A lightweight, compact, wireless Bluetooth-low-energy neuronal recording system for mice
Credit: COPYRIGHT (C) TOYOHASHI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
Overview:
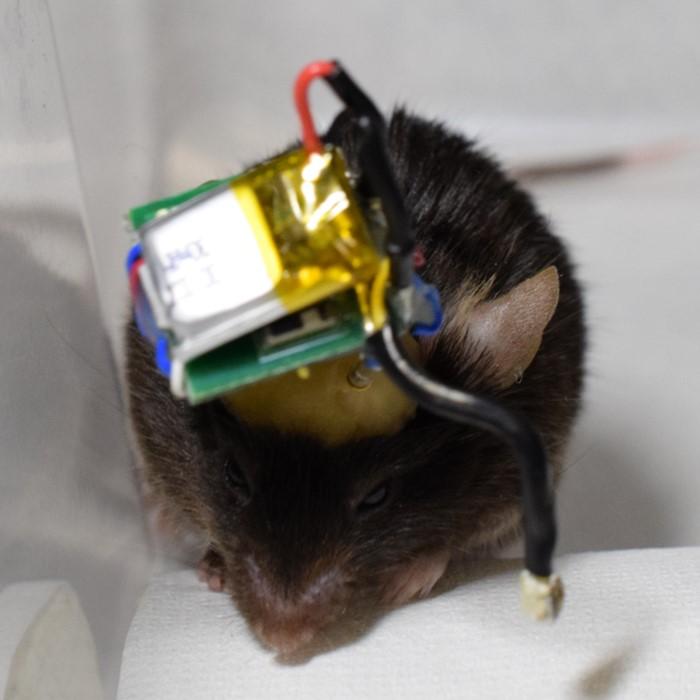
A research team at the Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Department of Applied Chemistry and Life Science, and the Electronics-Inspired Interdisciplinary Research Institute (EIIRIS) at Toyohashi University of Technology has developed a lightweight, compact, Bluetooth-low-energy-based wireless neuronal recording system for use in mice. The wireless system weighs 3 with the battery, having advantages of high signal quality, good versatility, and low cost, compared to wired recording with a commercial neurophysiology system. The study was published online in Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, on January 8, 2021.
Details:
Electrophysiological recording, which uses micro-scale needle-like electrodes penetrated into the brain tissue, has made significant contributions to fundamental neuroscience and medical applications. Electrophysiological recording, however, requires improvements in signal quality, invasiveness, and cable use. Although wireless recording can meet these requirements, conventional wireless systems are heavy and bulky for use in small animals such as mice, and systems based on their own custom technologies are costly and lack versatility.
The research team developed a lightweight, compact, wireless Bluetooth-low-energy neuronal recording system. As explained by the first author of the article, Ph.D. candidate Shinnosuke Idogawa, “We tackled the challenge of developing a lightweight and compact wireless neuronal recording system for use in mice and developed a 15 × 15 × 12 mm3 system weighing 3.9 g with the battery, which is less than 15% of a mouse’s weight (e.g., 33 g for a two-week-old C57BL/6 mouse). Surprisingly, the wireless system demonstrates advantages of not only recording without using any cables, but also improvements in signal quality, including signal-to-noise ratios, compared to wired recording with a commercial neurophysiology system. In addition to these advantages, the developed wireless system costs USD $79.90, which is less than the wired system.”
Development Background:
The leader of the research team, Associate Professor Takeshi Kawano said “We demonstrated the wireless system for single channel recording as our first step, but we can increase the channel numbers based on our system, and we are currently developing wireless systems for four-channels and more. Because we use Bluetooth technology, the device features will help us further develop small wireless neurophysiology systems with the advantages of good versatility and low cost for a wide range of users.”
Future Outlook:
The research team believes that the wireless recording system can also be used to study the behavioral characteristics of mice as well as drug screening using mice. Because of its light weight, compactness, and Bluetooth technology, the developed wireless neuronal recording system can also be used with other species, including rats and monkeys.
###
Funding agency:
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI (grant numbers 17H03250, 26709024, and 20H00244), the Strategic Advancement of Multi-Purpose Ultra-Human Robot and Artificial Intelligence Technologies program from NEDO, and the Nagai Foundation for Science & Technology. R.N. was supported by Takeda Science Foundation. K.K. was supported by JSPS KAKENHI (grant number 15H05917).
Reference:
Shinnosuke Idogawa, Koji Yamashita, Rioki Sanda, Rika Numano, Kowa Koida, and Takeshi Kawano (2021). “A lightweight, wireless Bluetooth-low-energy neuronal recording system for mice,” Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 10.1016/j.snb.2020.129423.
Media Contact
Yuko Ito
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




