New AI-based algorithm processes tissue oxygenation data faster and more accurately than conventional techniques
Credit: SPIE
Tissue oxygenation is a measure of the oxygen level in biological tissue and is a useful clinical biomarker for tissue viability. Abnormal levels may indicate the presence of conditions such as sepsis, diabetes, viral infection, or pulmonary disease, and effective monitoring is important for surgical guidance as well as medical care.
Several techniques exist for the measurement of tissue oxygenation, but they all have some limitations. For instance, pulse oximetry is robust and low-cost but cannot provide a localized measure of oxygenation. Near-infrared spectroscopy, on the other hand, is prone to noisy measurements due to pressure-sensitive contact probes. Spatial frequency domain imaging (SFDI) has emerged as a promising noncontact technique that maps tissue oxygen concentrations over a wide field of view. While simple to implement, SFDI has its own limitations: it requires a sequence of several images for its predictions to be accurate and is prone to errors when working with single snapshots.
In a new study published in the Journal of Biomedical Optics, researchers from Johns Hopkins University, Mason T. Chen and Nicholas J. Durr, have proposed an end-to-end technique for accurate calculation of tissue oxygenation from single snapshots, called OxyGAN. They developed this approach using a class of machine-learning framework called a conditional generative adversarial network (cGAN), which utilizes two neural networks — a generator and a discriminator — simultaneously on the same input data. The generator learns to produce realistic output images, while the discriminator learns to determine whether a given image pair forms a correct reconstruction for a given input.
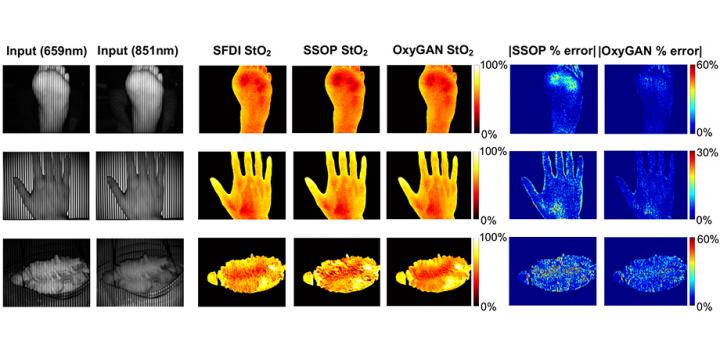
Using conventional SDFI, the researchers obtained oxygenation maps for the human esophagus (ex vivo), hands and feet (in vivo), and a pig colon (in vivo) under illumination with two different wavelengths (659 and 851 nm). They trained OxyGAN with the feet and esophagus samples and saved the hand and colon samples to later test its performance. Further, they compared its performance with a single-snapshot technique based on a physical model and a two-step hybrid technique that consisted of a deep-learning model to predict optical properties and a physical model to calculate tissue oxygenation.
The researchers found that OxyGAN could measure oxygenation accurately, not only for the samples it had seen during training (human feet), but also for the samples it had not seen (human hand and pig colon), demonstrating the robustness of the model. It performed better than both the single-snapshot model and the hybrid model by 24.9% and 24.7%, respectively. Moreover, the scientists optimized OxyGAN to compute ~10 times faster than the hybrid model, enabling real-time mapping at a rate of 25 Hz. Frédéric Leblond, Associate Editor for the Journal of Biomedical Optics, comments, “Not only does this paper represent significant advances that can contribute to the practical clinical implementation of spatial frequency domain imaging, but it will also be part of a relatively small (although rapidly increasing in size) pool of robust published work using AI-type methods to deal with real biomedical optics data.”
While the algorithm of OxyGAN could be optimized further, this approach holds promise as a novel technique to measure tissue oxygenation.
###
Read the original research article by M. T. Chen and N. J. Durr, “Rapid tissue oxygenation mapping from snapshot structured-light images with adversarial deep learning,” J. Biomed. Opt. 25(11), 112907 (2020), doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.25.11.112907.
Media Contact
Daneet Steffens
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




