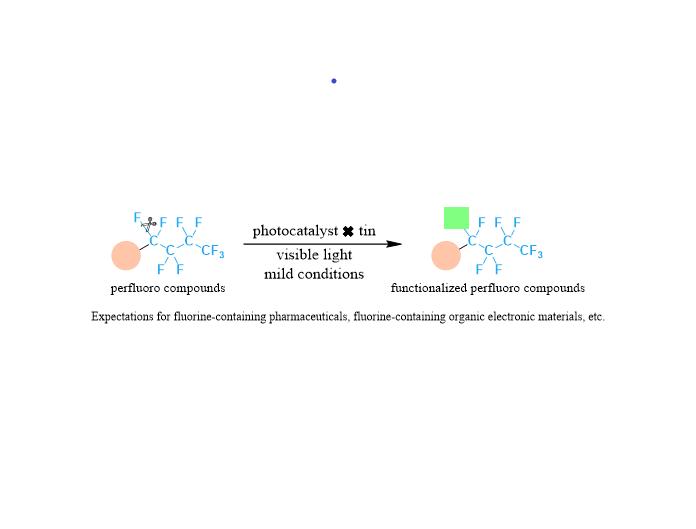
Scientists from Osaka University have succeeded in developing the world’s first organic reaction that selectively converts a specific carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond in perfluorinated compounds to other functional groups
Fluorinated compounds are an important group of compounds that are widely used in pharmaceuticals, agricultural chemicals, functional resins, and organic electronic materials. In particular, perfluorinated compounds with multiple carbon-fluorine bonds are attracting attention because of their high thermal and chemical stability and various excellent properties such as water and oil repellency and chemical resistance.
“C-F bonds are extremely strong; hence, their transformation under mild conditions is difficult, and the selective activation of a specific C-F bond from among multiple C-F bonds in perfluorinated compounds has not been achieved,” explains Prof. Makoto Yasuda, corresponding author of the study.
In this research, site-selective C-F bond transformation to valuable allylic groups has been accomplished by using a photocatalyst and organotin compounds under safe and common visible light irradiation (Figure 2a). The establishment of the methodology to activate strong carbon-fluorine bonds under such mild conditions is the key to achieving the targeted transformation of perfluorinated compounds at specific sites.
“We have attempted to elucidate this reaction mechanism using both experimental and theoretical chemical methods and have found that the cooperative action of the photocatalyst and organotin compound plays a very important role in the progression of the reaction. In particular, it is noteworthy that the organotin compound plays the dual role of capturing unstable radical intermediates and scavenging fluorine as a Lewis acid, which is a very significant finding for future research on carbon-fluorine bond conversion reactions,” explains Prof. Makoto Yasuda. Furthermore, by using this method, they have succeeded in synthesizing fluorine-substituted analogues of a compound that show promise for pharmaceutical applications (Figure 2b).
“Fluorine is an important element in pharmaceuticals, and many small-molecule drugs contain fluorine atoms. It is expected that the field of fluorine-containing drugs will continue to grow. As a result of this research, high value-added perfluorinated compounds, which were impossible to synthesize in the past, can now be synthesized in a simple and short process, which is expected to lead to the expansion of the library of seed compounds for fluorine-containing drug discovery,” says Prof. Makoto Yasuda.
###
The article, “Photoredox-catalyzed C-F bond allylation of perfluoroalkylarenes at the benzylic position” was published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society at DOI: https:/
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan’s leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan’s most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https:/
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.