirooka (1), Mizuho Tanaka (1), Takeru Shimoda (1), Hanako Chijiki (1), Shuichi Kojima (1), Keisuke Sasaki (1), Kengo Takahashi (1), Saneyuki Makino (1), Miku Takizawa (1), Masaki Takahashi (1), Yu Tahara (1), Shigeki Shimiba (4), Kazuyuki Shinohara (5), Shigenobu Shibata, Ph.D. (1)
Title of original paper: Distribution of dietary protein intake in daily meals influences skeletal muscle hypertrophy via the muscle clock
Journal: Cell Reports
DOI: https:/
Affiliations:
(1) Laboratory of Physiology and Pharmacology, School of Advanced Science and Engineering, Waseda University
(2) Organization for University Research Initiatives, Waseda University
(3) Institute for Liberal Arts, Tokyo Institute of Technology
(4) Department of Health Science, School of Pharmacy, Nihon University
(5) Department of Neurobiology & Behavior, Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Nagasaki University
About Waseda University
Located in the heart of Tokyo, Waseda University is a leading private research university that has long been dedicated to academic excellence, innovative research, and civic engagement at both the local and global levels since 1882. The University ranks number one in Japan in international activities, including the number of international students, with the broadest range of degree programs fully taught in English. To learn more about Waseda University, visit https:/
Media Contact
Jasper Lam
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.