Beyond plaques: Heidelberg scientists unravel the natural functions of the APP protein family
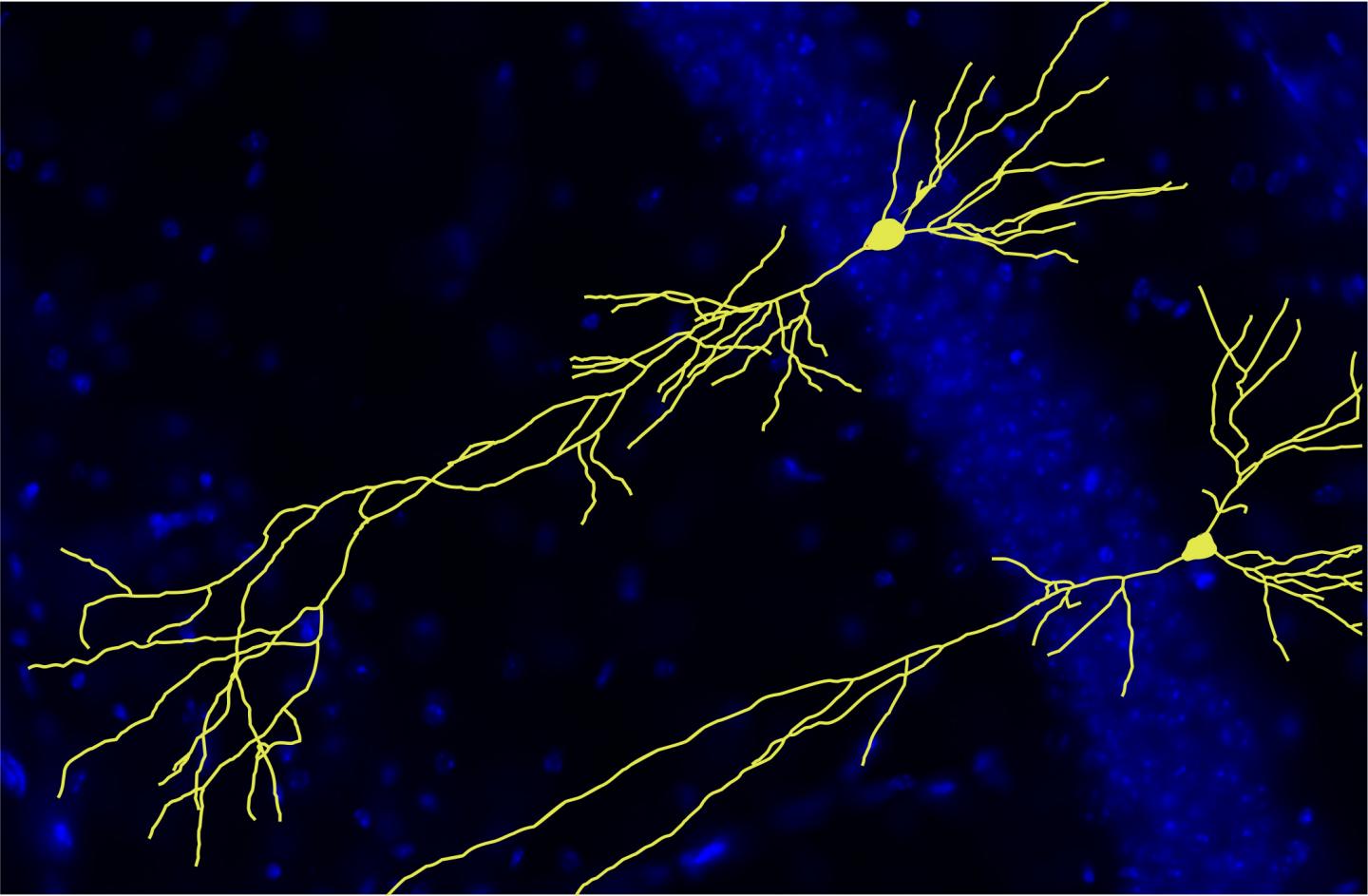
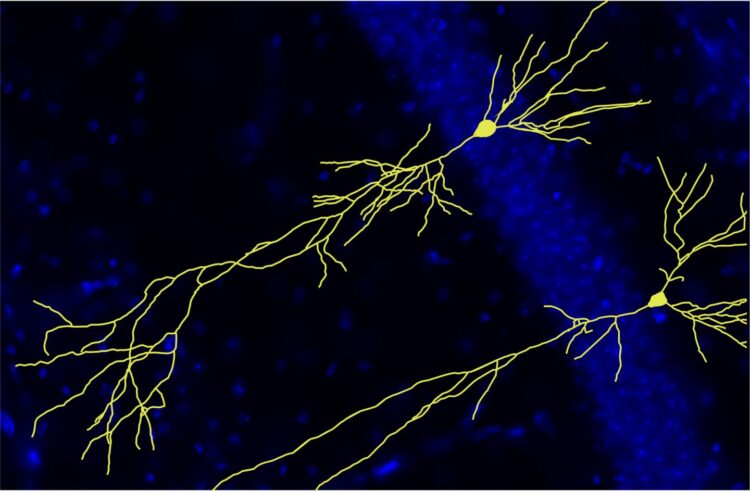
Credit: Susanne Klein, Prof. Müller’s research group, Heidelberg University
While the APP protein is well-known for its key role in Alzheimer’s disease, its contribution to healthy brain function, by contrast, has remained largely unknown until now. Recently, an international research team, led by molecular biologist Prof. Dr Ulrike Müller from Heidelberg University, gained new insights on the physiological functions of the APP protein family by using a mouse model lacking APP. The absence of APP during brain development was shown to result in the malformation of important brain regions implicated in learning and memory. Consequently, these mice were severely impaired in their learning abilities and exhibited autistic-like behaviour.
Alzheimer’s disease is triggered by insoluble protein deposits in the brain, which aggregate around nerve cells to form plaques. These plaques consist mainly of small β-amyloid peptides (Aβ), which are a cleavage product of the amyloid precursor protein (APP). Aβ peptides inflict damage on nerve cells and ultimately lead them to their death. While the detrimental effect of Aβ peptides on neurons has been recognised for many years, little is known about the natural physiological functions of APP. According to the researchers, this non-pathological perspective is worthy of investigation considering the fact that APP, as well as two other closely-related proteins, is produced by most nerve cells in the brain – particularly in critical regions for learning and memory formation.
