Monoamine neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine play important roles in our cognitive and emotional functions. Their evolutionary origins date back to metazoans, and while the function of related genes is strongly evolutionarily conserved, genetic variation within and between species has been reported to have a significant impact on animal mental characteristics such as sociality, aggression, anxiety, and depression.
Credit: ©Tohoku University
Monoamine neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine play important roles in our cognitive and emotional functions. Their evolutionary origins date back to metazoans, and while the function of related genes is strongly evolutionarily conserved, genetic variation within and between species has been reported to have a significant impact on animal mental characteristics such as sociality, aggression, anxiety, and depression.
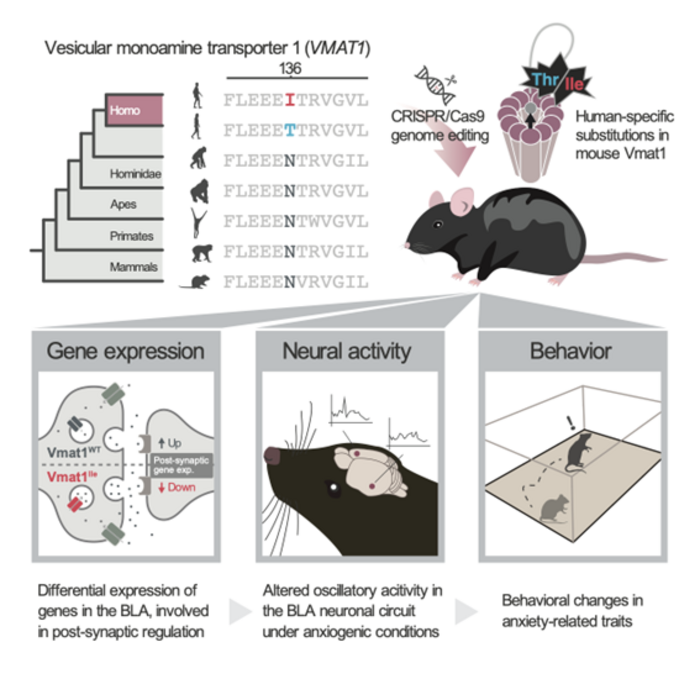
A research group led by Dr Daiki Sato and Professor Masakado Kawata has previously reported that the vesicular monoamine transporter 1 (VMAT1) gene, which transports neurotransmitters to secretory vesicles in neurons and secretory cells, has evolved through natural selection during human evolution. In particular, the 136th amino acid locus of this gene has evolved in the human lineage from asparagine (Asn) to threonine (Thr), and moreover, a new allele (isoleucine, Ile) has emerged and increased in its frequencies around the world. Previous reports suggested that people with the Ile genotype are less prone to depression and anxiety than those with the Thr genotype, but it was unclear how these human-specific mutations function in the brain and lead to changes in neuropsychiatric behavior.
In this study, Sato, Kawata (Tohoku University),Yukiko U. Inoue (National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry), and their colleagues prepared Vmat1 gene-edited mice in which the 136th amino acid locus was replaced with the human genotype (Thr or Ile) via genome editing technology, and compared gene expression, neural activity, and behavior among genotypes. The Ile-type mice showed decreased levels of anxiety-like behaviors, consistent with human studies. In addition, the genotype affected post-synaptic gene expression and neural activity in the amygdala, a brain region involved in emotional regulation. The functional role of the VMAT1 gene in the central nervous system remains unclear, and this study may provide a steppingstone toward elucidating its molecular mechanisms. Moreover, there are few studies in which the effects of single amino acid substitutions under natural selection during human evolution have been verified using genome editing technology. This study demonstrates the functional importance of human-specific variants in the regulatory circuits of neurotransmitters involved in cognitive and emotional functions and is expected to shed light on the pathogenic mechanisms of neuropsychiatric disorders such as anxiety and depression.
Journal
iScience
DOI
10.1016/j.isci.2022.104800
Article Title
Humanized substitutions of Vmat1 in mice alter amygdala-dependent behaviors associated with the evolution of anxiety
Article Publication Date
20-Jul-2022




