Metolazone, a drug used to treat hypertension, activates a mitochondrial stress response that prolongs lifespan in the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans
Credit: Eriko Kage-Nakadai, Osaka City University
Since time immemorial, people have been fascinated by ways to stop aging. Nearly every culture has stories to tell about people who lived for thousands of years, showing that extending lifespan has always been one a deep desire across humanity. While modern medicine does not strive to find the fountain of youth, keen interest in promoting longevity has prompted research into the mechanisms of aging and the possibility of anti-aging drugs. Researchers now know that mitochondria play an important role in aging. Specifically, when mitochondria are harmed in some way and their function is impaired, a process called mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt) occurs that repairs mitochondria and benefits cell survival. Therefore, some scientists think it is possible to increase lifespan by identifying drugs that activate UPRmt.
Dr. Eriko Kage-Nakadai and her colleagues from Osaka City University in Japan are one of the many research teams fascinated by aging research. As Dr. Kage-Nakadai explains, “Even though aging is not a disease, drugs may slow down aging and mitigate or prevent its negative effects on our health.” Current research shows promising signs. Experiments with Caenorhabditis elegans–a worm commonly used in biological research as a model–have found several compounds that increase the worm’s lifespan by triggering UPRmt.
Against the backdrop of these previous studies, this team, in their new study published in Biogerontology, screened about 3,000 drugs in worms that are engineered to glow if drug treatment activates hsp-6, a gene that is highly expressed when UPRmt occurs. It is interesting to note that of these 3000 drugs, 1300 were off-patent drugs approved by the USFDA, EMA, and other agencies, and the remaining 1700 were unapproved bioactive ones.
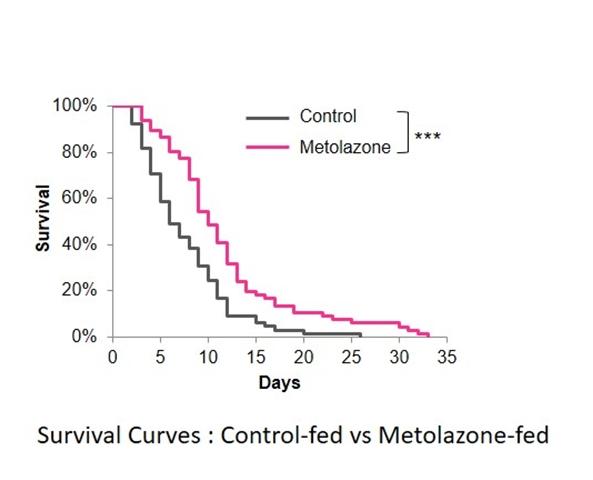
Through this method, Dr. Kage-Nakadai’s team identified metolazone, a drug used to treat heart failure and high blood pressure. They then tested the drug on C. elegans and found that it increased wild-type worm lifespan. Additionally, they found that metolazone did not extend lifespans in worms in whom the genes atfs-1, ubl-5, and nkcc-1 were mutated (non-working). The former two genes are known to be essential for UPRmt function, suggesting that metolazone is acting on the UPRmt pathway. The third gene, nkcc-1, “encodes” a protein that is part of a protein family targeted by metolazone in its usual function as an anti-hypertension drug. The fact that metolazone did not increase the lifespans of nkcc-1 mutated C. elegans suggests that the drug may need to block the nkcc-1 protein to activate the UPRmt pathway. Furthermore, metolazone “induced” hsp-6 (Hspa9 in humans) expression in HeLa cells (a human cell line commonly used in biological research), suggesting that the drug’s UPRmt-related effects possibly span multiple species.
When asked about the broader significance of her work, Dr. Kage-Nakadai comments, “What is particularly exciting is that we tested already available approved drugs here, and we have revealed the potential of repurposing existing drugs for aging control. Worms always give us many hints.”
As the researchers state, this work is just the start, but it opens up a new road to a future of anti-aging drugs. Perhaps a future where humans live longer than the expected 120 years is one step closer to becoming a reality.
###
Quick Summary Video is available at OCU YouTube:
https:/
About Osaka City University, Japan
Established in 1880, Osaka City University is Japan’s first municipal university, currently comprising eight faculties and ten graduate schools, as well as diverse research institutes. The university offers its students bachelor’s, master’s, doctoral, and vocational programs. Its undergraduate student body holds around 6500 people, its graduate student body is around 1600, and the number of international students is around 300. University staff (including faculty) number at around 2,200. Faculty members of this prestigious university are Nobel laureates in Physics and in Medicine. Its research aims encompass both basic and applied research, with an emphasis on giving back to the local community.
Website: https:/
Media Contact
Rina MATSUKI
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




