This article by Dr. Fahim Halim Khan et al. is published in Current Protein & Peptide Science, Volume 19, Issue 10, 2018
Credit: Bentham Science Publishers, Fahim Halim Khan
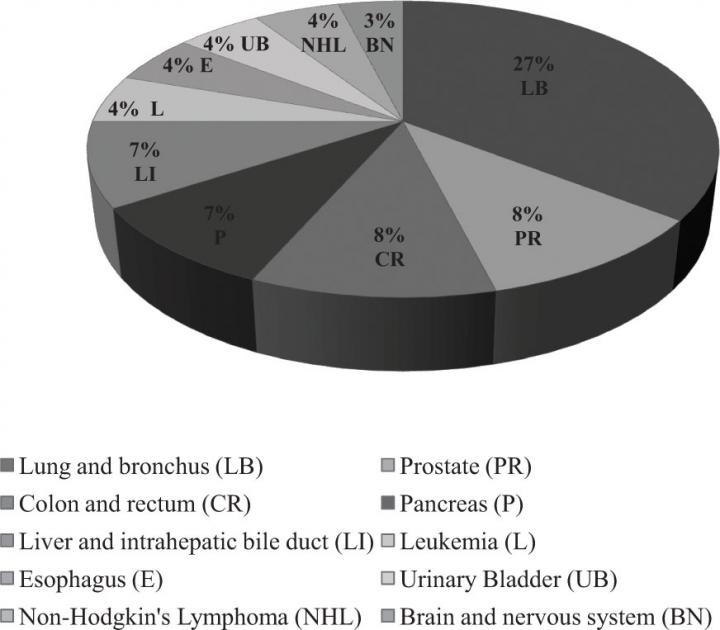
Chemotherapy is use of drugs to cure a disease but more specifically, it refers to drug therapy for cancer. Cancer chemotherapy can be done with a single drug or a combination of drugs and is usually systematic in nature, that is to say that a drug is administered through the blood circulation to eliminate cancer cells in many parts of the body. Within last few years, advancements in chemotherapy have given rise to successful patient outcomes and there is a large numbers of anti-cancer drugs which are present in the market.
Chemotherapeutic drugs are composed from different compounds. This review provides information about chemotherapeutic drugs that bind to plasma proteins. Cisplatin (a platinum based complex), 5-fluorouracil and ruthenium based drugs are a few examples. Cisplatin interacts covalently and alters the function of the key plasma protease inhibitor molecule -alpha-2-macroglobulin and induces the conformational changes in the protein molecule, thus inactivating it. 5-fluorouracil is metabolized at a large scale and it is associated with Human Serum Albumin. Ruthenium compounds bind with protein plasma serum-albumin and serum transferrin rendering them toxic to cancer cells. The review also details the use of these drugs based on cancer types and their side effects.
###
This article is Open Access. To obtain the article please visit http://www.
Media Contact
Faizan ul Haq
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




