Chemists from Japan develop a thiol-free technique for synthesizing aryl sulfides using a nickel catalyst
Credit: Waseda University
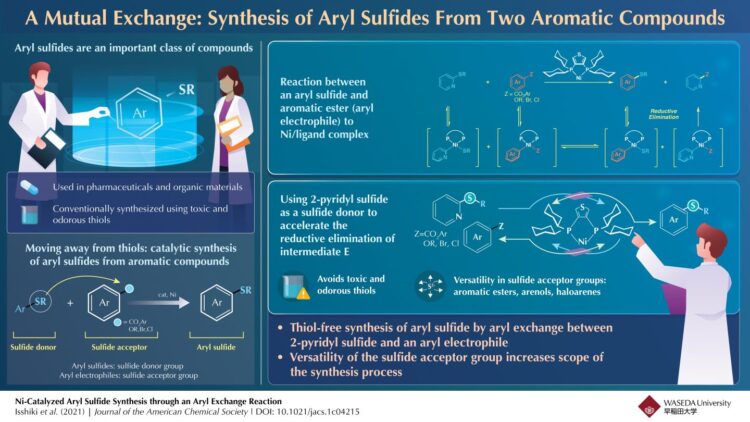
Aryl sulfide, an aromatic compound in which sulfur is attached to an aryl (a functional group derived from an aromatic ring), is found in biologically active materials effective against asthma, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer. As a result, chemists have shown a lot of interest in synthesizing aryl sulfides. Traditionally, carbon-sulfur (C-S) bond formation reactions between thiols and aryl electrophiles catalyzed by transition metals have been employed for aryl sulfide synthesis because of their high reliability. However, thiols have an unpleasant smell and are toxic. Could there be a way to synthesize aryl sulfides that avoids the use of thiols?
A team of chemists from Waseda University, Japan, led by Professor Junichiro Yamaguchi addresses this question in a recent study published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, and has come up with a technique that gets the job done without thiols. The team took the hint from a previous study where they used a nickel catalyst to synthesize aromatic esters from two aromatic compounds. “In 2020, we developed the first ester synthesis method using aromatic ring exchange reactions and decided to apply the knowledge gained from this reaction to realize a thiol-free sulfide synthesis,” explains Yamaguchi, speaking of the origin of the study.
Against this backdrop, the team set out to synthesize aryl sulfides and aromatic esters. They started out by reacting 4-tolyl sulfide and 4-phenylbenzoate in presence of a nickel catalyst and found that the desired aryl sulfide was synthesized in the presence of a ligand, dcypt, and a zinc additive, Zn(OAc)2.
Encouraged by the results, the team moved on to investigate the mechanism of the reaction. They reacted the aryl sulfide with the nickel catalyst (Ni(cod)2) and the ligand, dcypt, and observed the formation of a nickel complex consisting of the catalyst, the ligand, and the aryl sulfide. This nickel complex could react with the aromatic ester to form a pair of nickel complexes which could react with each other to form the desired aryl sulfide.
From these reactions, the team concluded that the Ni-catalyzed aryl sulfide synthesis occurred in a sequence of steps. Initially, the aryl sulfide and aromatic esters underwent simultaneous oxidative addition reactions to the nickel/ligand catalyst forming nickel complexes. These nickel complexes could engage in an aryl exchange reaction to form a set of nickel intermediates. This was then followed by the reductive elimination of the intermediates to regenerate the Ni/ligand catalyst and form the desired aryl sulfide.
The reductive elimination of the nickel intermediates, however, reduced the yield of the aryl sulfide. To combat this, the team employed 2-pyridyl sulfide, which accelerated this limiting step, improving the yield. Additionally, the synthesis method worked with several aryl electrophiles such as aromatic esters, arenol derivatives and aryl halides.
“The sulfide synthesis method developed can proceed for a variety of complex bioactive compounds such as probenecid, flavone, estrone, phenylalanine, umbelliferone, and β-isocupreidine derivatives,” comments an excited Yamaguchi, contemplating the prospects of their novel synthesis technique. “Furthermore, the ability to use environmentally friendly aromatic esters and phenol derivatives as feedstock and pyridyl sulfide as a sulfide agent could make this technology suitable for both laboratory and industrial-scale applications.”
###
Reference
Authors: Ryota Isshiki, Miki B. Kurosawa, Kei Muto, Junichiro Yamaguchi
Title of original paper: Ni-Catalyzed Aryl Sulfide Synthesis through an Aryl Exchange Reaction
Journal: Journal of the American Chemical Society
DOI: https:/
Affiliations: Waseda University, Japan
About Waseda University
Located in the heart of Tokyo, Waseda University is a leading private research university that has long been dedicated to academic excellence, innovative research, and civic engagement at both the local and global levels since 1882. The University ranks number one in Japan in international activities, including the number of international students, with the broadest range of degree programs fully taught in English. To learn more about Waseda University, visit https:/
Media Contact
Jasper Lam
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.