More than half of our brains are made up of glial cells, which wrap around nerve fibers and insulate them–similarly to how the plastic casing of an electric cable insulates the copper wire within–allowing electrical and chemical impulses to travel faster. In the past, neuroscientists considered the glial cell an essential yet passive helper of nerve cells. But scientists in Rockefeller's Laboratory of Developmental Genetics, headed by Shai Shaham, have accumulated compelling evidence that this cell type plays a much more active and dynamic role in the brain than previously thought.
Shaham's lab now reports in Cell that glial cells can control the shape of specific nerve endings by interacting with them through a previously unknown molecular pathway. "In the nervous system, shape is everything," he says. "The shape a neuron takes dictates which other neurons it connects to and even the strength of those connections. But we know precious little about how that shape is dictated."
Multilingual cells
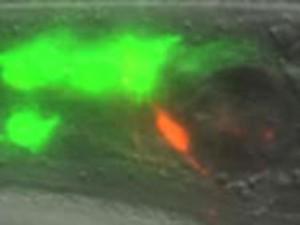
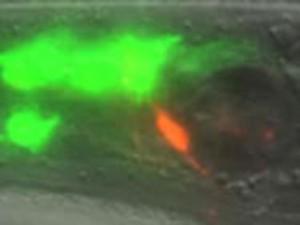
In this study, Aakanksha Singhvi, a postdoc in the lab and first author of the report, studied a glial cell that encases the nerve endings of 12 neurons in the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans, including one that responds to temperature–called a thermosensory neuron–and some that respond to odors. The investigators wondered how the glial cell appropriately regulates the requisite shapes of these neurons. They discovered that it uses different molecular mechanisms to control the shape of each neuronal cell type it encloses.
"The glial cells are, surprisingly, multilingual," is how Singhvi puts it. "They can interact with different neurons differently."
She and her colleagues found that the glial cell expresses an ion transporter protein, called KCC-3, specifically on its surface near the thermosensory neuron, but away from other neurons. In this way it affects and maintains the shape of the thermosensory nerve ending only, without affecting the other nerve endings it surrounds.
The researchers also found that KCC-3 affects the function of the thermosensory neuron in addition to its shape. Normally, worms can "remember" the temperature at which they were raised–and if adult worms are given a choice, they will seek out similarly tepid spots. But when the scientists engineered worms in which KCC-3 can't work, they found that these animals don't migrate to their favorite cultivation temperature.
"This idea that glial cells may directly mold neural functions is not new," says Shaham. "Our findings are direct proof that it actually happens."
The researchers found that the local concentration of ions can influence the shape of nerve endings. They showed that KCC-3 modulates extracellular levels of chloride, which then controls the shape and function of neurons. Then they went further and identified the proteins in the neuron whose activity is controlled by chloride ions, which manipulate the cell's skeleton and give the nerve ending its shape.
It was not previously known that glial cells communicate to neurons through specific ions to regulate their shape, and the researchers speculate that glial cells may in fact be able to use ions to mold the shapes and functions of many types of neurons.
Clinical implications
KCC-3 is expressed in our ears, retinas, and Schwann cells–glial cells present throughout our peripheral nervous system. People who carry mutations in the gene that produces it suffer from sensory neuropathy, a condition that causes tingling, pain, numbness, or weakness in the hands and feet. The protein is also present in glial cells in the central nervous system, and other research has indicated its function may be relevant for conditions associated with defects in the shape of neurons, including Huntington's disease and epilepsy.
The formation and maintenance of nerve ending shapes are important for learning and memory, and perturbation in shape is associated with neuronal disorders including dementia, schizophrenia, and Alzheimer's disease. In another recent study published in Cell Reports, Shaham and Sean Wallace, a postdoc in the lab, showed that glial cells control the shapes of many nerve endings in worms, suggesting that additional shape pathways remain to be discovered.
The finding that glial cells can modulate nerve endings by expressing an ionic transporter only where it contacts a particular type of neuron is one that opens up many new avenues for research. If it turns out to be a widely used mechanism by which glial cells selectively affect particular neurons, it could be manipulated for therapeutic purposes.
###
Media Contact
Katherine Fenz
[email protected]
212-327-7913
@rockefelleruniv
http://www.rockefeller.edu
The post A common brain cell shapes the nervous system in unexpected ways appeared first on Scienmag.