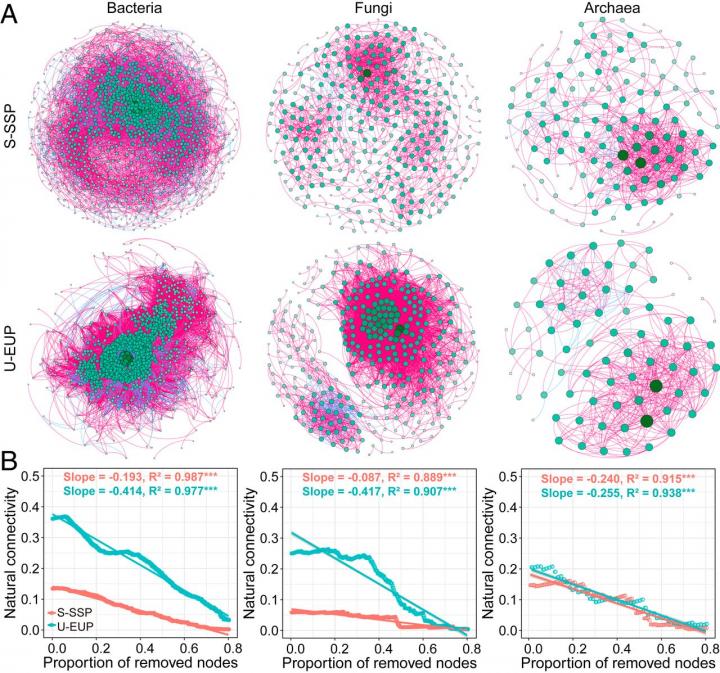
Chinese researchers have recently discovered links between reduction in microbial stability and soil carbon loss in the active layer of degraded alpine permafrost on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (QTP).
The researchers, headed by Prof. CHEN Shengyun from the Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources (NIEER) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), and XUE Kai from University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, conducted a combined in-depth analysis of soil microbial communities and their co-occurrence networks in the active permafrost layer along an extensive gradient of permafrost degradation.
The QTP encompasses the largest extent of high-altitude mountain permafrost in the world. This permafrost is different than high-latitude permafrost and stores massive soil carbon. An often ignored characteristic of permafrost is that the carbon pool in the active layer soil is more active and directly affected by climate change, compared to deeper layers.
Triggered by climate warming, permafrost degradation may decrease soil carbon stability and induce massive carbon loss, thus leading to positive carbon-climate feedback. However, microbial-mediated mechanisms for carbon loss from the active layer soil in degraded permafrost still remain unclear.
In this study, the researchers found that alpine permafrost degradation reduced the stability of active layer microbial communities as evidenced by increased sensitivity of microbial composition to environmental change, promoted destabilizing network properties and reduced resistance to node or edge attacking of the microbial network.
They discovered that soil organic carbon loss in severely degraded permafrost is associated with increased microbial dissimilarity, thereby potentially contributing to a positive carbon feedback in alpine permafrost on the QTP.
###
The results were published in PNAS in an article entitled “Reduced microbial stability in the active layer is associated with carbon loss under alpine permafrost degradation”.
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Strategic Priority Research Program (A) of CAS and the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research Program.
Media Contact
CHEN Shengyun
[email protected]
Original Source
http://english.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.