Cryo-EM study show how structural alterations in G614 variants stabilize the spike
Credit: Bing Chen, PhD, Boston Children’s Hospital
BOSTON – March 16, 2021 – The fast-spreading UK, South Africa, and Brazil coronavirus variants are raising both concerns and questions about whether COVID-19 vaccines will protect against them. New work led by Bing Chen, PhD, at Boston Children’s Hospital analyzed how the structure of the coronavirus spike proteins changes with the D614G mutation — carried by all three variants — and showed why these variants are able to spread more quickly. The team reports its findings in Science (March 16, 2020).
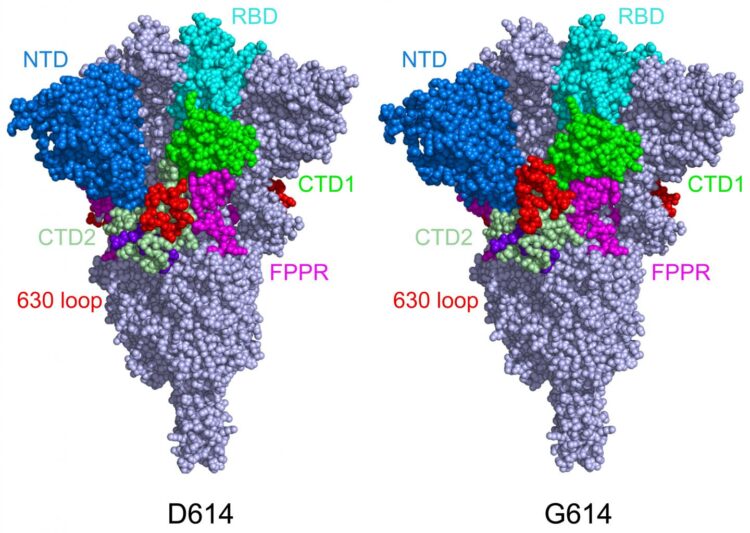
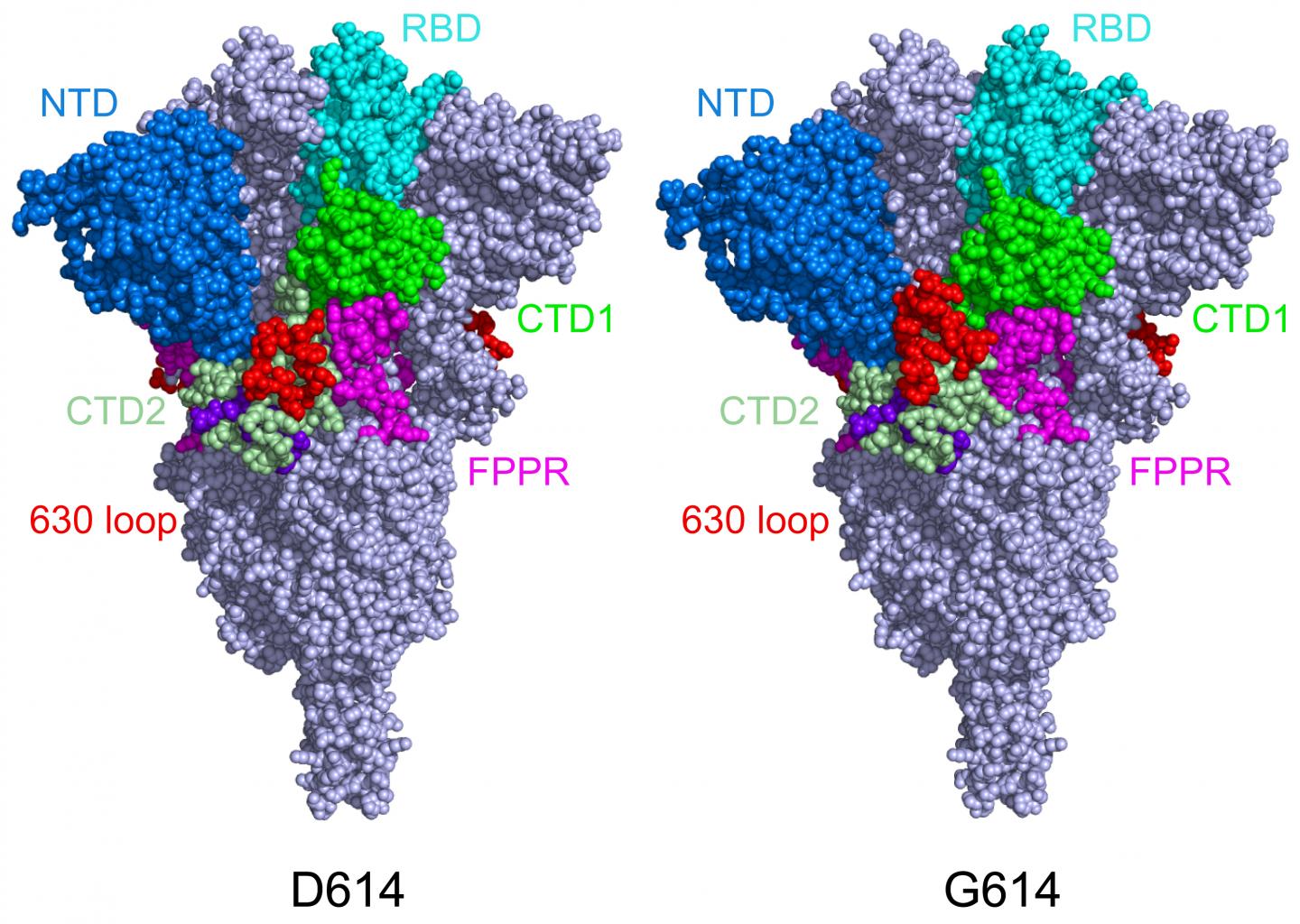
Chen’s team imaged the spikes with cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), which has resolution down to the atomic level. They found that the D614G mutation (substitution of in a single amino acid “letter” in the genetic code for the spike protein) makes the spike more stable as compared with the original SARS-CoV-2 virus. As a result, more functional spikes are available to bind to our cells’ ACE2 receptors, making the virus more infectious.
