Credit: Carnegie Mellon University
Researchers from Carnegie Mellon University’s Department of Chemistry have found a way to control the lifetime of the quantum states of gold nanoclusters by three orders of magnitude, which could lead to improvements in solar cell and photocatalysis technologies. Their study is published in the April 18 issue of Science.
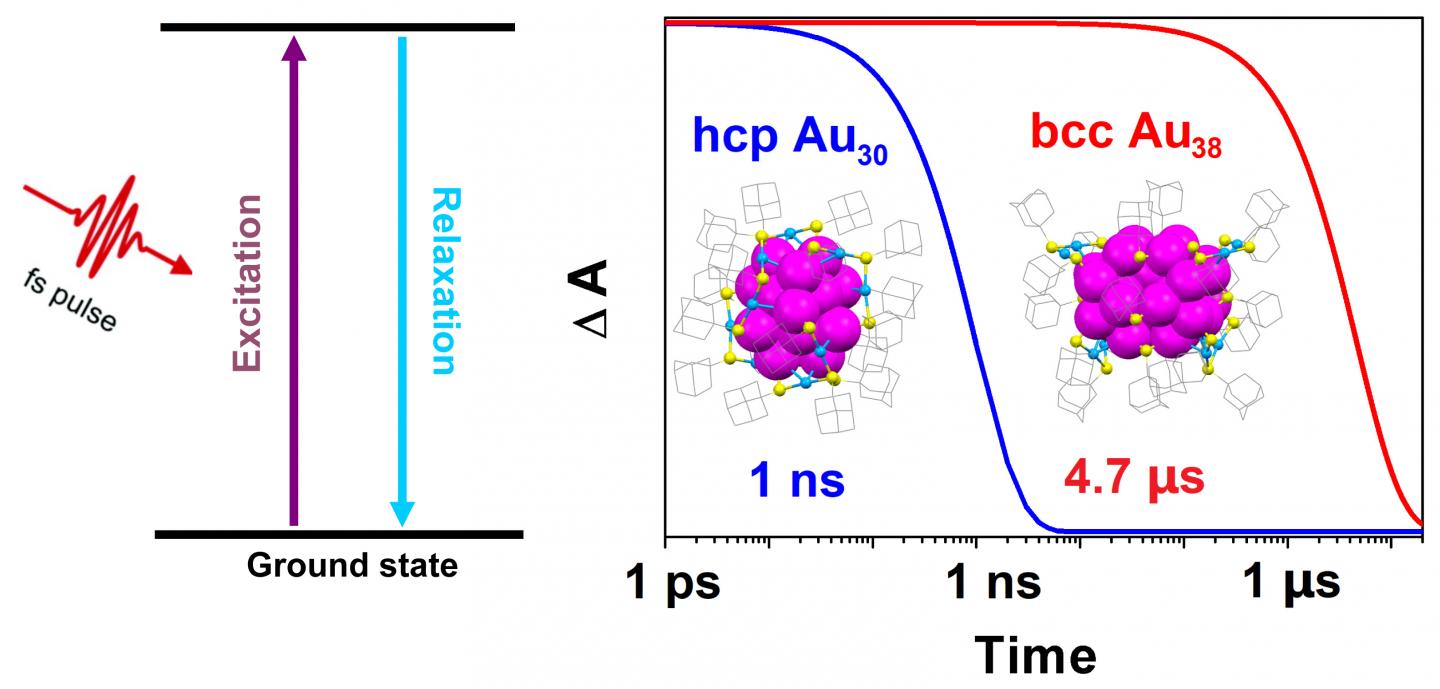
Excited quantum states occur when light is absorbed by a particle and the energy from that light is temporarily stored within the particle, making its energy higher than its ground state. The energy decays quickly and can be lost as heat in the span of a nanosecond, or one billionth of a second. Extending this quantum state could provide researchers with more time and opportunity to harness the stored energy.
Carnegie Mellon Chemistry Professor Rongchao Jin is world renowned for developing precisely sized gold nanoparticles. In this extension of his work, post-doctoral researcher Meng Zhou and Ph.D. student Tatsuya Higaki, who are co-first authors of the paper, studied atomically precise gold nanoclusters containing between 30 and 38 atoms. They altered the structures of clusters by rearranging the atoms into exotic configurations and protecting them with a capping ligand.
The researchers measured the lifetimes of the nanoclusters’ quantum states by using femtosecond and nanosecond time-resolved spectroscopy to take snapshots of the nanoclusters from the time when they absorbed energy from light, in this case a femtosecond laser pulse, until they released the energy. Collaborators at University of California, Riverside confirmed the results using density function theory calculations to analyze the molecular orbitals of the nanoclusters.
They found that a 30-atom gold nanocluster, with a hexagonal close-packed (hcp) structure, had a quantum lifetime of one nanosecond. But a 38-atom gold nanocluster with a body-centered cubic (bcc) structure had a much longer lifetime of 4.7 microseconds. Extending the lifetime by three magnitudes gives researchers ample time to extract the absorbed light energy from the nanoclusters — a finding that has significant implications.
“The strategy of manipulating the excited-state lifetime from very short to very long is exciting. The exceptionally long quantum lifetime of 4.7 microseconds is comparable to that of bulk silicon, which is used for commercial solar cells,” said Jin. “It should give us enough time to efficiently extract the energy into external circuits as an electronic current without losing too much energy to heat.”
The tailored quantum lifetime can also be used to increase the efficiency of visible light-based photocatalysis used to convert solar energy storage into chemicals, such as converting methanol and ethanol from carbon dioxide.
###
Additional study authors include: Guoxiang Hu and De-en Jiang, UC Riverside; Matthew Y. Sfeir, Brookhaven National Laboratory; and Yuxiang Chen, Carnegie Mellon.
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation (1808675); the Air Force Office of Scientific Research; and the U.S. Department of Energy (U.S. DOE), Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences and Chemical Sciences, Geosciences and Biosciences Division. The work used resources of the Center for Functional Nanomaterials, a U.S. DOE Office of Science Facility at Brookhaven National Laboratory.
Media Contact
Jocelyn Duffy
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.



