Credit: Dexter Dean, Ph.D.
WASHINGTON, April 7, 2021 — On the surface, Parkinson’s disease — a neurodegenerative disorder — and melanoma — a type of skin cancer — do not appear to have much in common. However, for nearly 50 years, doctors have recognized that Parkinson’s disease patients are more likely to develop melanoma than the general population. Now, scientists report a molecular link between the two diseases in the form of protein aggregates known as amyloids.
The researchers will present their results today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Spring 2021 is being held online April 5-30. Live sessions will be hosted April 5-16, and on-demand and networking content will continue through April 30. The meeting features nearly 9,000 presentations on a wide range of science topics.
“Several studies have shown that melanoma occurs two to six times more frequently in the Parkinson’s population than the healthy population,” says Dexter Dean, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), who is presenting the work at the meeting. “What’s more, the protein involved in Parkinson’s disease, α-synuclein, is elevated in melanoma cells.”
In Parkinson’s disease, α-synuclein forms amyloid deposits that are thought to kill dopamine-producing neurons in the brain, causing symptoms such as tremor, slow movements and dementia. While intense research has focused on the effects of α-synuclein in the brain, much less is known about its presence or activities in other tissues. However, scientists have evidence that the amyloid-forming protein is expressed more in melanoma cells than in healthy skin. Furthermore, higher levels of α-synuclein in melanocytes (the skin cells that give rise to melanoma) correlate with reduced pigment, or melanin, production. Melanin protects skin from damage by the sun’s ultraviolet rays.
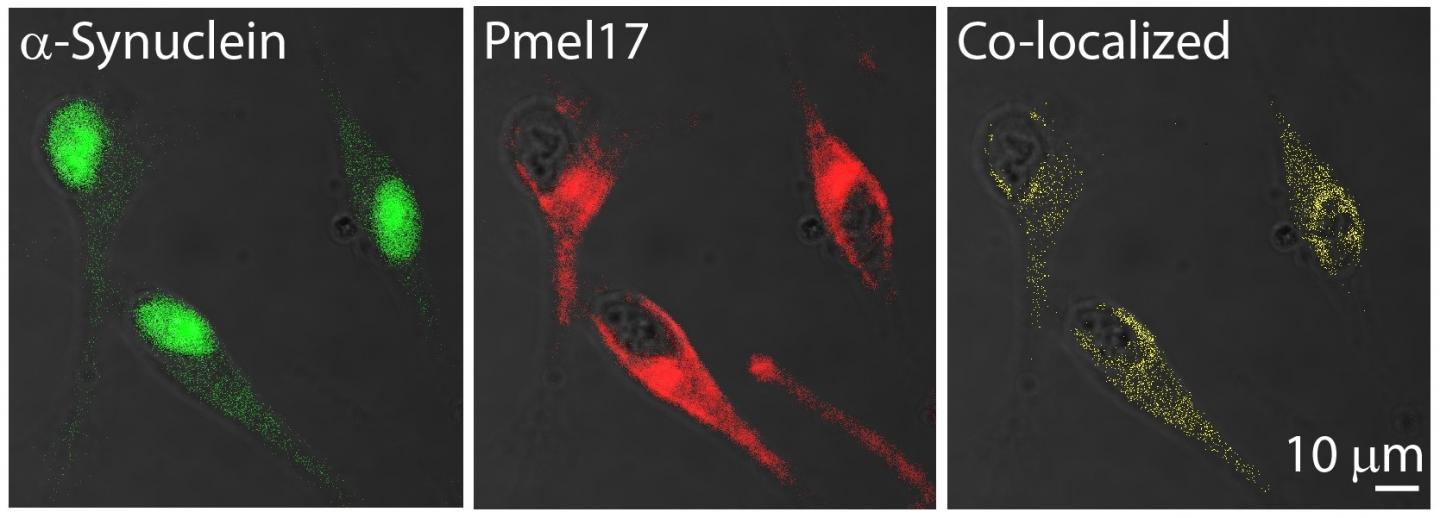
Jennifer Lee, Ph.D., Dean’s postdoctoral advisor at NHLBI, part of the National Institutes of Health, had previously studied another amyloid-forming protein called premelanosomal protein (Pmel). “Most people know that amyloids are involved in diseases, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, but it’s less well-known that some amyloids, like Pmel, actually serve a useful function,” Lee says. In healthy melanocytes, Pmel forms amyloid fibrils that act as scaffolds to store melanin in melanosomes (the organelle where the pigment is produced, stored and transported). “Because both α-synuclein and Pmel are expressed in melanoma cells, we wondered if these two amyloid proteins could interact, and whether this interaction could be relevant to the correlation between Parkinson’s disease and melanoma,” Lee says.
