Credit: Fanxing Li, NC State University
A research team led by North Carolina State University has engineered a new catalyst that can more efficiently convert ethane into ethylene, which is used in a variety of manufacturing processes. The discovery could be used in a conversion process to drastically reduce ethylene production costs and cut related carbon dioxide emissions by up to 87%.
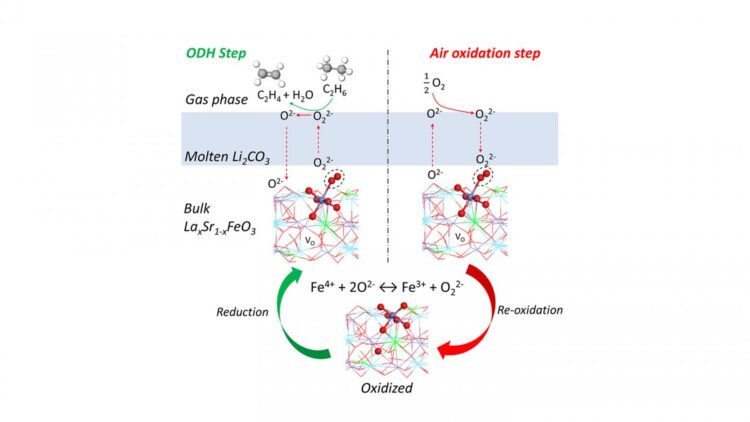
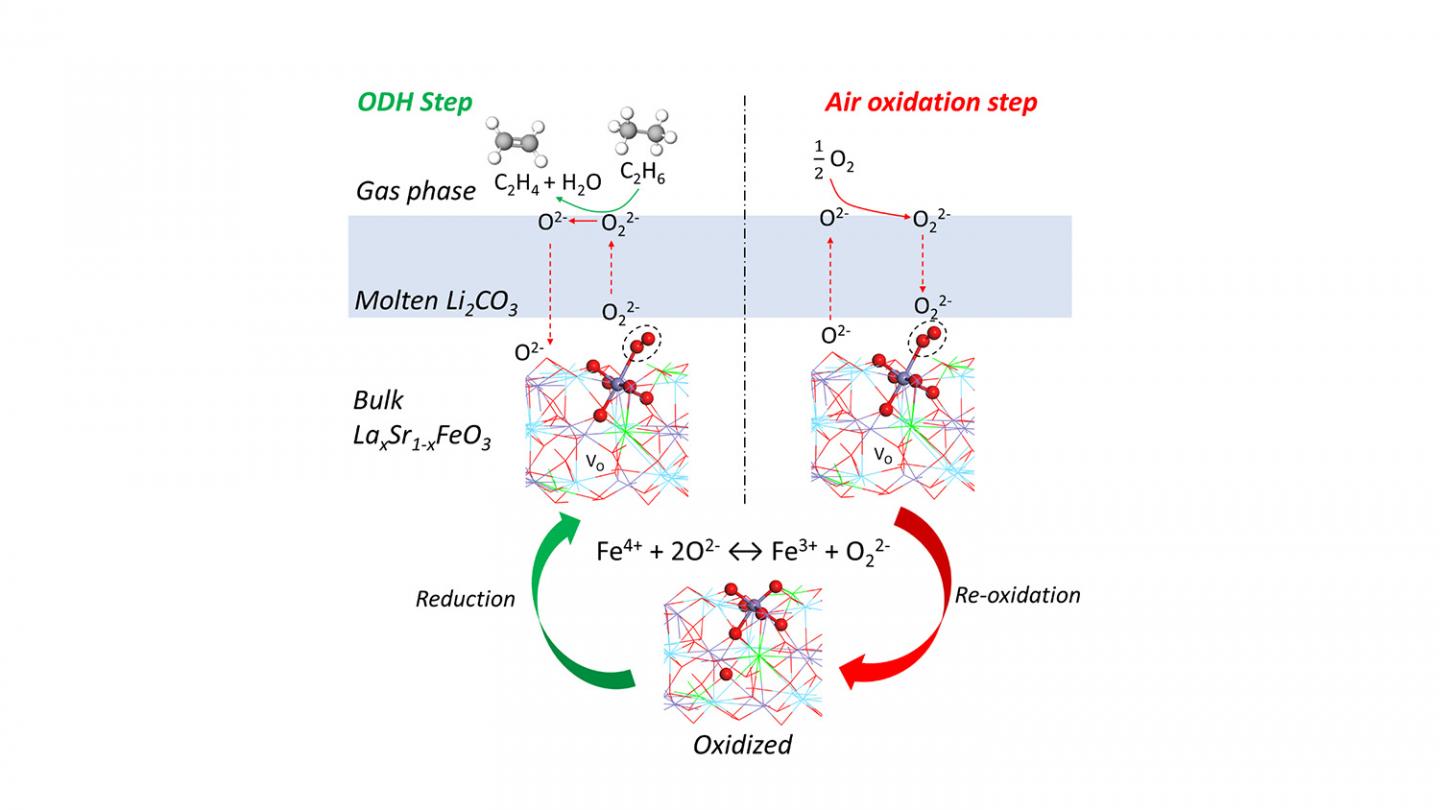
“Our lab previously proposed a technique for converting ethane into ethylene, and this new redox catalyst makes that technique more energy efficient and less expensive while reducing greenhouse gas emissions,” says Yunfei Gao, a postdoctoral scholar at NC State and lead author of a paper on the work. “Ethylene is an important feedstock for the plastics industry, among other uses, so this work could have a significant economic and environmental impact.”
“Ethane is a byproduct of shale gas production, and the improved efficiency of our new catalyst makes it feasible for energy extraction operations in remote locations to make better use of that ethane,” says Fanxing Li, corresponding author of the paper and an associate professor and University Faculty Scholar in NC State’s Department of Chemical Engineering.
“It is estimated that more than 200 million barrels of ethane are rejected each year in the lower 48 states due to the difficulty of transporting it from remote locations,” Li says. “With our catalyst and conversion technique, we think it would be cost effective to convert that ethane into ethylene. The ethylene could then be converted into liquid fuel, which is much easier to transport.
“The problem with current conversion techniques is that you can’t scale them down to a size that makes sense for remote energy extraction sites – but our system would work well in those locations.”
The new redox catalyst is a molten carbonate promoted mixed metal oxide, and the conversion process takes place at between 650 and 700 degrees Celsius with integrated ethane conversion and air separation. Current conversion techniques require temperatures higher than 800 degrees C.
“We estimate that the new redox catalyst and technique cut energy requirements by 60-87%,” Li says.
“Our technique would require an initial investment in the installation of new, modular chemical reactors, but the jump in efficiency and ability to convert stranded ethane would be significant,” Li says.
###
The paper, “A Molten Carbonate Shell Modified Perovskite Redox Catalyst for Anaerobic Oxidative Dehydrogenation of Ethane,” will be published April 24 in the journal Science Advances. The paper was co-authored by Xijun Wang, a postdoctoral researcher at NC State, and Junchen Liu, a Ph.D. student at NC State.
The work was done with support from the National Science Foundation, under grant number CBET-1604605; the Department of Energy’s RAPID Institute, under grant number DE-EE007888-05-6; and the Kenan Institute for Engineering, Technology, and Science.
Media Contact
Matt Shipman
[email protected]