Credit: University of Louvain (UCLouvain)
Renewable sources of energy such as wind or photovoltaic are intermittent. The production peaks do not necessarily follow the demand peaks. Storing green energy is therefore essential to moving away from fossil fuels. The energy produced by photovoltaic cells is stored during the day and by wind-power when the wind blows to be used later on when needed.
What do we have now?
The Li-ion technology is currently the best performing technology for energy storage based on batteries. Li-ion batteries are used in small electronics (smartphones, laptops) and are the best options for electric cars. Their drawback? Li-ion batteries can catch fire, for instance because of a manufacturing problem. This is due in part to the presence of liquid organic electrolytes in current batteries. These organic electrolytes are necessary to the battery but highly flammable.
The solution? Switching from a liquid flammable electrolyte to a solid (i.e., moving to « all-solid-state » batteries). This is a very difficult step as lithium ions in solids are less mobile than in liquids. This lower mobility limits the battery performances in terms of charge and discharge rate.
The discovery made by UCLouvain
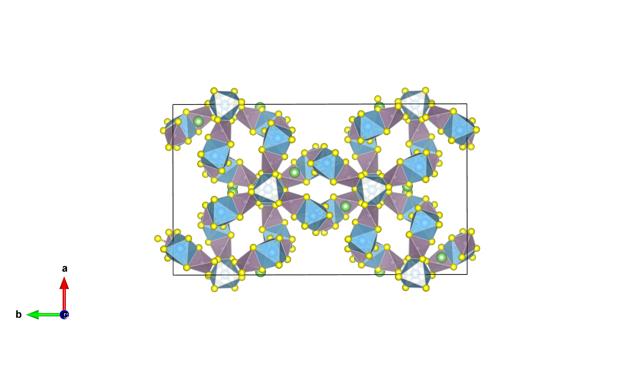
Scientists have been looking for materials that could enable these future all-solid-state batteries. Researchers from UCLouvain recently discovered such material. Its name? LiTi2(PS4)3 or LTPS. The researchers observed in LTPS the highest lithium diffusion coefficient (a direct measure of lithium mobility) ever measured in a solid. LTPS shows a diffusion coefficient much higher than known materials. The results are published in the prestigious scientific journal Chem from Cell Press.
The discovery? This lithium mobility comes directly from the unique crystal structure (i.e., the arrangement of atoms) of LTPS. The understanding of this mechanism opens new perspectives in the field of lithium ion conductors and, beyond LTPS, opens an avenue towards the search for new materials with similar diffusion mechanisms.
What’s next? The researchers need for further study and improve the material to enable its future commercialization. This discovery is nevertheless an important step in the understanding of materials with extremely high lithium ion mobility which are ultimately needed for the developing the “all-solid-state” batteries of the future. These materials including LTPS might end up being used in many the technologies that we use in our daily lives from cars to smartphones.
###
This research was performed in collaboration with Toyota, which supported scientifically and financially the study. A patent has been filed listing the UCLouvain researchers as inventors.
Media Contact
Isabelle Decoster
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




