Credit: TMIMS
Autophagy is an intracellular degradation process of cytosolic materials and damaged organelles. Researchers at Ubiquitin Project of TMIMS have been studying the molecular mechanism of mitophagy, the selective autophagy process to eliminate damaged mitochondria. PINK1 (a serine/threonine kinase) and Parkin (a ubiquitin ligating enzyme: E3) work together to ubiquitylate the outer membrane proteins of damaged mitochondria, then ubiquitin chains are recognized as signals for autophagy degradation. Dysfunction of mitophagy causes a decrease in mitochondrial quality with overproduction of ROS, and is linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s disease.
In Autophagy machinery, cellular components targeted for degradation are engulfed by phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PI3P)-rich membranes. Membranes are elongated and enclosed to form autophagosomes, which then fuse with lysosomes to degrade the cargo inside. Many proteins function in autophagy machinery and they were initially identified by genetic screens in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and Caenorhabditis elegans. Essential autophagy proteins are evolutionarily conserved from yeast to humans. However, in mammals, there should be unidentified autophagic proteins, and accessory components, whose single gene deletions only manifest as mild defects in autophagy activity, might be missed by these types of genetic screens.
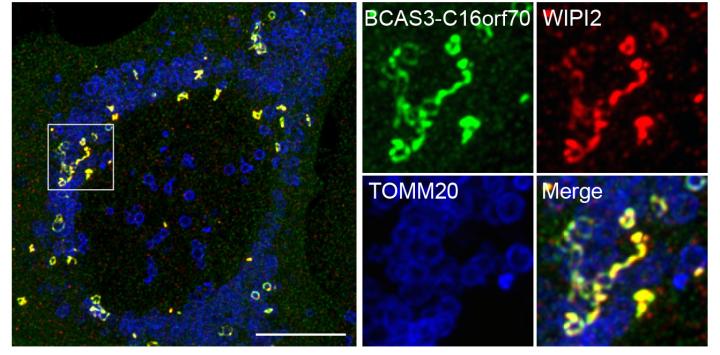
In this study, by immunoprecipitating WIPI1, the well-known autophagy protein, upon Parkin-mediated mitophagy-inducing conditions, researchers identified human BCAS3 (Breast Carcinoma Amplified Sequence 3) and C16orf70 (chromosome 16 open reading frame 70) as novel autophagic proteins.
While BCAS3 and C16orf70 are dispersed throughout the cytosol under normal condition, they accumulated around the damaged mitochondria after mitophagy induction. They also formed puncta in the cytosol in response to amino-acid starvation, which suggests that BCAS3 and C16orf70 are recruited to the autophagosome in both non-selective and selective autophagy. Researchers then found that BCAS3 and C16orf70 interact each other, and this interaction is required for their accumulation on the autophagosome formation site.
Autophagy efficiencies in response to mitochondrial damage and amino-acid starvation were not affected by BCAS3 and/or C16orf70 gene deletions at least in cultured cells. On the other hand, overexpression of the BCAS3-C16orf70 complex impairs the assembly of several autophagy core proteins. These findings demonstrate important accessory functions of BCAS3 and C16orf70 in autophagy machinery.
Furthermore, in silico structural modeling of BCAS3 followed by mutational analyses in immunocytochemistry and in vitro phosphoinositide-binding assays indicate that BCAS3 directly binds phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate on the autophagosome membranes.
###
This work was conducted by researchers in TMIMS, The University of Tokushima, and National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Japan.
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant JP17J03737, JP18H05500, JP18K06237, JP18KK0229, JP19H04966, JP20K06628, JP18H02443, JP19H05712, JP19H00997, 16K21680, 18K11543, the Chieko Iwanaga Fund for Parkinson’s Disease Research, the Takeda Science Foundation and Joint Usage and Joint Research Programs, the Institute of Advanced Medical Sciences, Tokushima University and Platform Project for Supporting Drug Discovery and Life Science Research (Basis for Supporting Innovative Drug Discovery and Life Science Research (BINDS)) from AMED under grant numbers JP19am0101114.
Media Contact
Waka Kojima
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




