New technology means solar panels could be integrated into windows, cladding
Credit: David Fermin
A team of researchers, led by chemists from the University of Bristol, has received significant funding from the UKRI to revolutionise the fabrication and application of photovoltaic devices, used to produce solar energy.
Imagine a city in the near future where buildings have solar panels integrated into windows, cladding and rooftops – allowing urban areas to generate their own clean and renewable energy. Thanks to a new grant from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) and Bristol’s Cabot Institute, that vision is set to become reality.
The Bristol-led team, together with colleagues from Northumbria University and Loughborough University, will focus on developing the formulation and processing of inorganic semiconductor junctions at the centre of thin-film PV devices. In contrast to established technologies, thin-film PV devices have a lower energy payback time (i.e. they emit less carbon during fabrication/installation). They can also be made flexible, semi-transparent and adapted to a variety of systems and infrastructures.
Professor David Fermin, Head of Bristol Electrochemistry and Solar Team at the University of Bristol, said:
“If we are to achieve a target of Net-Zero by 2050, we need technology that can mitigate our increasing demand for electricity, which is set to at least double in response to energy intensive sectors such as transport, building and manufacturing.
“Consequently, we need to deploy low-carbon energy systems into every sector of the economy. Out of all renewable energy technologies, solar is the only one with the capacity to be integrated into cities and high population areas. We need technologies that will allow us to integrate solar panels into cladding, windows and every possible infrastructure. Our project aims to develop the adaptable and low-cost PV technology which can meet this huge challenge.
“What’s more, our research can substantially decrease the fabrication costs as well as removing critical (In, Ga, Te) and toxic elements (Cd) present in current commercial technologies.”
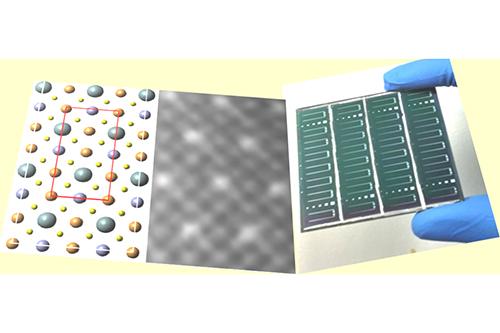
The team will investigate complex semiconductor compounds such as Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 with a very precise crystal structure. Their challenge is to formulate precursors and processing methods to ensure that each atom goes in the right place.
Professor Neil Fox from Bristol explains: “If you have the rogue Sn atom occupying a site in which we expect to find Cu or Zn, then we are in trouble. You don’t want to find SnS making a separate crystal either within your device. If the material has little grains of SnS at the surface, electrons will be emitted at lower energies (shunting), decreasing the power output of the solar cells.
“An incredibly exciting aspect of our research is that we can actually ‘see’ those atoms and how they arrange themselves.”
The 3.5 year programme is set to start in early June and the team aims to produce minimodules with power conversion efficiencies above 15 %, fabricated by scalable processes. The Centre for Process Innovation Catapult is a key project partner and will be assessing manufacturability across each innovation step in the research.
Dr Devendra Tiwari is leading the research team at Northumbria University and said: “To me, the highlight and challenge of the proposal are right there in the project title – ‘Solution Processing’. Solution processing is much less capitally intensive and is much readily suited to allow integration of solar cells to scaffoldings and windows than current manufacturing technology prevalent for thin-film solar cells. It therefore offers the opportunity to produce cost-effective integrated PV systems. The challenge is to demonstrate marketable performance and process scalability and solve issues from atomistic to device level. Such multilevel versatility and expertise to realise this lab-to-fab transition is what Northumbria brings to the team.”
Dr Jake Bowers is leading the research carried out at Loughborough University and said “This project is really exciting. Fabricating thin film solar cells with low cost solution processes has the potential to significantly reduce the cost of electricity produced from photovoltaics to the end user. What’s more, the fabrication processes used require significantly less energy than the manufacturing processes used traditional silicon based photovoltaics. This provides an extra added benefit as the UK aims for its net zero targets.”
###
Media Contact
Shona East
[email protected]