Preventing spikes’ shape change
In the original coronavirus, the spike proteins would bind to the ACE2 receptor and then dramatically change shape, folding in on themselves. This enabled the virus to fuse its membrane with our own cells’ membranes and get inside. However, as Chen and colleagues reported in July 2020, the spikes would sometimes prematurely change shape and fall apart before the virus could bind to cells. While this slowed the virus down, the shape change also made it harder for our immune system to contain the virus.
“Because the original spike protein would dissociate, it was not good enough to induce a strong neutralizing antibody response,” says Chen.
When Chen and colleagues imaged the mutant spike protein, they found that the D614G mutation stabilizes the spike by blocking the premature shape change. Interestingly, the mutation also makes the spikes bind more weakly to the ACE receptor, but the fact that the spikes are less apt to fall apart prematurely renders the virus overall more infectious.
“Say the original virus has 100 spikes,” Chen explains. “Because of the shape instability, you may have just 50 percent of them functional. In the G614 variants, you may have 90 percent that are functional, so even though they don’t bind as well, the chances are greater that you will have infection.”
Chen proposes that redesigned vaccines incorporate the code for this mutant spike protein. The more stable spike shape should make any vaccine based on the spike (as are the Moderna, Pfizer, and Johnson & Johnson vaccine) more likely to elicit protective neutralizing antibodies, he says.
Future direction: A drug to block coronavirus entry
Chen and his colleagues are further applying structural biology to better understand how SARS-CoV-2 binds to the ACE2 receptor, with an eye toward therapeutics to block the virus from gaining entry to our cells.
In January, the team showed in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology that a structurally-engineered “decoy” ACE2 protein binds the virus 200 times more strongly than the body’s own ACE2. The decoy potently inhibited the virus in cell culture, suggesting it could be an anti-COVID-19 treatment. Chen is now planning to advance this research into animal models.
###
Chen is senior investigator on the paper in Science. Jun Zhang and Yongfei Cai in Boston Children’s Division of Molecular Medicine were co-first authors. Coauthors were Tianshu Xiao, Hanqin Peng, Sophia Rits-Volloch, and Piotr Sliz of Boston Children’s; Jianming Lu of Codex BioSolutions, Inc., Sarah Sterling and Richard Walsh Jr. of the Harvard Cryo-EM Center for Structural Biology (Harvard Medical School); and Haisun Zhu, Alec Woosley, and Wei Yang of the Institute for Protein Innovation (Harvard Institutes of Medicine). The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health (AI147884, AI147884-01A1S1, AI141002, AI127193), a COVID-19 Award by MassCPR, and Emergent Ventures.
About Boston Children’s Hospital
Boston Children’s Hospital is ranked the #1 children’s hospital in the nation by U.S. News & World Report and is the primary pediatric teaching affiliate of Harvard Medical School. Home to the world’s largest research enterprise based at a pediatric medical center, its discoveries have benefited both children and adults since 1869. Today, 3,000 researchers and scientific staff, including 9 members of the National Academy of Sciences, 23 members of the National Academy of Medicine and 12 Howard Hughes Medical Investigators comprise Boston Children’s research community. Founded as a 20-bed hospital for children, Boston Children’s is now a 415-bed comprehensive center for pediatric and adolescent health care. For more, visit our Discoveries blog and follow us on social media @BostonChildrens, @BCH_Innovation, Facebook and YouTube.
Media Contact
Erin Tornatore
[email protected]