Credit: Ko Matsui
Tohoku University scientists and their colleagues in Germany have revealed that a first-time exposure to only a brief period of brain hyperactivity resulted in an acute breakdown of the inter-cellular network of glial cells. Pharmacological intervention of the glial plasticity may provide a new preventative strategy for fighting epilepsy.
The findings were detailed in the Journal of Neuroscience.
Epilepsy is a disorder characterized by neuronal hyper-excitation and a progression of seizures with each episode. Anti-epileptic drugs are mostly aimed at suppressing hyperactivity, but approximately 30% of patients worldwide show drug-resistance.
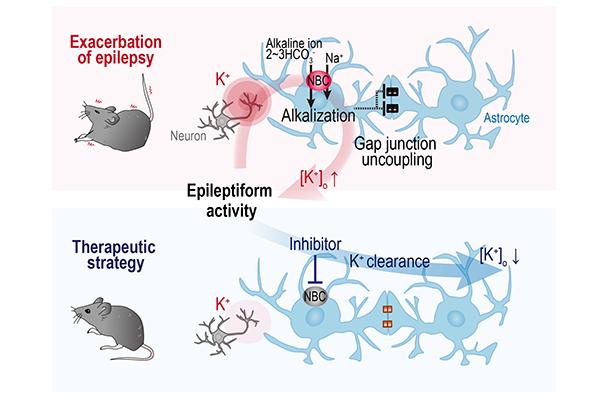
Half of the brain is occupied by non-neuronal glial cells. Astrocytes are star-shaped glial cells that are connected to each other via gap junctions. Neuronal excitation leads to potassium extrusion from neurons. The excess potassium is picked up by astrocytes and diluted in the astrocyte network. Efficacy of the potassium clearance can affect neuronal signal processing.
“Astrocytes have a strong control over neuronal activity,” says professor Ko Matsui of the Super-network Brain Physiology lab at Tohoku University, who led the research. “Plasticity of the neuronal network underlies learning and memory but apparently astrocyte function is also susceptible to plastic change.”
A collaborative research group led by Matsui, doctoral student Mariko Onodera and researchers at Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf, studied the plastic change of astrocytes associated with epileptogenesis in mice.
In response to hyperactivity of the surrounding neurons, Na+/HCO3- co-transporter (NBC) in astrocytes was activated. The resulting intracellular alkalization led to gap junction uncoupling and impairment of prompt potassium clearance. Pharmacological blockade of the NBC suppressed the plastic change of the astrocyte network and prevented intensification of epileptiform activity.
“Astrocytes play a crucial role in taking control of neuronal activity in healthy brains as well, said Matsui. “Our research reveals the presence of glial plasticity and suggests a future therapeutic strategy can be aimed to control the glial function for treating disease.”
###
Media Contact
Ko Matsui
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




