Credit: UH
An astronomer from the University of Hawaii Institute for Astronomy and an international team published a new study that reveals more of the vast cosmic structure surrounding our Milky Way galaxy.
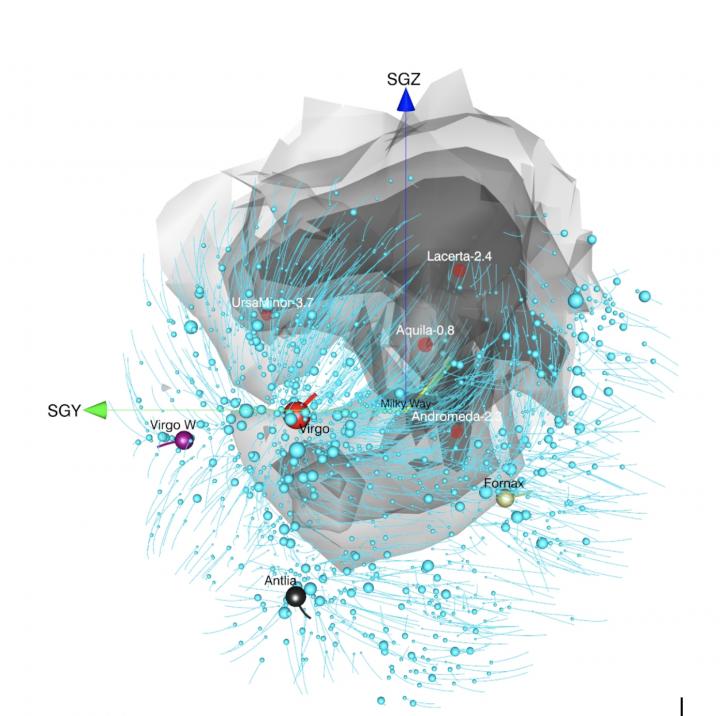
The universe is a tapestry of galaxy congregations and vast voids. In a new study being reported in The Astrophysical Journal, Brent Tully’s team applies the same tools from an earlier study to map the size and shape of an extensive empty region they called the Local Void that borders the Milky Way galaxy. Using the observations of galaxy motions, they infer the distribution of mass responsible for that motion, and construct three-dimensional maps of our local Universe.
Galaxies not only move with the overall expansion of the universe, they also respond to the gravitational tug of their neighbors and regions with a lot of mass. As a consequence, relative to the overall expansion they are moving towards the densest areas and away from regions with little mass – the voids.
Although we live in a cosmic metropolis, back in 1987 Tully and Richard Fisher noted that our Milky Way galaxy is also at the edge of an extensive empty region that they called the Local Void. The existence of the Local Void has been widely accepted, but it remained poorly studied because it lies behind the center of our galaxy and is therefore heavily obscured from our view.
Now, Tully and his team have measured the motions of 18,000 galaxies in the Cosmicflows-3 compendium of galaxy distances, constructing a cosmographic map that highlights the boundary between the collection of matter and the absence of matter that defines the edge of the Local Void. They used the same technique in 2014 to identify the full extent of our home supercluster of over one hundred thousand galaxies, giving it the name Laniakea, meaning “immense heaven” in Hawaiian.
For 30 years, astronomers have been trying to identify why the motions of the Milky Way, our nearest large galaxy neighbor Andromeda, and their smaller neighbors deviate from the overall expansion of the Universe by over 600 km/s (1.3 million mph). The new study shows that roughly half of this motion is generated “locally” from the combination of a pull from the massive nearby Virgo Cluster and our participation in the expansion of the Local Void as it becomes ever emptier.
###
An 11-minute video demonstrating the shape and extend of these cosmic structures is available online at https:/
Interactive visualizations that allow the user to rotate, pan, and zoom maps of the mass distribution can be found at
https:/
https:/
The paper was published on July 22, 2019 in The Astrophysical Journal, and is available at https:/
Media Contact
Roy Gal
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