To investigate the role of the APP protein family in the development and functionality of the nervous system, Prof. Müller’s research group used mice as a model organism, which had been genetically engineered to block the production of all APP family proteins. Close examination of their brains revealed that the loss of APP during brain development led to malformations in the layered structure of the hippocampus – an essential brain region for memory formation. “We observed that the absence of APP led to impaired neuronal wiring and a decrease in the number of synaptic connections. It also greatly reduced communication between nerve cells and severely affected the animal’s performance in behaviour tests that assess learning,” says Ulrike Müller, who heads the department of Functional Genomics at the Institute of Pharmacy and Molecular Biotechnology of Heidelberg University.
According to Prof. Müller, the team was surprised to discover that these disruptions in brain development also gave rise to behavioural changes that resembled those occurring in autism spectrum disorder. The mice displayed the characteristic recurring movement patterns and lack of interest in social interactions with other mice. “Our findings suggest that the APP family plays a crucial role in the normal development of the nervous system, learning, memory formation and social communication,” explains the scientist. “In the future, these understandings may aid the development of novel therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease.”
###
Funded by the German Research Foundation, this study was an international collaborative effort involving the research team based in Heidelberg as well as scientists from Technische Universität Braunschweig, the University of Mainz, and the University of Zurich (Switzerland). The results were published in “The EMBO Journal“.
Media Contact
Ulrike Müller
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.