To investigate whether α-synuclein and Pmel could interact, the researchers used microscopy and western blotting to show that the two proteins both resided in the melanosomes of human melanoma cells. When Dean added preformed α-synuclein amyloid to a test tube containing the amyloid-forming region of Pmel (known as the repeat, or RPT, domain), the α-synuclein fibrils stimulated Pmel to aggregate and form a twisted fibril structure that the protein does not normally adopt on its own.
Because α-synuclein in melanoma cells may also be found in its soluble, or non-amyloid, form, the researchers performed other in vitro experiments in which they added soluble α-synuclein to the Pmel RPT domain. In this case, α-synuclein inhibited Pmel’s ability to self-aggregate and form amyloid in a concentration-dependent manner. They traced this activity to the first 60 amino acids of α-synuclein.
“We now have preliminary data that suggest an amyloid from one protein can ‘seed’ or template amyloid from another, and in the soluble form, α-synuclein prevents Pmel aggregation.” Lee says. “Therefore, we think that both forms of α-synuclein could diminish melanin biosynthesis — the amyloid form by causing Pmel to form an unusual twisted structure, and the soluble form by stopping Pmel from aggregating like it should.” Loss of skin pigmentation could contribute to the increased melanoma risk in Parkinson’s disease patients, the researchers say.
“I think we’re just at the tip of the iceberg of appreciating what α-synuclein might be doing in melanoma,” Dean says. “In future experiments, I’m really interested in understanding more about what α-synuclein is doing to promote melanoma proliferation, in addition to this interaction with Pmel.”
###
A press conference on this topic will be held Wednesday, April 7, at 11 a.m. Eastern time online at http://www.
The researchers acknowledge funding from the National Institutes of Health Intramural Research Program.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and its people. The Society is a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a specialist in scientific information solutions (including SciFinder® and STN®), its CAS division powers global research, discovery and innovation. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Note to journalists: Please report that this research was presented at a meeting of the American Chemical Society.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
Title
Defining an amyloid link between Parkinson’s disease and melanoma
Abstract
While Parkinson’s disease (PD), a neurodegenerative disorder leading to cell death, and melanoma, a cancer of melanocytes leading to uncontrolled cell growth, fundamentally differ, a unique connection between the two diseases has been observed for nearly 50 years. Epidemiological studies have shown that melanoma occurs 2-6 times more frequently in PD patients as compared to the general population, and that individuals with melanoma are more susceptible to PD. α-Synuclein (α-syn), the hallmark pathological protein observed in Lewy bodies from brains of PD patients, is elevated in melanoma, suggesting that α-syn could be a molecular link between the two diseases. A consistent observation is that α-syn expression is inversely correlated to the amount of pigment or melanin found in melanoma cells. Currently, little is known about the role that α-syn plays in melanoma progression. We propose a novel hypothesis that there is an amyloid link between α-syn and Pmel (pre-melanosomal protein), a functional amyloid that promotes melanin biosynthesis in melanocytes. Using confocal immunofluorescence microscopy and western blotting of SK-MEL 28 human melanoma cells, we recently reported that endogenous α-syn and Pmel compartmentalize within the melanosome, the organelle in which melanin is synthesized, and that α-syn fibrils stimulate the aggregation of Pmel repeat domain (RPT) in vitro. Here, we further define this interaction by showing that soluble (disordered) α-syn acts as an inhibitor of RPT aggregation in a concentration-dependent manner, with an estimated half maximum inhibition (IC50) of 200 nM. Using two different truncated α-syn constructs spanning N- and C-terminal residues, 1-60 and 66-140, we show that the amphipathic N-terminus of α-syn alone can inhibit RPT aggregation, while the latter half has no impact. Taken together, these results support our hypothesis that α-syn, a pathogenic amyloid, infiltrates and disrupts conventional Pmel amyloid formation, thus leading to the modulation of melanin production, the biological function of Pmel.
Media Contact
ACS Newsroom
[email protected]