Credit: ©Science China Press
New particle formation (NPF) is a key process for haze formation, leading to the deterioration of air quality. Chemical and photochemical processes have been intensively studied over the past decades to understand their roles in NPF, but the physical process has drawn much less attention.
Observational Evidence
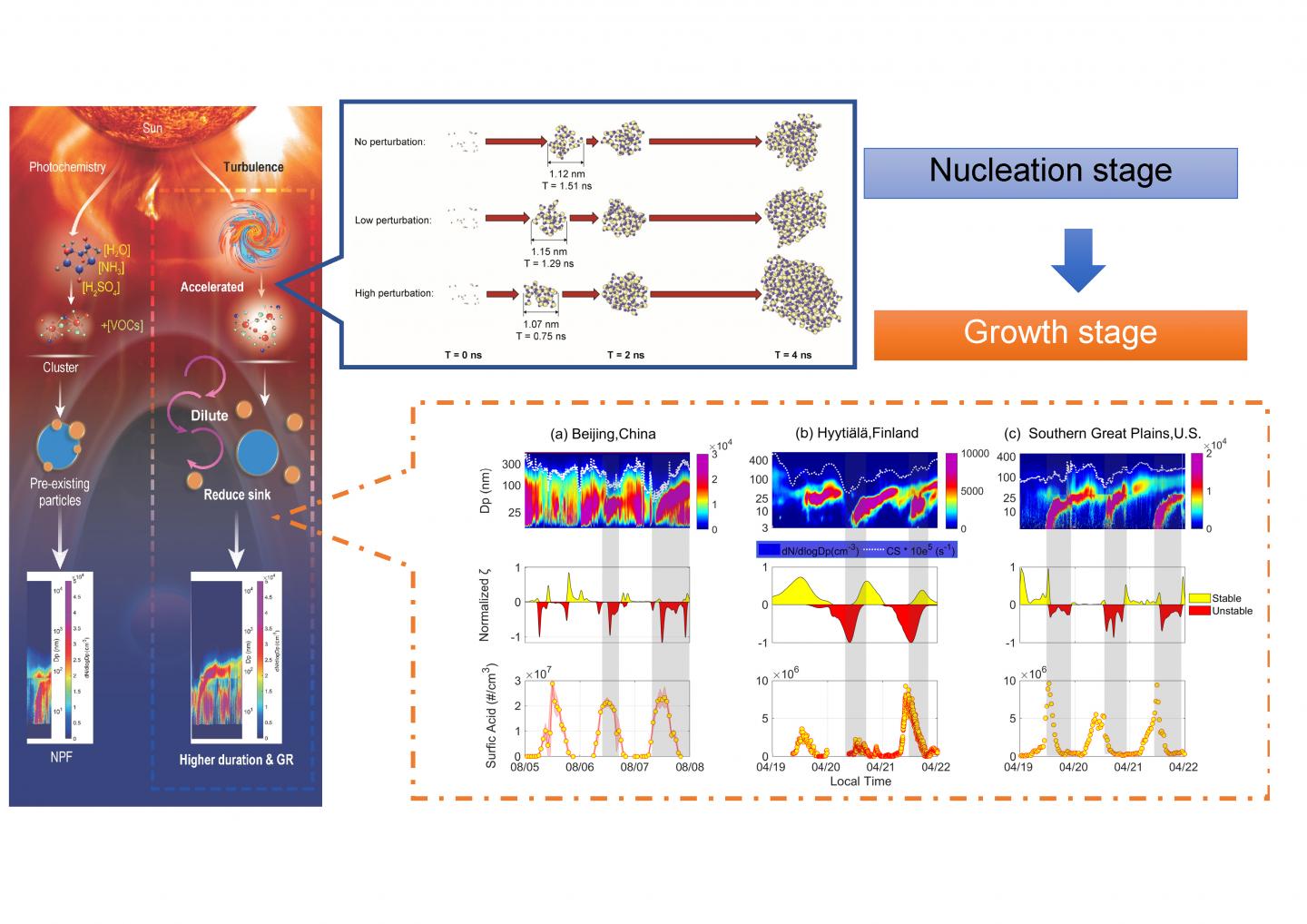
A ubiquitous relationship is found between the intensity of atmospheric stability in the surface layer and NPF features, based on a large number of observations made at three sites in three countries (China, Finland, and the USA). Numerous factors impacting NPF are identified and quantified in our observational analyses. Besides facilitating NPF, increasing the turbulence intensity depresses the condensation sink of NPF, preventing small particles from being scavenged on the surface of preexisting particles. The growth rate is faster under strengthening turbulence conditions (> 3.2 nm h-1) than under weakening turbulence conditions (
Proposed Mechanism
In general, enhanced turbulence generates a higher local supersaturation that facilitates the clustering of condensable vapor to form new particles, favoring the nucleation process. Enhanced turbulence also dilutes the pre-existing particle concentration, causing the condensation sink to decrease. This favors the growth of newly formed particles, which also prolongs the duration of NPF events. These findings suggest a physical mechanism that may act on top of the traditional mechanisms of NPF that are solely based on chemical and photochemical processes. This may help elucidate the NPF process from a physical perspective, leading to improvements in predicting the occurrence and duration of haze events.
Model Simulations
The hypothesis of the new physical mechanism is tested using a molecular dynamics model. Model results suggest that molecule clusters are compressed and overcome the kinetic energy barrier to form a particle. Due to turbulent diffusion, strong coherent structures of dilution effectively segregate preexisting particles, which also exerts an influence on the particle size distribution, thus favoring the growth of nucleated particles.
###
See the article:
Hao Wu, Zhanqing Li, Hanqing Li, Kun Luo, Yuying Wang, Peng Yan, Fei Hu, Fang Zhang, Yele Sun, Dongjie Shang, Chunsheng Liang, Dongmei Zhang, Jing Wei, Tong Wu, Xiaoai Jin, Xinxin Fan, Maureen Cribb, Marc L Fischer, Markku Kulmala, Tuukka Petäjä. The impact of the atmospheric turbulence development tendency on new particle formation: a common finding on three continents. National Science Review, https:/
Media Contact
Zhanqing Li
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.