Levels and distribution of syntaphilin within tumors may differentiate the subset of patients with prostate cancer who require more aggressive management and treatment, according to a new study in The American Journal of Pathology
Credit: The American Journal of Pathology
Philadelphia, PA, May 9, 2019 – For about 90 percent of men with prostate cancer, the cancer remains localized to the primary site, resulting in a five-year survival rate of almost 100 percent. Unfortunately, the remaining 10 percent of patients develop locally invasive and metastatic disease, which increases the severity of the disease and likelihood of death and limits treatment options. A report in The American Journal of Pathology indicates that a significantly lower presence of syntaphilin (SNPH)–a mitochondrial protein–within the tumor’s central core versus at the tumor’s invasive outer edge, may identify patients at increased risk of metastasis. These patients may require more rigorous testing, surveillance, and treatment.
“Predicting aggressive behavior in prostate cancer is an entirely unmet and urgent need. There are currently no tissue-based biomarkers to help clinicians reliably identify the subset of prostate cancer patients who will progress to life-threatening, disseminated disease and who would, therefore, benefit from systemic therapies before or following prostatectomy. If our findings are supported by larger studies, SNPH measurement in tumors could be developed into a predictive biomarker,” explained Marie E. Robert, MD, of the Department of Pathology, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA.
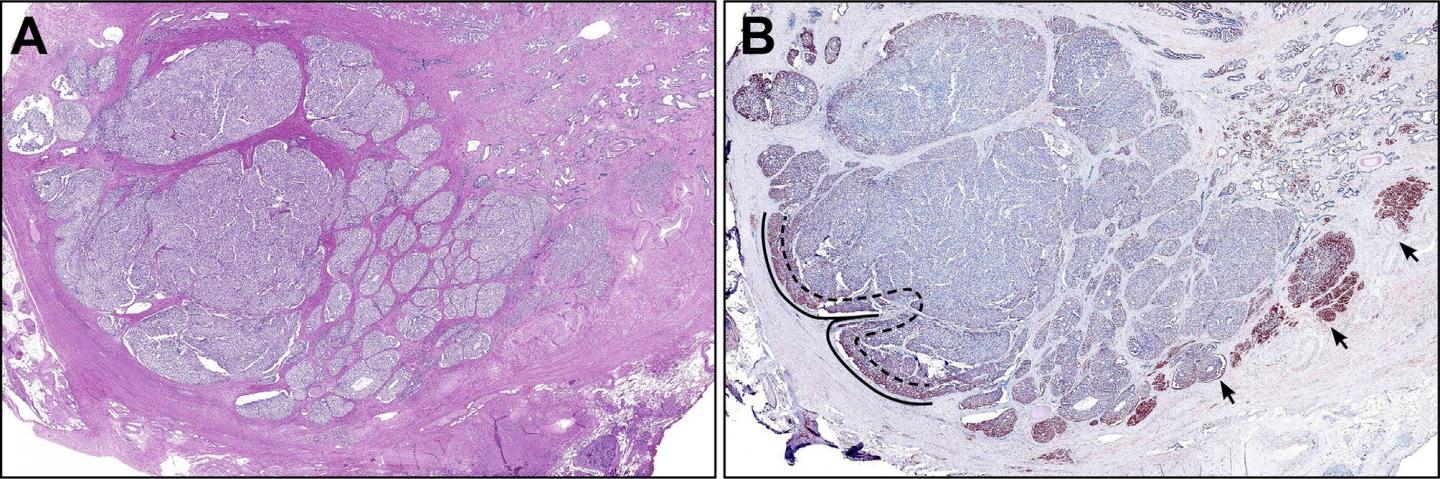
In this study, investigators found that SNPH, a key determinant of the balance between tumor cell proliferation and tumor cell invasion, is abundantly expressed in prostate cancer, where it exhibits high expression at the invasive tumor edge compared to the central tumor bulk, correlating with greater cell proliferation at the tumor edge location. They also found that SNPH expression increases with increasing Gleason pattern. Of potential vital clinical relevance, low central tumor expression correlated with an increased risk of metastasis in a group of patients undergoing radical prostatectomy.
The investigators analyzed tissue specimens from 89 men with prostate adenocarcinoma who had undergone removal of the prostate. They found that SNPH manifests a unique, biphasic spatial distribution in prostate tumors, meaning that in 96 percent of the prostate cancer tumors analyzed, SNPH levels were elevated at the outer invasive edge where it correlates with increased tumor cell proliferation, but decreased within the central tumor core. This differential was more pronounced in more advanced tumors.
Importantly, central tumor SNPH measures (H scores) were significantly lower in 16 patients with metastases compared to patients without metastases, whereas SNPH scores at the invasive edges were not different in patients with or without metastases. Most of the metastases also expressed SNPH strongly. The researchers suggest that SNPH acts as a negative regulator of mitochondrial activity and that its down-regulation in the central portions of primary prostate cancer is associated with an increased risk of metastatic disease.
“This is the first study to suggest a clinical role for SNPH assessment in prostate cancer prognosis, potentially confirming recent evidence in experimental models of its importance in the phenotypic switch between proliferative and metastatic tumor states. Our results also reaffirm a critical, emerging role of mitochondrial biology in influencing tumor behavior,” Dr. Robert noted.
###
Media Contact
Eileen Leahy
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




