A new type of green low surface energy surfactant that is stable in the harsh conditions of enhanced oil recovery (EOR) has been reported
Credit: Sajad Kiani, Swansea University.
This efficient surfactant was examined by a research team led by Dr Shirin Alexander and Professor Andrew R. Barron at ESRI, Swansea University. It is shown to improve the oil recovery by 72% in both low and high brine solutions, a remarkable result for only a single chain surfactant flooding, compared to 45% recovery in the presence of other surfactants alone.
Fabrication of a glass micromodel and testing of these materials were carried out by PhD student Sajad Kiani.
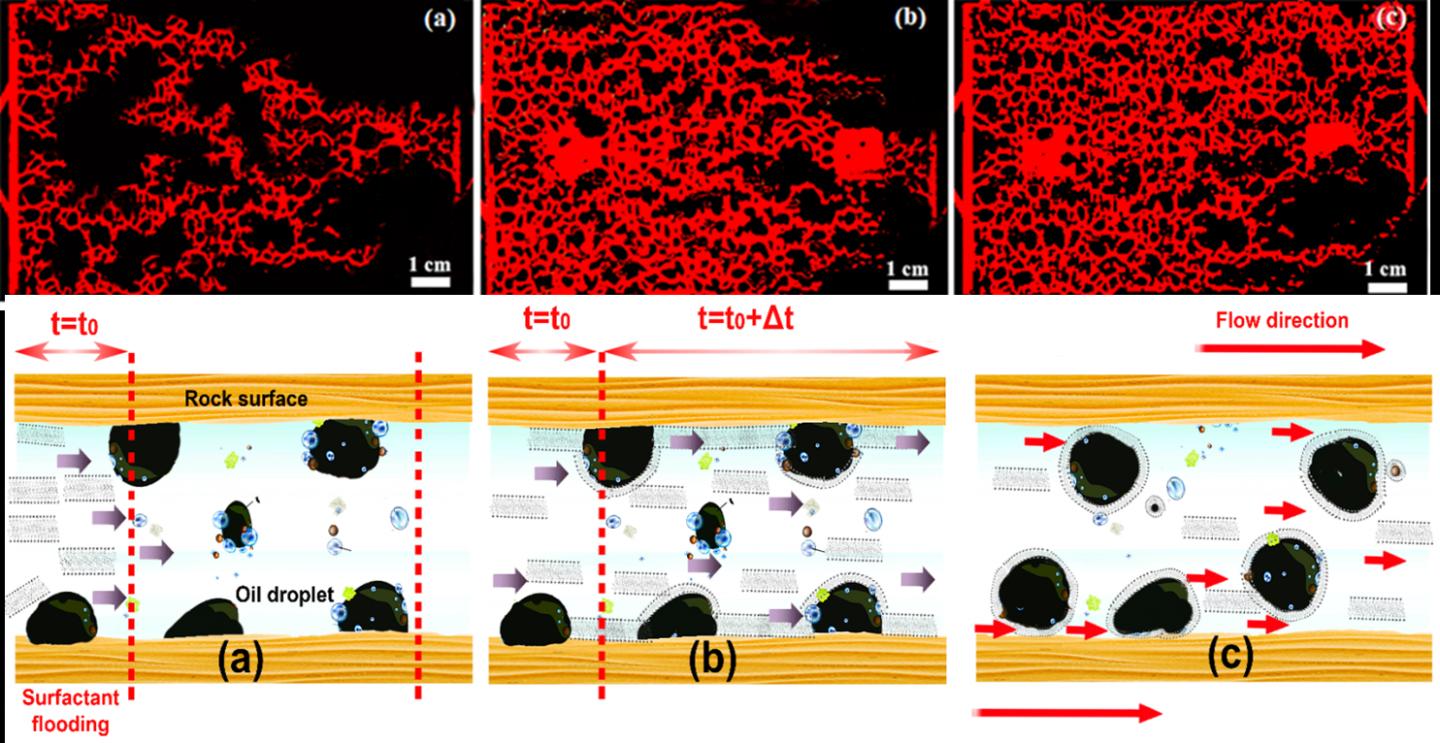
Sajad designed a quasi-two-dimensional glass microfluidic pattern with heterogeneous form to evaluate the suitability of the surfactant for oil displacing in EOR. Such heterogeneous pattern was replicated from a cross-section of sandstone rock and has been used to investigate the visual mechanism of the fluid flow on porous mediums.
Dr Alexander said: “It is a revelation that a single chain surfactant alone, without addition of any nanoparticle, polymer or alkaline, can achieve such a large recovery of oil. The effectiveness of this surfactant in EOR is due to its ability in reducing the surface and interfacial tension of the water/oil remarkably, compared to the other single chain surfactants. This is also because of its effective wettability alteration and capability to maintain the aggregation structure under extreme heat and salinity.”
Professor Barron said: “Despite the desire to shift to renewable energy, the global demand for oil is not abating, and we must find ways to enhance recovery of resources using methods with low environmental impact. So-called green hydrocarbon technology is one of the focus areas of ESRI, along with CCUS and alternative sustainable energy sources, for a multifaceted approach to lowering emissions and the environmental impact of energy and resource production”.
The results of this work opens up insight into the future role of this green and cost effective LSES in EOR formulations.
###
Co-authors of the papers are Dr Masanobu Sagisaka an associate professor at Department of Frontier Materials Chemistry in Hirosaki University, Japan and Dr Sarah Rogers an instrument scientist for SANS2D at ISIS-STFC, in Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, UK. Professor Barron is the Founder and Director of ESRI and the Sêr Cymru Chair of Low Carbon Energy and Environment at Swansea. Dr Alexander is a Sêr Cymru Research Fellow.
Media Contact
Delyth Purchase
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




