The discovery comes just as new data are revealing that some of the hardest hit victims of COVID-19 suffer from obesity and other chronic conditions
Credit: By Yekaterina Kadyshevskaya, USC
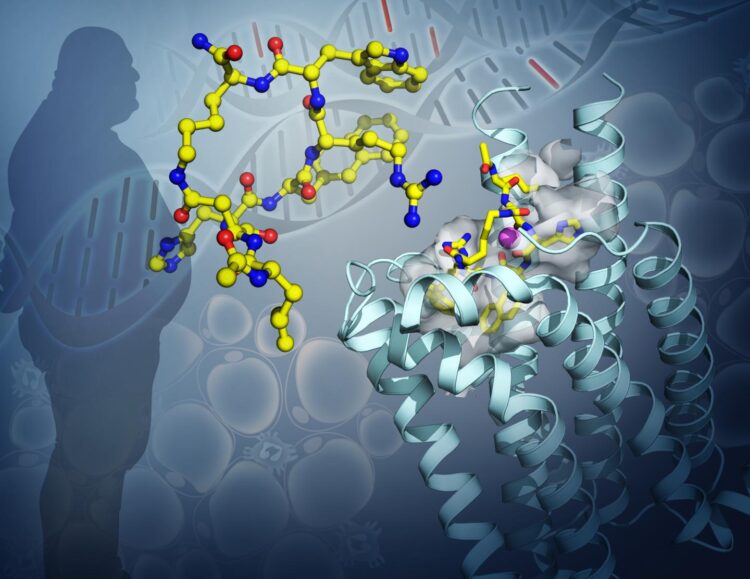
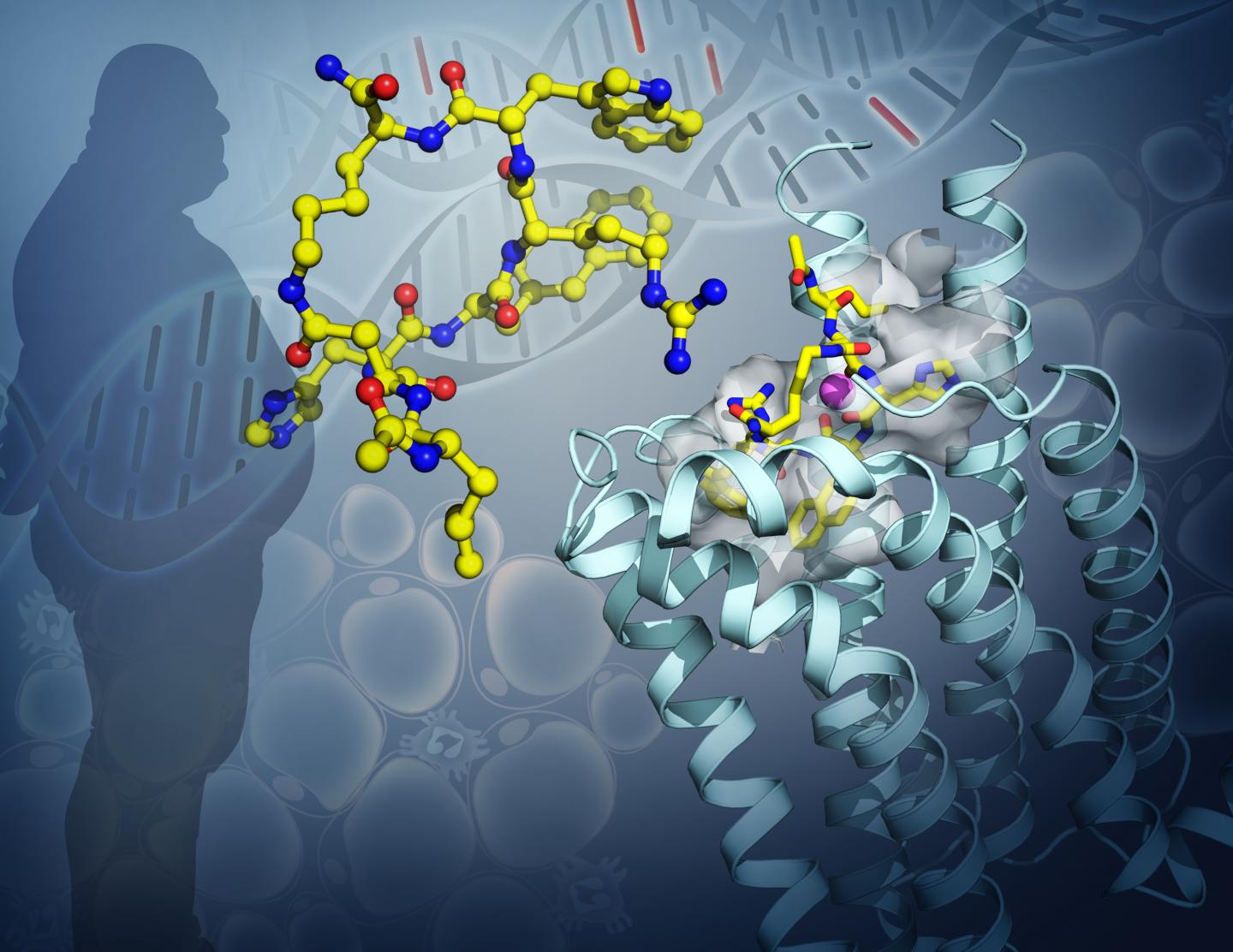
A USC-led international team of scientists has found the precise shape of a key player in human metabolism, which could lead the way to better treatments for obesity and other metabolic disease.
