Credit: American Chemical Society
Skin has a remarkable ability to heal itself. But in some cases, wounds heal very slowly or not at all, putting a person at risk for chronic pain, infection and scarring. Now, researchers have developed a self-powered bandage that generates an electric field over an injury, dramatically reducing the healing time for skin wounds in rats. They report their results in ACS Nano.
Chronic skin wounds include diabetic foot ulcers, venous ulcers and non-healing surgical wounds. Doctors have tried various approaches to help chronic wounds heal, including bandaging, dressing, exposure to oxygen and growth-factor therapy, but they often show limited effectiveness. As early as the 1960s, researchers observed that electrical stimulation could help skin wounds heal. However, the equipment for generating the electric field is often large and may require patient hospitalization. Weibo Cai, Xudong Wang and colleagues wanted to develop a flexible, self-powered bandage that could convert skin movements into a therapeutic electric field.
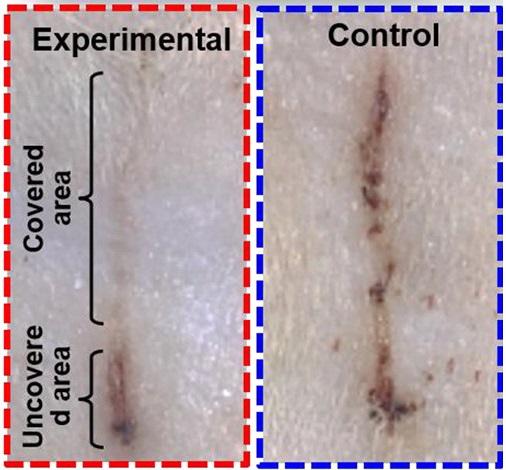
To power their electric bandage, or e-bandage, the researchers made a wearable nanogenerator by overlapping sheets of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), copper foil and polyethylene terephthalate (PET). The nanogenerator converted skin movements, which occur during normal activity or even breathing, into small electrical pulses. This current flowed to two working electrodes that were placed on either side of the skin wound to produce a weak electric field. The team tested the device by placing it over wounds on rats’ backs. Wounds covered by e-bandages closed within 3 days, compared with 12 days for a control bandage with no electric field. The researchers attribute the faster wound healing to enhanced fibroblast migration, proliferation and differentiation induced by the electric field.
###
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering of the National Institutes of Health.
The study is freely available as an Editor’s Choice article here.
The American Chemical Society, the world’s largest scientific society, is a not-for-profit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS is a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news release from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Follow us on Twitter | Facebook
Media Contact
Katie Cottingham
[email protected]
301-775-8455




