A stem cell capable of regenerating both bone and cartilage has been identified in bone marrow of mice. The discovery by researchers at Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) is reported today in the online issue of the journal Cell.
The cells, called osteochondroreticular (OCR) stem cells, were discovered by tracking a protein expressed by the cells. Using this marker, the researchers found that OCR cells self-renew and generate key bone and cartilage cells, including osteoblasts and chondrocytes. Researchers also showed that OCR stem cells, when transplanted to a fracture site, contribute to bone repair.
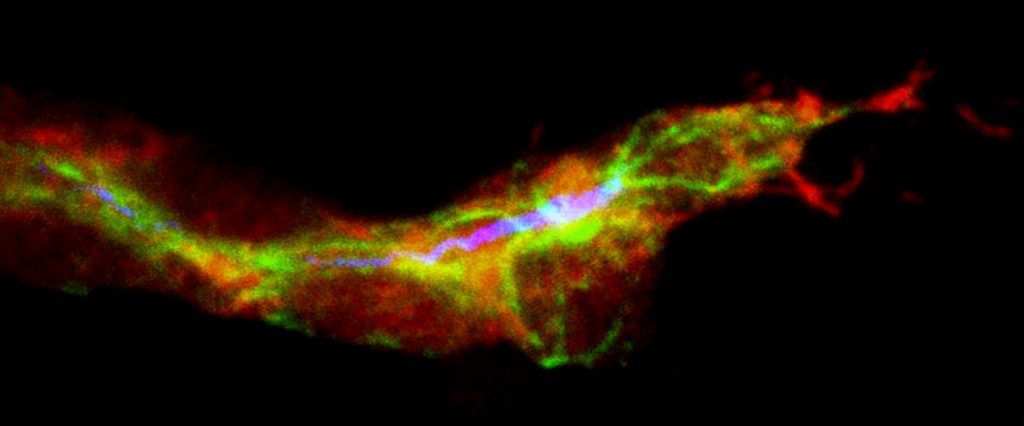
Schematic of the head of a femur (the thigh bone), showing OCR stem cells in red and the growth of bone (green), cartilage and stromal cells. (Credit: Mike Barnett for Columbia University Medical Center)
“We are now trying to figure out whether we can persuade these cells to specifically regenerate after injury. If you make a fracture in the mouse, these cells will come alive again, generate both bone and cartilage in the mouse—and repair the fracture. The question is, could this happen in humans,” says Siddhartha Mukherjee, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine at CUMC and a senior author of the study.
The researchers believe that OCR stem cells will be found in human bone tissue, as mice and humans have similar bone biology. Further study could provide greater understanding of how to prevent and treat osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, or bone fractures.
“Our findings raise the possibility that drugs or other therapies can be developed to stimulate the production of OCR stem cells and improve the body’s ability to repair bone injury—a process that declines significantly in old age,” says Timothy C. Wang, MD, the Dorothy L. and Daniel H. Silberberg Professor of Medicine at CUMC, who initiated this research. Previously, Dr. Wang found an analogous stem cell in the intestinal tract and observed that it was also abundant in the bone.
“These cells are particularly active during development, but they also increase in number in adulthood after bone injury,” says Gerard Karsenty, MD, PhD, the Paul A. Marks Professor of Genetics and Development, chair of the Department of Genetics & Development, and a member of the research team.
The study also showed that the adult OCRs are distinct from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which play a role in bone generation during development and adulthood. Researchers presumed that MSCs were the origin of all bone, cartilage, and fat, but recent studies have shown that these cells do not generate young bone and cartilage. The CUMC study suggests that OCR stem cells actually fill this function and that both OCR stems cells and MSCs contribute to bone maintenance and repair in adults.
The researchers also suspect that OCR cells may play a role in soft tissue cancers.
Researchers from the Stanford University School of Medicine have also just released a similar study that used a different methodology to identify the same stem cell type.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by Columbia University Medical Center.