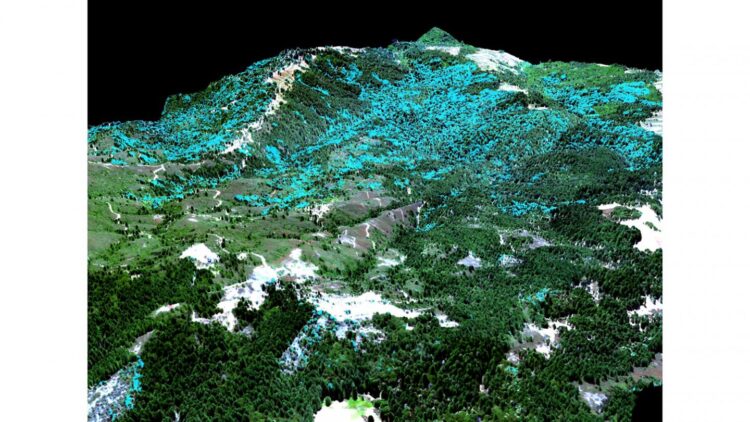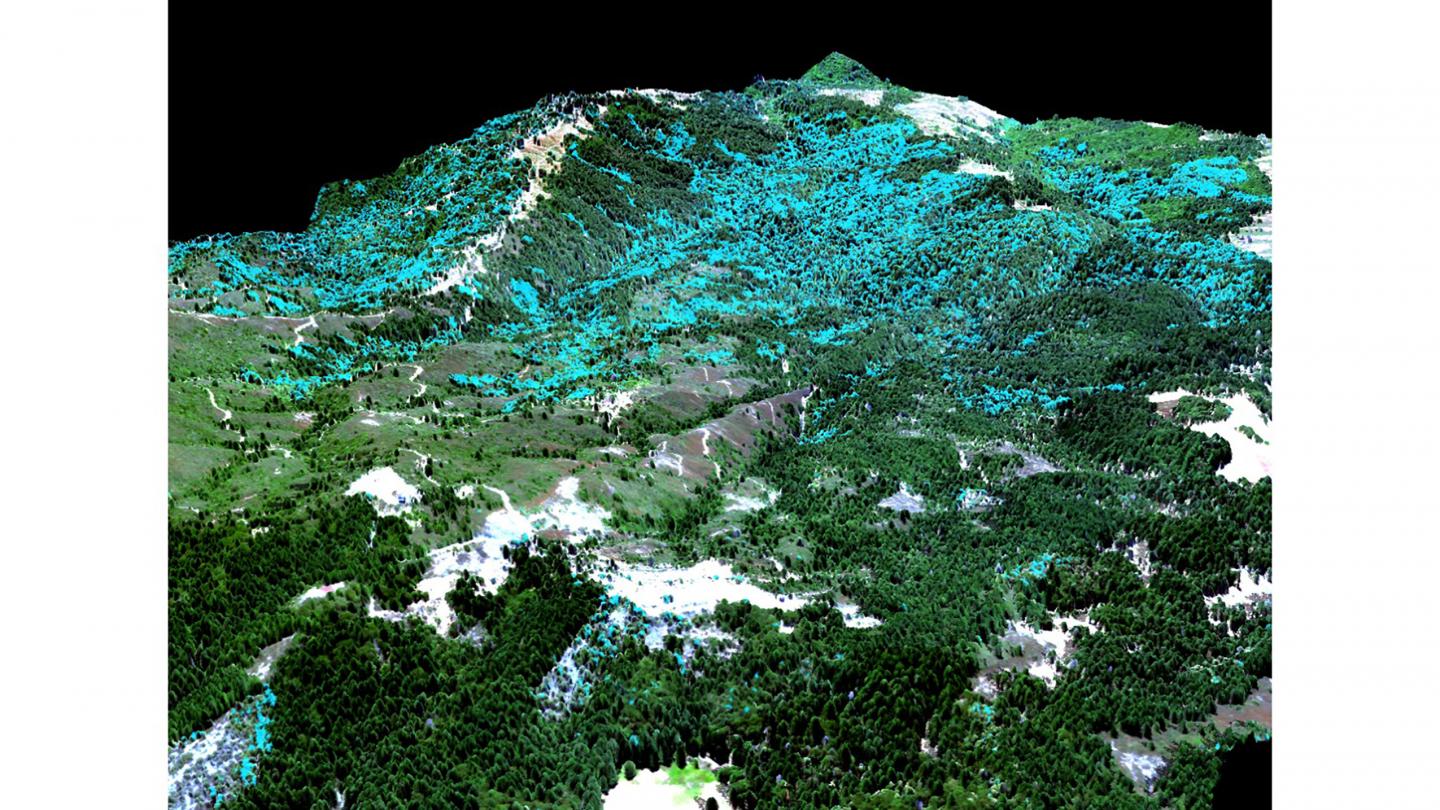
Credit: Global Airborne Observatory, ASU Center for Global Discovery and Conservation Science.
Throughout California, the effects of climate change are evident from increasing frequencies of intense wildfires and mudslides to widespread and prolonged droughts. These changes also threaten one of California’s most iconic endemic species: coastal redwoods. Coastal redwoods are not only some of the tallest and oldest trees on Earth, but redwood forests are also capable of storing three times more carbon than any other forests on Earth. Identifying suitable habitats for these vulnerable species has important implications for carbon sequestration and redwood forest biodiversity. This is especially urgent given that some regions within the current redwood distribution in California (south of SF Bay) could become unsuitable for redwoods as soon as 2030.
To better understand redwood habitat suitability, a team of researchers from the University of Texas, Arizona State University, University of Miami, and Stanford University combined high-resolution redwood distribution maps with data on moisture availability to identify the environmental factors that shape redwood distribution. The study was published today in Ecography.
“Habitat suitability of coast redwood has been studied before, but not using high-resolution data at the landscape scale. The approach we employed here could be applied in other forest types to gain new insight into the role of moisture availability in landscape-scale patterns of habitat suitability for many tree species that may be vulnerable to climate change,” said Emily Francis, lead author of the study.
The research was conducted in three redwood forests in California spanning approximately one-third of redwood latitudinal range. After analyzing spatial patterns in redwood distributions over more than 34,800 hectares (87,000 acres) across the three forests, the scientists found that redwood habitat suitability significantly varied in relation to moisture availability and fog across different landscape elevations. Redwood habitats were consistently more suitable at sites located closer to streams. The study also found that habitat suitability for redwoods ranged from 22-75% within a single landscape, underlining the importance of considering landscape-scale variation while identifying sites that will continue to be suitable for redwoods, even as surrounding areas become inhospitable due to climate change.
“This study highlights the value of mapping the composition of our forests at high spatial resolution. Doing so provides leverage to say something about the individual inhabitants within a forest, not just the forest as a blanket average. This, in turn, both enhances our knowledge and presents possible options for managing sensitive ecosystems undergoing climate change,” said co-author Greg Asner, director of the ASU Center for Global Discovery and Conservation Science.
The authors emphasized that predicting how climate change will impact future redwood distribution will require additional study to understand how both environmental and biological factors, such as tree seed dispersal and plant competition, will influence where redwoods are able to grow and survive.
###
This work was supported by the David and Lucile Packard Foundation, John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation, a Stanford Graduate Fellowship, and Save the Redwoods League.
Media Contact
Heather D’Angelo
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.





