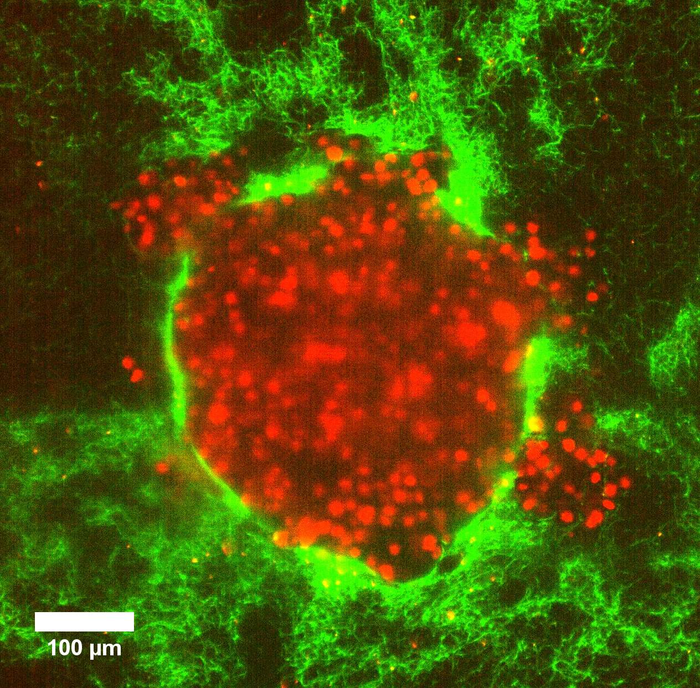
Biological processes such as wound healing and cancer cell invasion rely on the collective and coordinated motion of living cells. A little understood aspect that influences these processes is the pressure differences within and between different parts of the body. Researchers from Göttingen University and Münster University designed model tumour systems using cervical cancer cells in collagen matrices to investigate whether pressure differences can push cancer cells into their surroundings. Upon embedding the model tumours into a soft matrix, an increased pressure led to a sudden burst of rapid and coordinated cellular motion that sprayed outwards from the tumour. Their results were published in Advanced Science.
Credit: Dr Swetha Raghuraman
Biological processes such as wound healing and cancer cell invasion rely on the collective and coordinated motion of living cells. A little understood aspect that influences these processes is the pressure differences within and between different parts of the body. Researchers from Göttingen University and Münster University designed model tumour systems using cervical cancer cells in collagen matrices to investigate whether pressure differences can push cancer cells into their surroundings. Upon embedding the model tumours into a soft matrix, an increased pressure led to a sudden burst of rapid and coordinated cellular motion that sprayed outwards from the tumour. Their results were published in Advanced Science.
The researchers designed their model system using clumps of cervical cancer cells in simple 3D tissues that they could control, enabling them to systematically study the behaviour of the cells in different pressures and environments. Usually, individual cells exert forces on their environment in order to move, and collective motion is coordinated by cell-to-cell forces because they stick and clump together. However, this new model allowed the researchers to measure other mechanisms that encourage cellular movement such as pressure differences between different regions within the body.
Using imaging techniques that allowed the scientists to follow the tumour deformation even at the level of a single cell, the researchers discovered that increased pressure in a soft matrix drove coordinated cellular motion independent of cell-to-cell stickiness by triggering cell swelling. Eight hours after the 3D clumps of cervical cancer cells were embedded in soft collagen matrices, they burst out in a sudden rapid stream of cancer cells. This fluid-like pushing mechanism exhibits high cell velocities and a sudden super-spreading motion like water spraying from a hose when you press your thumb over the top. In fact, the rapid burst seemed to kill about 80% of the cells but surprisingly the remaining cells succeeded in embedding in the same environment over the following four days, and multiplied. “This signified that after the initial burst, the remaining live cells could still divide substantially and migrate. Importantly, when this happens in a person’s body, this can prove to be extremely dangerous, often beating current cancer treatments,” explains Professor Timo Betz, Biophysics Institute, University of Göttingen.
Tumour models embedded in a stiffer collagen did not behave in the same way. In fact, even after seven days, there was a complete absence of bursts, showing that the pressure difference in the tissue was the important part of the effect. The only way that researchers could trigger the “cell burst” in stiffer collagen was by introducing weak spots in specific regions.
In this newly observed phenomenon, cell swelling in groups increased the intrinsic pressure that pushed the cancer cells out into less resistant regions of the matrix. “Such pressure-driven effects may provide primary tumours in the body an exceptional advantage: it enables them to breach the first membrane barrier and gives them the opportunity to spread to other parts of the body, or metastasize,” says Betz. He adds: “This provides new evidence that pressure-driven effects should be considered to help us better understand the mechanical forces involved in cell and tissue movement as well as cancer cell invasion. Understanding this cellular mass movement is fundamental for describing and treating cancer and similar illnesses.”
Original Publication: Raghuraman, S. et al. “Pressure Drives Rapid Burst‐Like Coordinated Cellular Motion from 3D Cancer Aggregates” Advanced Science (2022) DOI:10.1002/advs.202104808 Text also available at: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/advs.202104808
Contact:
Professor Timo Betz
University of Göttingen
Faculty of Physics
Friedrich-Hund-Platz 1, 37077 Göttingen, Germany
Tel: +49 (0) 551 39 26921
Email: [email protected]
www.betzlab.uni-goettingen.de/
Journal
Advanced Science
DOI
10.1002/advs.202104808
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Publication Date
7-Jan-2022




