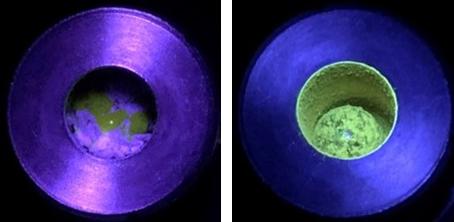
Credit: Koji Kubota et al., Angewandte Chemie International Edition. May 14, 2021
Hokkaido University researchers have developed a simple method that converts existing generic polymers into luminescent polymers using mechanical force.
Researchers from Hokkaido University have successfully developed a new method to give luminescent properties to generic polymers, such as polystyrene and polyethylene. The technique, which was published in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition, makes it possible to easily prepare luminescent polymers without using complicated organic synthetic methods.
“Luminescent polymers are widely used in modern society, in applications such as organic lasers, solar cells, sensors and bioimaging, but their preparation often requires multiple chemical synthesis steps, which are both time and labor intensive,” explains Professor Hajime Ito, one of the authors of the study and Vice Director of the Institute for Chemical Reaction Design and Discovery (WPI-ICReDD) at Hokkaido University.
To overcome this problem, the research team investigated whether luminescent polymers could be prepared using mechanical force as opposed to sophisticated chemical synthesis.
“It is well known that mechanically stimulating polymers, for example by grinding or crushing them, generates reactive species called free radicals,” says Associate Professor Koji Kubota from Hokkaido University, a paper co-author. “Inspired by this phenomenon, as well as our previous research into mechanical-force-induced luminescence and reactions, we wanted to investigate whether we could find a simpler method for preparing functional luminescent materials.”
In this study, the researchers placed the polymer and pre-fluorescent radical reactants together in a ball milling jar containing stainless steel balls. The jar was then shaken, causing the balls to grind the solid compounds and initiate a reaction. During this process, the covalent bonds in the polymer chains were cleaved and the pre-fluorescent molecules were inserted into the polymer, gaining significantly higher emission intensity. The researchers successfully applied this method to polystyrene, polyethylene, polyphenylene sulfide, polysulfone, and other generic polymers.
“With further development, the method could potentially be adapted to introduce other functions to generic polymers,” says Hokkaido University Assistant Professor Mingoo Jin.
“In the future, we hope to use this method to develop novel sensing and recording materials that change colour in response to mechanical stimuli,” Hajime Ito added.
This could pave the way for “smart” materials for a wide range of applications, such as bioimaging reagents and pressure-sensitive sensors.
###
Media Contact
Naoki Namba
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.