For the study, the scientists focused on a protein in the brain, the melanocortin 4 receptor (or MC4R). This receptor helps with regulating the body’s energy balance by controlling how much energy is stored as fat. Mutations in the gene that encodes the MC4R protein are linked to severe childhood obesity and other forms.
Obesity has tripled worldwide since 1975, according to the World Health Organization. More than 40 million children aged 5 and younger are obese, while more than 650 million adults worldwide are.
“A lot of people think obesity is a lifestyle choice,” said Raymond Stevens, a USC Provost Professor and director of the Bridge Institute at the USC Michelson Center for Convergent Bioscience. “That’s just not true in all cases. Some people have mutations of this gene. And if they have mutations of this gene, many cannot control their eating. It’s this receptor causing this issue in the brain.”
The results are set to appear in the journal Science on April 23.
Severe obesity is often linked to other health issues. Recent data on coronavirus have shown that adults 65 and older who are severely obese are among the hardest hit by the illness, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Working with the iHuman Institute at ShanghaiTech University and the Life Sciences Institute at the University of Michigan, Stevens was interested in the MC4R as part of a larger effort to elucidate the structures of a class of proteins called G protein-coupled receptors that control many human functions. MC4R is among them.
As Stevens and his team began to tackle the MC4R structure, they looked for the world’s expert in this area and turned to Roger Cone at the University of Michigan Life Sciences Institute for help on the function of this important receptor.
Scientists at the University of Michigan discovered the MC4R and have been studying its biology and pharmacology for more than 25 years. Since then, four drugs have been developed to target melanocortin receptors in humans. The drug setmelanotide targets the MC4R to treat rare forms of syndromic obesity, which affects about 1 out of 1,500 people. However, the drug is not potent enough to treat dietary obesity — a more common form of the disease.
By determining the structure of MC4R, the scientists were able to see how it binds to and interacts with other drug molecules. Knowing how the protein is configured will enable scientists to develop and test new therapies that can more precisely treat obesity.
Stevens and Cone, senior author’s of the study, highlight the findings as an example of the importance and power of international collaboration.
“We were able to contribute our knowledge of the MC4R to help further the structural biology studies,” says Cone. “And key structural findings from the USC and iHuman Institute researchers are helping us answer more questions about how this receptor functions in human metabolism.”
###
This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health (Cone Lab at Univ Michigan), the Shanghai Municipal Government (Zhao Lab, ShanghaiTech) and the GPCR Consortium (Stevens Lab at USC). Study authors were: Jing Yu, Yiran Wu, Lijie Wu, Sophia Stevens and Suwen Zhao of ShanghaiTech University; Luis E. Gimenez, Ciria C. Hernandez, Alys Peisley, Savannah Y. Williams and Roger D. Cone of the Univesity of Michigan; Ariel H. Wein, Gye Won Han, Kyle McClary, Sanraj R. Mittal, Kylie Burdsall and Benjamin Stauch of the University of Southern California; Raymond Stevens of ShanghaiTech University and the University of Southern California; and Valerie Chen and Glenn L. Millhauser of the University of California Santa Cruz.
Disclosure: Raymond Stevens is the founder of a GPCR structure-based drug discovery company called ShouTi, and Roger Cone is a founder of a melanocortin receptor drug discovery company called Courage Therapeutics.
Media Contact
Emily F Gersema
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.