Credit: Tamura/Osaka City University
For the first time, researchers have used a novel catalyst process to recycle a type of plastic found in everything from grocery bags and food packaging to toys and electronics into liquid fuels and wax.
The team published their results on Dec. 10 in Applied Catalysis B: Environmental.
“Plastics are essential materials for our life because they bring safety and hygiene to our society,” said paper co-authors Masazumi Tamura, associate professor in the Research Center for Artificial Photosynthesis in the Advanced Research Institute for Natural Science and Technology in Osaka City University, and Keiichi Tomishige, professor in the Graduate School of Engineering in Tohoku University. “However, the growth of the global plastic production and the rapid penetration of plastics into our society brought mismanagement of waste plastics, causing serious environmental and biological issues such as ocean pollution.”
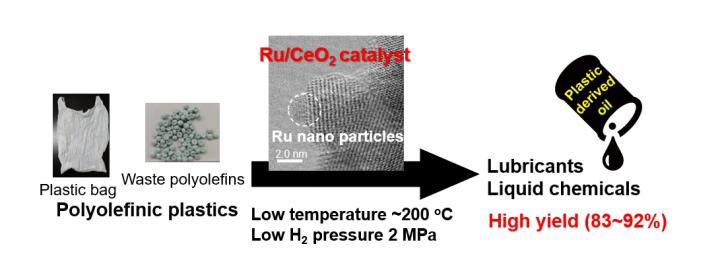
Polyolefinic plastics — the most common plastic — have physical properties that make it difficult for a catalyst, responsible for inducing chemical transformation, to interact directly with the molecular elements to cause a change. Current recycling efforts require temperatures of at least 573 degrees Kelvin, and up to 1,173 degrees Kelvin. For comparison, water boils at 373.15 degrees Kelvin, and the surface of the Sun is 5,778 degrees Kelvin.
The researchers looked to heterogenous catalysts in an effort to find a reaction that might require a lower temperature to activate. By using a catalyst in a different state of matter than the plastics, they hypothesized that the reaction would be stronger at a lower temperature.
They combined ruthenium, a metal in the platinum family, with cerium dioxide, used to polish glass among other applications, to produce a catalyst that caused the plastics to react at 473 degrees Kelvin. While still high for human sensibilities, it requires significantly less energy input compared to other catalyst systems.
According to Tamura and Tomishige, ruthenium-based catalysts have never been reported in the scientific literature as a way to directly recycle polyolefinic plastics.
“Our approach acted as an effective and reusable heterogeneous catalyst, showing much higher activity than other metal-supported catalysts, working even under mild reaction conditions,” Tamura and Tomishige said. “Furthermore, a plastic bag and waste plastics could be transformed to valuable chemicals in high yields.”
The researchers processed a plastic bag and waste plastics with the catalyst, producing a 92% yield of useful materials, including a 77% yield of liquid fuel and a 15% yield of wax.
“This catalyst system is expected to contribute to not only suppression of plastic wastes but also to utilization of plastic wastes as raw materials for production of chemicals,” Tamura and Tomishige said.
###
Other contributors include Yosuke Nakaji, Shuhei Miyaoka and Yoshinao Nakagawa, all affiliated with the Graduate School of Engineering at Tohoku University; and Shogo Kumagai, Mifumi Tanji and Toshiaki Yoshioka, all affiliated with the Graduate School of Environmental Studies at Tohoku University.
This work was supported by the Environment Research and Technology Development Fund of the Environmental Restoration and Conservation Agency of Japan.
Media Contact
Rina MATSUKI
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




