Credit: KAIST
A research team at KAIST reported clinically accurate multiplexed electrical biosensor for detecting Alzheimer’s disease by measuring its core biomarkers using densely aligned carbon nanotubes.
Alzheimer’s disease is the most prevalent neurodegenerative disorder, affecting one in ten aged over 65 years. Early diagnosis can reduce the risk of suffering the disease by one-third, according to recent reports. However, its early diagnosis remains challenging due to the low accuracy but high cost of diagnosis.
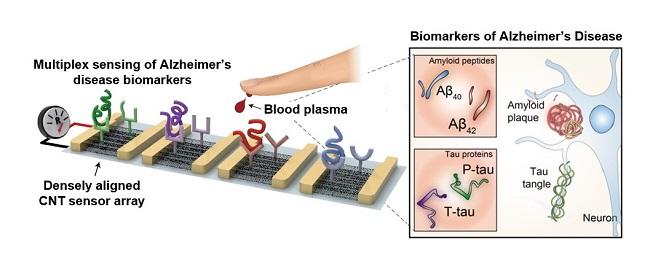
Research team led by Professors Chan Beum Park and Steve Park described an ultrasensitive detection of multiple Alzheimer’s disease core biomarker in human plasma. The team have designed the sensor array by employing a densely aligned single-walled carbon nanotube thin films as a transducer.
The representative biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease are beta-amyloid42, beta-amyloid40, total tau protein, phosphorylated tau protein and the concentrations of these biomarkers in human plasma are directly correlated with the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease.
The research team developed a highly sensitive resistive biosensor based on densely aligned carbon nanotubes fabricated by Langmuir-Blodgett method with a low manufacturing cost.
Aligned carbon nanotubes with high density minimizes the tube-to-tube junction resistance compared with randomly distributed carbon nanotubes, which leads to the improvement of sensor sensitivity. To be more specific, this resistive sensor with densely aligned carbon nanotubes exhibits a sensitivity over 100 times higher than that of conventional carbon nanotube-based biosensors.
By measuring the concentrations of four Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers simultaneously Alzheimer patients can be discriminated from health controls with an average sensitivity of 90.0%, a selectivity of 90.0% and an average accuracy of 88.6%.
This work, titled “Clinically accurate diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease via multiplexed sensing of core biomarkers in human plasma”, were published in Nature Communications on January 8th 2020. The authors include PhD candidate Kayoung Kim and MS candidate Min-Ji Kim.
Professor Steve Park said, “This study was conducted on patients who are already confirmed with Alzheimer’s Disease. For further use in practical setting, it is necessary to test the patients with mild cognitive impairment.” He also emphasized that, “It is essential to establish a nationwide infrastructure, such as mild cognitive impairment cohort study and a dementia cohort study. This would enable the establishment of world-wide research network, and will help various private and public institutions.”
###
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT, Human Resource Bank of Chungnam National University Hospital and Chungbuk National University Hospital.
Media Contact
Younghye Cho
[email protected]
82-423-502-294
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




