Understanding structure of human TIM-3 provides new insights for cancer and autoimmune drug development
Credit: Richard Blumberg, Brigham and Women’s Hospital
A new study by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital provides a biophysical and structural assessment of a critical immune regulating protein called human T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain containing protein-3 (hTIM-3). Understanding the atomic structure of hTIM-3 provides new insights for targeting this protein for numerous cancer and autoimmune therapeutics currently under clinical development. The findings of this study were published online in Scientific Reports on Nov. 30.
“The hTIM-3 protein is an important immune regulator, yet it has been difficult to target for drug development as high-resolution structure conformational details have been elusive,” said senior author Richard Blumberg, MD, chief of the Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Endoscopy in the Department of Medicine at the Brigham. “We resolved the structure of hTIM-3 and established a novel biochemical assay to define its functionality, which will be useful for understanding the role of hTIM-3 in the immune system.”
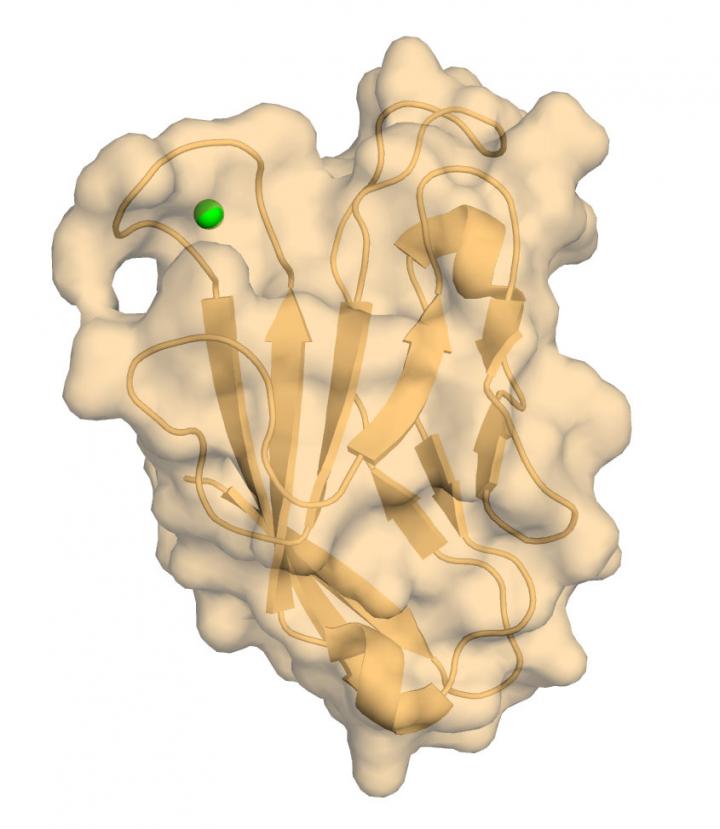
The team captured a high-resolution X-ray crystal structure and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) image of the hTIM-3 IgV domain that is involved in functional interactions with CEACAM1, which is a crucial immune escape mechanism for many cancers. Importantly, the team determined the precise location of a calcium atom, an essential co-factor, bound to the hTIM-3 IgV domain.
“This is the first NMR analysis of any immune-related TIM molecule and the first high resolution structural report of the hTIM-3 IgV domain with association of critical co-factors such as calcium,” said author Amit Gandhi, PhD, a researcher in Blumberg’s laboratory in the Department of Medicine. “No one has been able to do this before. Hopefully this will help with the targeting of human hTIM-3 and the development of useful therapeutics.”
“This structure shown here represents a high resolution, physiologically relevant hTIM-3 molecule,” said author Walter Kim, MD, PhD, a researcher in Blumberg’s laboratory and associate physician in the Department of Medicine. “Now we can understand what specific regions of the protein are accessible for therapeutic drugs to bind.”
###
The NMR structural studies were led by Zhen-Yu Jim Sun, PhD, a researcher at Harvard Medical School. Funding for this work was supported by the NIH Grants 5R01DK051362-21 and the High Pointe Foundation to R.S.B. and 5P01AI073748-09 to V.K.K., and GM047467 and AI037581 to G.W.
Paper cited: Gandhi, A et al. “High resolution X-ray and NMR structural study of human T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain containing protein-3” Scientific Reports DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-35754-0
Media Contact
Haley Bridger
[email protected]
617-525-6383
Related Journal Article
http://dx.
News source: https://scienmag.com/




