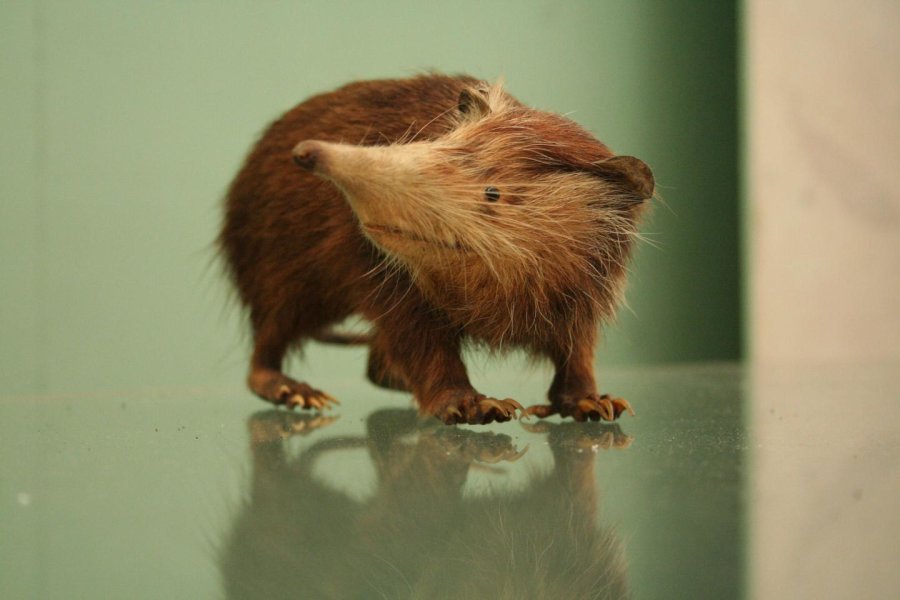
From skeletal remains found among ancient owl pellets, a team of scientists has recovered the first ancient DNA of the extinct West Indian mammal Nesophontes, meaning “island murder.” They traced its evolutionary history back to the dawn of mammals 70 million years ago.
The authors, including Selina Brace, Jessica Thomas, Ian Barnes et al., published their findings in the advanced online edition of Molecular Biology and Evolution.
The insect-eating creature existed in the Caribbean islands until the 16th century when, perhaps, they were outcompeted as the first Spanish ships arrived — introducing rats as stowaways. “Nesophontes was just one of the dozens of mammals that went extinct in the Caribbean during recent times,” said Professor Ian Barnes, Research Leader at London’s Natural History Museum.
Scientists used a 750-year-old specimen to generate many thousands of base pairs of DNA sequence data. This allowed the research team to uncover its evolutionary origins and finally resolve the relationships between its closest relatives, the insectivores, a group including shrews, hedgehogs and moles. Phylogenetic and divergence time scenarios clearly demonstrate that Nesophontes is a deeply distinct sister group to another group of living native Caribbean insectivores, the solenodons. The time of the split between these two correlates with an era when the northern Caribbean was formed of volcanic islands, well before the origins of the islands we see today.
Obtaining DNA from tropical fossils is notoriously difficult, and the team made use of the latest developments in ancient DNA technology to conduct the study.
“Once we’d dealt with the tiny size of the bone samples, the highly degraded state of the DNA, and the lack of any similar genomes to compare to, the analysis was a piece of cake,” said Natural History Museum scientist Dr. Selina Brace.
The findings will be of considerable interest for evolutionary biologists studying mammalian biogeography, and the significant role that humans may have played in a recent extinction.
Story Source:
The above post is reprinted from materials provided by Molecular Biology and Evolution (Oxford University Press).
The post Ancient DNA traces extinct Caribbean ‘Island Murderer’ back to the dawn of mammals appeared first on Scienmag.