PORTLAND, Ore. – Patients with a prescription for an opioid use disorder medication may have a tough time getting it filled if their pharmacy is in a community that’s racially and economically segregated, according to a new study led by scientists at Oregon State University and Johns Hopkins University.
PORTLAND, Ore. – Patients with a prescription for an opioid use disorder medication may have a tough time getting it filled if their pharmacy is in a community that’s racially and economically segregated, according to a new study led by scientists at Oregon State University and Johns Hopkins University.
The findings shed additional light on inequities in health care as the U.S.’s overdose crisis continues to accelerate, with fatality rates rising fastest in Black and Hispanic/Latinx communities.
“While there have been notable policy changes over the past decade that have improved access to meds used for opioid use disorder and made headway against racial disparities, those efforts haven’t taken into consideration the issue of whether patients can actually get their prescription filled,” said study co-author Dan Hartung, who has dual appointments with the OSU College of Pharmacy and Oregon Health & Science University.
In the past decade, those populations have seen their overdose fatality rates nearly triple, compared to a 58% increase among white individuals.
More than 640,000 Americans died from opioid overdose in the years 1999 to 2021, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. In 2022 alone, greater than 100,000 people lost their lives to overdose and 75% of those fatalities involved an opioid.
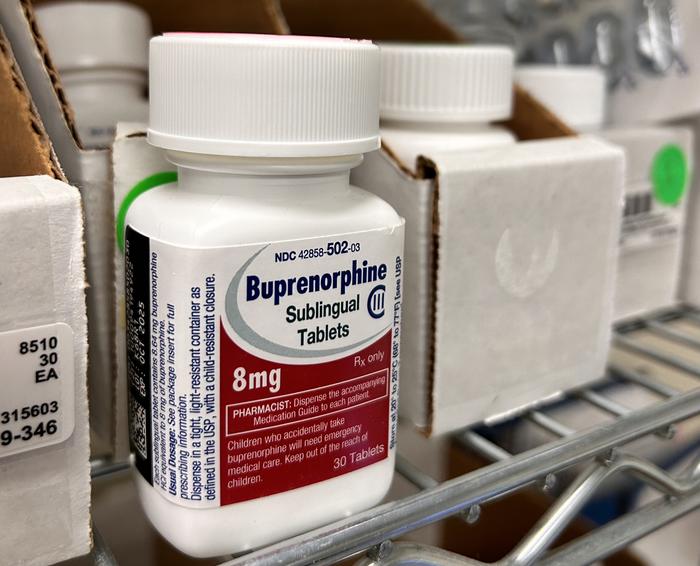
A key tool for helping with opioid use disorder recovery is the prescription drug buprenorphine, which binds to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord in a way that produces effects similar to but lesser than those of hydrocodone, oxycodone, morphine and fentanyl.
Treatment with buprenorphine, which helps to mitigate pain, cravings, withdrawal and ultimately overdose risk, has been shown to reduce the risk of death from overdose by 50%, according to Hartung and Johns Hopkins’ Kyle Moon.
Similar to other opioids, distribution of buprenorphine is overseen by the Drug Enforcement Agency. That can lead to pharmacies being extra cautious in how much of the drug they purchase from wholesalers, who are required to report orders that strike them as suspicious to the agency. Innocent or not, being investigated by the DEA can have disastrous effects for pharmacies, the scientists note.
Previous studies have shown that fewer than one in five individuals diagnosed with opioid use disorder will get any kind of drug therapy, and white patients are about four times more likely to receive buprenorphine than non-whites.
Hartung, Moon and collaborators at OSU, OHSU, Johns Hopkins and the Boise VA Medical Center analyzed data from a telephone audit of 858 community pharmacies in 473 counties around the United States. The audit involved someone calling each pharmacy and inquiring about getting a buprenorphine prescription filled.
The analysis showed that in counties with the highest levels of racial and economic segregation, pharmacies were more than two times as likely to restrict their buprenorphine dispensing than pharmacies in the “most economically privileged” counties.
“These pharmacy dispensing barriers have the potential to exacerbate inequities in access to treatment,” Moon said. “And it shows that future policy interventions aimed at improving health care equity need to target dispensing capacity to augment the ones already put in place that make it easier for providers to prescribe buprenorphine.”
Adriane Irwin of the OSU College of Pharmacy contributed to the study, which was published in Drug and Alcohol and Dependence Reports.
Journal
Drug and Alcohol Dependence Reports
DOI
10.1016/j.dadr.2024.100255
Method of Research
Survey
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Association of economic and racial segregation with restricted buprenorphine dispensing in U.S. community pharmacies
Article Publication Date
9-Aug-2024