Philadelphia, PA, April 8, 2016 – Sepsis represents a serious complication of infection and is one of the leading causes of death and critical illness worldwide due in part to the lack of effective therapies. A report in the American Journal of Pathology provides evidence from both mouse and human studies that SHARPIN, a protein involved in regulating inflammation, has anti-septic effects. These findings may spur development of novel sepsis treatments.
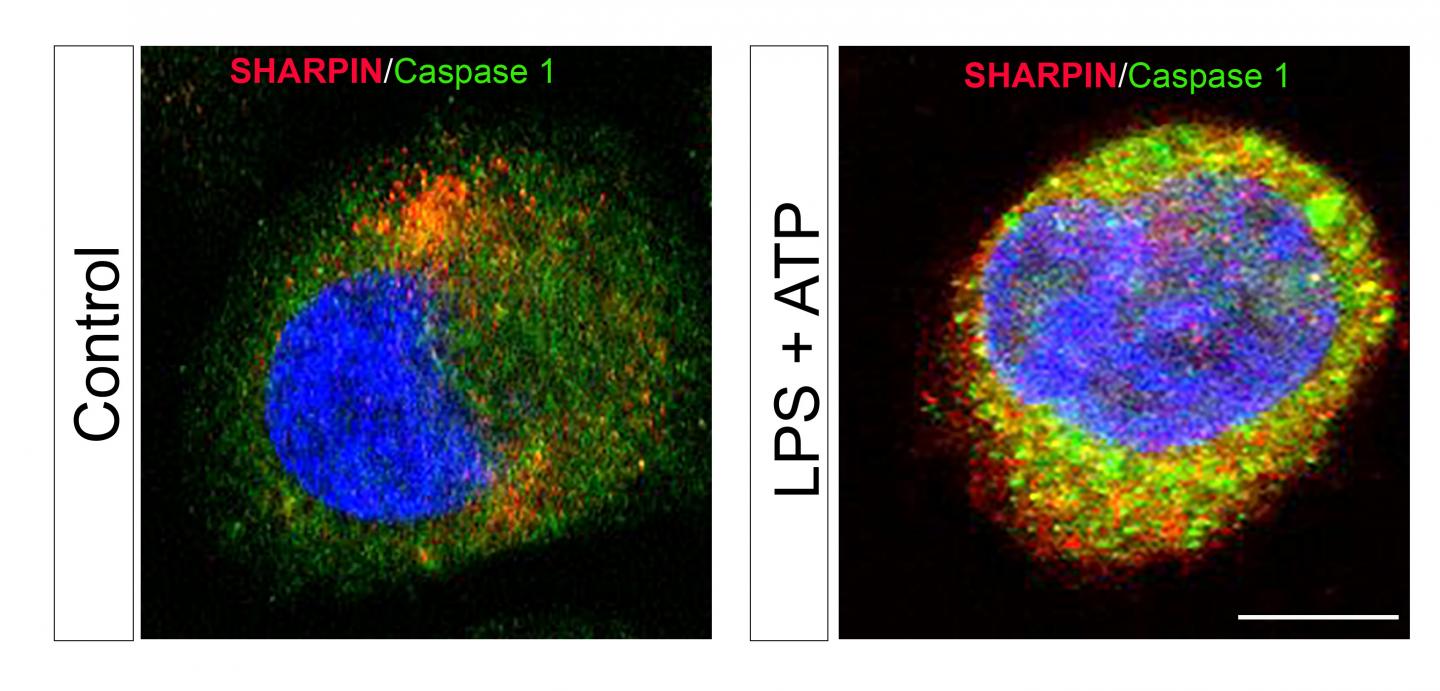
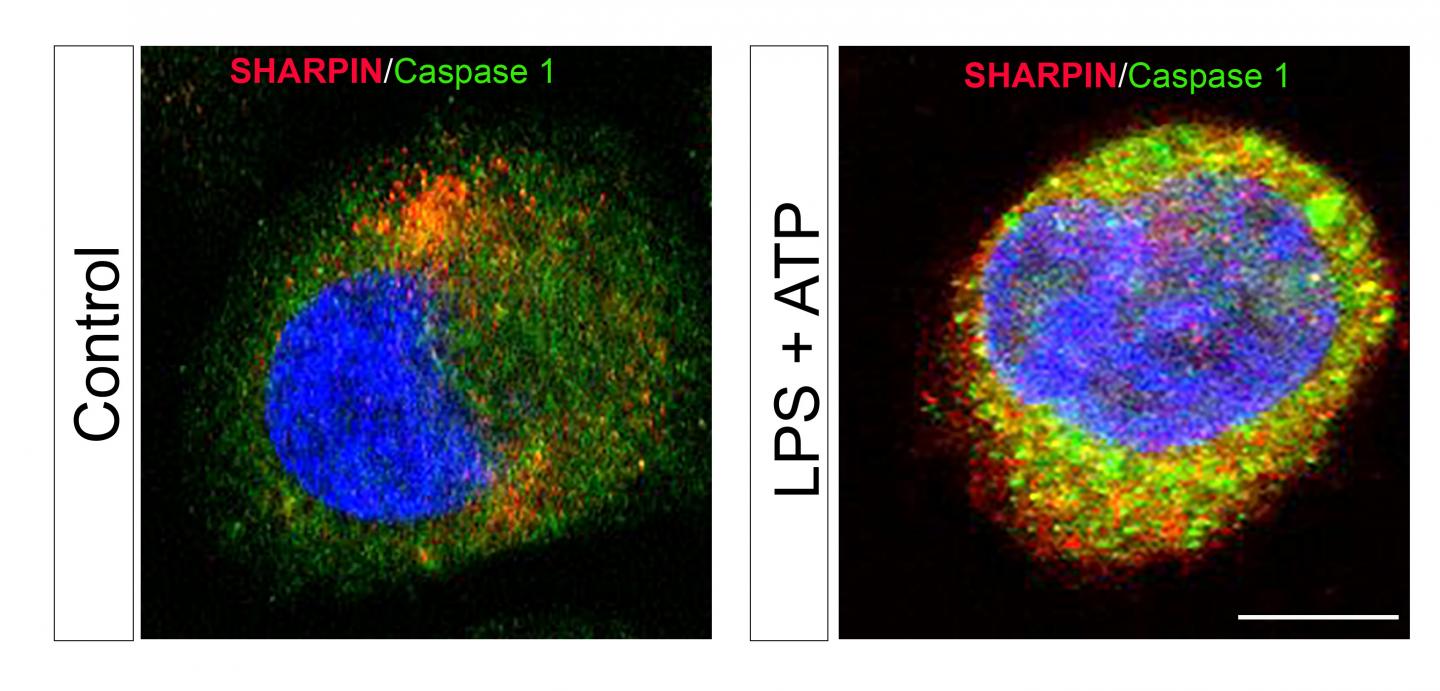
"Sepsis has been linked to enhanced activity of the enzyme caspase 1 and aberrant expression of pro-inflammatory interleukins 1β and 18. SHARPIN binds to caspase 1 and inhibits its activation. Our study proposes that the caspase 1/SHARPIN interaction may be a key pharmacological target in sepsis and, perhaps, in other inflammatory conditions where SHARPIN is involved," explained Liliana Schaefer, MD, Professor of Pharmacology at the Institut fur Allgemeine Pharmakologie und Toxikologie of the Klinikum der Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main (Germany).
The investigators found that sepsis in mice bred to be deficient in SHARPIN resulted in enhanced levels of interleukins 1β and 18 and active caspase 1, as well as shortened survival. Treatment with a caspase 1 inhibitor reversed these effects by reducing levels of interleukins 1β and 18, decreasing cell death in the spleen, and prolonging survival.
The investigators also reported for the first time that this mechanism may be relevant to human sepsis. "We found a decline in SHARPIN levels in septic patients correlating with enhanced activation of caspase 1 in circulating mononuclear cells and an increase of interleukin1β/18 in the plasma," noted Dr. Schaefer. "Our findings suggest that using pharmacological caspase 1 inhibitors could be beneficial in septic patients with low SHARPIN levels and these therapies may be more efficient than other anti-inflammatory therapies."
A recent Task Force convened by the Society of Critical Care Medicine and the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (JAMA 2016;315:801) define sepsis as "a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection." Septic shock comprises a subset of sepsis in which underlying circulatory and cellular metabolism abnormalities are severe enough to substantially increase the risk of death. Symptoms of sepsis include changes in body temperature, rapid heart rate, and rapid breathing. Other indicators are reduced urine output, changes in mental status, breathing difficulty, abdominal pain, and low platelet count.
###
Media Contact
Eileen Leahy
[email protected]
732-238-3628
@elseviernews
http://www.elsevierhealth.com